* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Animalia
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Remote control animal wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
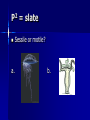
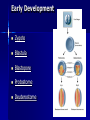
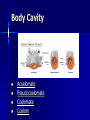
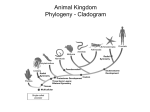
2/13/15 Discussion Questions Using your textbook, journal, handouts, or smart phone please complete the following: 1. What are the characteristics of the animal kingdom? 2. How are animal-like protists different from animals? Reminders Review your discussion questions and ppt notes ~5 min each night for the daily quizzes. Animal Exam 3-12-15 Zoo Trip 3-4-15 Go to room 1135 Tues or Thurs for Science Peer Tutoring during PLC Today’s Objective: OBJECTIVES: Describe and Explain the general characteristics of the Animal Kingdom Evolutionary Trends Animalia Phyla Invertebrates vs. Vertebrates 95% of all species of animals are invertebrates Other 5% of animals are vertebrates – Fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals Kingdom Animalia: Evolutionary Advancements of Phyla Phylum Chordata Echinodermata Arthropoda Annelida Mollusca Nematoda Platyhelminthes Cnidaria Porifera Characteristics notocord deuterostome jointed appendages segmentation coelomate; body systems psuedocoelomate organs; bilateral symmetry tissues; radial symmetry multicellular Cephalization Cephalization - concentration of sense organs & nerve cells at the front end of the body In general, the more complex an animal is, the more pronounced is their cephalization (head formation) Kingdom Animalia General Infomation Multicellular & Eukaryotic Organisms Cells lack cell walls & are specialized to carry out different functions Groups of specialized cells form tissues, which form organs and organ systems Multicellular & Eukaryotic Organisms Most animals have 4 types of tissues: – Epithelial – Muscular – Connective – Nervous 7 Essential Functions 1. Feeding – HETEROTROPHIC Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Detritivores Filter Feeders 7 Essential Functions 2. Respiration All animals respire (take in oxygen and give off carbon dioxide) Gas exchange methods range from simple diffusion to complex tissues/organs 7 Essential Functions 3. Circulation Transport oxygen, nutrients, and waste among an animal’s cells Small aquatic animals rely on diffusion Larger animals have a circulatory system – Open C.S. - blood is pumped through a series of sinuses or cavities and comes in direct contact with tissues – Closed C.S. - blood is always contained within vessels 7 Essential Functions 4. Excretion Most animals have an excretory system to eliminate or neutralize ammonia (a primary waste product of cells) Excretory systems vary from cells that pump water out of the body to complex structures like kidneys 7 Essential Functions 5. Response Animals respond to stimuli using nerve cells Nervous systems are present in most animals Simple nervous systems - networks of nerve cells Complex nervous systems - include a brain which directs the whole organism 7 Essential Functions 6. Movement Sessile – attached to a surface; have muscles or muscle-like tissues that allow some movement – feeding by pumping water through the body Motile – free to move by muscle contractions P2 = slate a. Sessile or motile? b. 7 Essential Functions 7. Reproduction Sexually – through the combining of haploid gametes – Creates and maintains genetic diversity in populations – Improves the ability to adapt to environmental changes Asexually – through budding or fission – Allows for quick reproduction – Allows for mass reproduction Early Development Zygote Blastula Blastopore Protostome Deuterostome Body Cavity Acoelomate Pseudocoelomate Coelomate Coelom Symmetry Bilateral Symmetry Radial Symmetry Posterior end Dorsal side Anterior end Ventral side Plane of symmetry Planes of symmetry Radial Symmetry – multiple planes of symmetry Bilateral Symmetry – one plane Asymmetry – no apparent symmetry anterior – toward the head posterior – toward the tail dorsal – back side ventral – belly side Phyla Book Work on your phyla book