* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation2
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
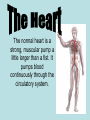
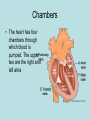
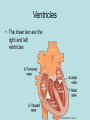
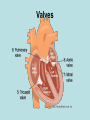
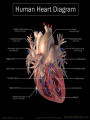
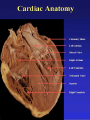
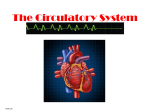
The normal heart is a strong, muscular pump a little larger than a fist. It pumps blood continuously through the circulatory system. • Each day the average heart "beats" (expands and contracts) 100,000 times and pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood. In a 70-year lifetime, an average human heart beats more than 2.5 billion times. • The circulatory system is the network of elastic tubes that carries blood throughout the body. It includes the heart, lungs, arteries, arterioles (ar-TE're-olz) (small arteries), and capillaries (KAP'ih-lair"eez) (very tiny blood vessels). • These blood vessels carry oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to all parts of the body • The circulatory system also includes venules (VEN' yoolz) (small veins) and veins. These are the blood vessels that carry oxygen- and nutrient-depleted blood back to the heart and lungs • If all these vessels were laid end-to-end, they'd extend about 60,000 miles. That's enough to encircle the earth more than twice. • The circulating blood brings oxygen and nutrients to all the body's organs and tissues, including the heart itself. It also picks up waste products from the body's cells. These waste products are removed as they're filtered through the kidneys, liver and lungs. Chambers • The heart has four chambers through which blood is pumped. The upper two are the right and left atria Ventricles • The lower two are the right and left ventricles • Four valves open and close to let blood flow in only one direction when the heart beats: • The tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle. • The pulmonary or pulmonic valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. • The mitral valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle. • The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta. Valves The End http://www.heartpoint.com/theheart.htm l http://health.howstuffworks.com/adam-200083.htm http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/circ.htm http://www.medindia.net/animation/heart_attack.asp