* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lymphatic System
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Alveolar macrophage wikipedia , lookup
Hemodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Biofluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Common raven physiology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
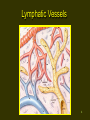
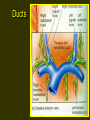
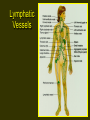
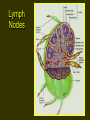
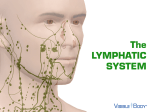
Lymphatic System 1 Lymphatic System • • • • Functions Return fluid to general circulation Production of WBCs Immunity 2 Lymphatic Vessels • Open circulatory system • Originate blindly in tissue interstices throughout the body except CNS and those without blood supply • Thin walled - endothelium only • Permeable 3 Lymphatic Vessels 4 Lymphatic Vessels • Parallel venous flow • Asymmetrical distribution • Two major junctions with cardiovascular system – Thoracic duct into left subclavian vein – Right lymphatic duct into right subclavian vein 5 Ducts 6 Lymphatic Vessels 7 Lymphatic Physiology • Movement into lymphatic capillaries function of osmotic pressure • Valves and muscular activity assist return flow 8 Lymphatic Organs • • • • • Lymph nodes Spleen Tonsils Thymus Diffuse tissue 9 Lymph Nodes • • • • Distributed along vascular pathway Filter lymph Encapsulated by dense CT stroma/framework of reticular fibers, trabeculae • Parenchyma of cortex and medulla • Lymphocytes/t cells 10 Lymph Nodes 11 Lymph Nodes • • • • Macrophages B lymphocytes/b cells Multiple afferent lymphatics Usually a single efferent exiting at hilus/hilum • Size variable 1-25 mm, change with infection • Secondary tumor sites via metastasis 12 Spleen • • • • • Functions Fetal blood development Store and release blood during stress Recycle old blood cells B cell maturation into plasma cells 13 Spleen Structure • 12 cm oval body in left hypochondriac region • Splenic artery and vein enter at hilus • Covered with peritoneum • Structure similar to lymph node • Parenchyma of two types 14 Spleen Structure • • • • • Red pulp Blood filled venous sinuses Splenic cords/Billroth’s cords White pulp Lymphocyte production 15 Tonsils • Aggregated lymph nodes • Concentrated in Waldeyer’s tonsilar ring – Lingual – Palatine – Pharyngeal/adenoid 16 Thymus • • • • • In superior mediastinum Two lobes Surrounded by CT capsule Cortex = reticular fibers + lymphocytes Medulla - epithelial cells produce thymosin stimulating maturation of T cells, form Hassall’s corpuscles • Maximum size 10-12 yrs old ~ 40 grams, degenerates with age 17 Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue • Not encapsulated • Widely distributed throughout body • Found in lamina propria of digestive tract, respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems 18 Pathology • Lymphangitis • Lymphadenopathy • Edema 19