* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Areas - AaronFreeman
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
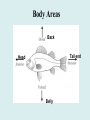
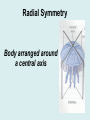
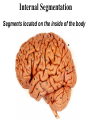
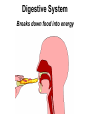
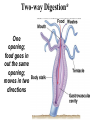
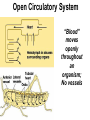
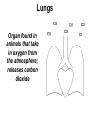
Animal Kingdom Basics Body Areas Back Tail end Head Belly Symmetry: Arrangement of the body parts around a central axis Asymmetry Body that cannot be divided into equal parts Radial Symmetry Body arranged around a central axis Bilateral Symmetry Body that can be divided into equal halves Identify the following examples of symmetry as asymmetrical, radial, or bilateral External Segmentation Segments located on the outside of the body Internal Segmentation Segments located on the inside of the body Skeletal System Provides structure and support for animals Exoskeleton Skeleton on the outside of the body; external skeleton * Endoskeleton Skeleton on the inside of the body; internal skeleton Hydrostatic skeleton Fluid-filled cavity surrounded by muscles; fluid provides support Digestive System Breaks down food into energy Two-way Digestion* One opening; food goes in out the same opening; moves in two directions One-way Digestion Two openings; Food goes in the “mouth” and out the “anus”; moves in one direction Circulatory System Transports oxygen throughout an organism Closed Circulatory System Blood moves throughout an organism closed within blood vessels Open Circulatory System “Blood” moves openly throughout an organism; No vessels Respiratory System Exchange gases; Oxygen is taken in and Carbon Dioxide is released. Diffusion Oxygen moves across a thin membrane; carbon dioxide is release Gills Feather-like structures that take in dissolved oxygen from aquatic environments; releases carbon dioxide Lungs Organ found in animals that take in oxygen from the atmosphere; releases carbon dioxide Nervous System Transmits signals throughout an organism; allows a response to a stimulus Nerve Net Net of nerves that spreads throughout an organism; lacks a control center Nerve Cell Control center; nerve cords extend throughout body; receive and carry messages Integument Outermost layer of an animal; functions in protection from dehydration, freezing, etc. Excretory System Gets rid of waste in an organism Reproductive System Produces offspring Budding Offspring grows from parent; Asexual reproduction; Identical to parent Fragmentation An organism is broken into pieces; the pieces grow into a new organism Hermaphrodite Both sexes are present; produce sperm/egg External Fertilization Union of the egg and sperm outside of the organism Internal Fertilization Union of egg and sperm on the inside of an organism