* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marine Invertebrate Phyla
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
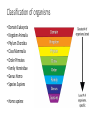
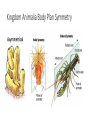
Marine Invertebrate Phyla Focus on Porifera Cnidaria Mollusca Platyhelminthes Annelid Echinodermata Arthropoda Classification of organisms • Domain Eukaryota • Kingdom Animalia • Phylum Chordata • Class Mammalia • Order Primates • Family Hominidae • Genus Homo • Species Sapiens • Homo sapiens Kingdom Animalia Body Plan Symmetry Porifera – “pore bearers” - sponges • Cellular level of organization – cells are largely independent of one another and do not form true tissues or organs • Asymmetrical or radial symmetry • Exoskeleton of spongin fibers (elastic protein), calcareous (calcium) and siliceous (silica) spicules, or both • Sessile • Suspension feeders – filter feeders • Broadcast spawners Cnidaria – sea anemones, jellyfish, corals • Tissue level of organization – have nerve cells • Radial symmetry • Tentacles • Oral surface, aboral surface, gut – gastrovascular cavity • Mostly carnivorous • Nematocysts – stinging cells • Two forms – polyp and medusa Platyhelminthes - Flatworms • Bilateral symmetry - anterior and posterior ends, dorsal and ventral surface • Central nervous system – simple • Flat backs and bellies (dorsoventrally flattened) • Simplest organisms with real tissues and organs Annelida – segmented worms • Bilateral symmetry • Body is broken up into similar compartments called segments • Segments act as a skeleton and can be contracted by muscles • Coelom – body cavity where organs are bathed in fluid • Closed circulatory system • Gills Mollusca – snails, clams, octopuses • Gastropoda – snails, nudibranchs (gastropods who have lost their shell) • Bivalvia – clams, mussels, oysters, etc. • Cephalopoda – octopus, squid • Bilateral symmetry • Most have a soft body in calcium carbonate shell, all have internal or external shell • Mantle – thin layer of tissue that secretes the shell • Muscular foot • Radula – ribbon of small teeth used to feed made of chitin (carbohydrate) • Coelom – fluid filled cavity • Gastropods and bivalves have ganglia – “local brains”, cephalopods have most complex nervous system of all invertebrates Echinodermata – sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, feather stars, sea lillies • Pentamerous radial symmetry in adult form (larvae are bilaterally symmetrical) • More complex body plan - complete digestive tract, coelom, interntal skeleton • Endoskeleton • Water vascular system • Regeneration in some species • Two sexes in most species • Reproduce by spawning Arthropoda – barnacles, crabs, shrimp, lobster, crabs, sea spiders • Largest animal phylum • Exoskeleton • Molt to grow • Bilateral symmetry • Separate sexes in most • Males transfer sperm to female (no spawning) • Simple brain but well-developed sensory organs (compound eyes, “smell” • Behaviorally complex