* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animalia Kingdom
Territory (animal) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Animal testing wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Remote control animal wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Terrestrial locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Invertebrate wikipedia , lookup
Animalia
Kingdom
Welcome
Home
Animals
• Most diverse kingdom in
appearance
95% = invertebrates (do not
have backbone)
• 5% = vertebrates (have a
backbone)
What is an Animal?
• Heterotrophic
• Eukaryotic
• Multicellular
• Lack cell walls
7 Essential Functions of
Animals
Feeding
• Herbivore = eats plants
• Carnivore = eats animals
• Omnivore = eats plants and
animals
• Detritivore = feed on
decaying organic material
• Filter Feeders = aquatic
animals that strain food
from water
• Parasite = lives in or on
another organism
Respiration
• Take in O2 and give off CO2
• Small animals can undergo diffusion
(exchange of O2 and CO2 via moist
surfaces)
• Larger Animals
– Diffusion not enough
– Specialized respiratory structures
• Gills (must be kept moist)
– provide large surface area for O2 and CO2 exchange
» (mudpuppy)
• Lungs (don’t need moisture)
– Evolved for terrestrial
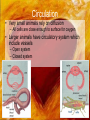
Circulation
• Very small animals rely on diffusion
– All cells are close enough to surface for oxygen
• Larger animals have circulatory system which
include vessels
– Open system
– Closed system
Excretion
• Primary waste product is ammonia, liquid
waste filtered by the kidneys
Response
• Receptor cells = sound, light, external
stimuli
• Nerve Cells = Nervous system
Movement/Support
• Most animals are motile (can move)
• Muscles usually work with a skeleton
– Endoskeleton: hard material inside
– Exoskeleton: external skeleton (crabs, clams,
insects)
Reproduction
• Most reproduce sexually = genetic
diversity
Many invertebrates can also reproduce
asexually = to increase their numbers
rapidly
In parthenogenesis ("virgin birth"), the females produce eggs, but these
develop into young without ever being fertilized. Female Komodo dragons (the
largest lizard) can produce offspring by parthenogenesis when no male is
available for sexual reproduction
Body Symmetry
• The body plan of an animal, how
its parts are arranged
• Asymmetry – no pattern (corals,
sponges)
• Radial Symmetry – shaped like
a wheel (starfish, hydra, jellyfish)
• Bilateral Symmetry – has a right
and left side (humans, insects,
cats, etc)
– Major evolutionary change in
animals
– Enabled different parts of the body
to become specialized in different
ways
Bilateral Symmetry
• Bilateral animals
can be divided
into 4 regions
– Anterior (front)
– Posterior (back)
– Ventral
(underside)
– Dorsal (top)