* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Puppy nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Simple living wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition transition wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
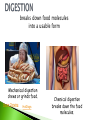
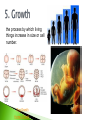
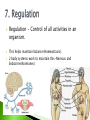
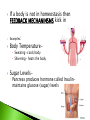
How many can you name? - the process by which living things take in materials from its environment for growth and repair; there are 2 types 1) autotrophic nutrition - where a living Organism can make its own food 2) heterotrophic nutrition--where a organism must ingest (take in) its food taking in food from the environment breaks down food molecules into a usable form Mechanical digestion chews or grinds food. Horse Chewing HotDogs Chemical digestion breaks down the food molecules. The removal of undigested waste from the body. the process by which usable materials are taken into the living thing (ABSORPTION) and distributed throughout the living thing (CIRCULATION) ◦ Examples: Circulatory system- blood carries materials needed for body ( oxygen, nutrients, hormones) Cytoplasm – liquid within the cell Respiration – The release of energy from the food and oxygen we take in. Mitochondria is the Organelle that performs _____________ respiration. There are two types: ◦ Aerobic- uses oxygen to make energy long sustained periods of energy. ◦ Anaerobic- does not use oxygen to make energy. It is Short bursts of energy. The process by which smaller, simple substances are combined chemically to form larger, more complex substances. Think Legos Lego Prank the process by which living things increase in size or cell number. Dog Growth Human Growth Excretion – the removal of liquid and gaseous wastes. Egestion - the removal of solid wastes undigestable wastes. (Remember eGestion is Gross) City Kitty METABOLIC WASTES are produced as organisms perform their life processes. In humans, these wastes include: WATER SALT CARBON DIOXIDE and UREA. Organisms that perform photosynthesis produce oxygen as a waste. Regulation - Control of all activities in an organism. This helps maintain balance (Homeostasis). 2 body systems work to maintain this-Nervous and Endocrine(hormones) Production of a new individual. (Not needed for the individual to survive. BUT Must have for the species to survive.) Two Types: Sexual- 2 Parents Asexual- 1 Parent ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Only one parent contributes DNA. Offspring are genetically identical to that parent. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Two parents contribute DNA. Offspring show a combination of the characteristics of both parents. male lion female tiger Liger Video baby liger tigon offspring male tiger x female lion Video male donkey x female horse male horse x female donkey mule hinny R- Respiration R- Regulation R- Reproduction E- Excretion G- Growth N- Nutrition T- Transport S- Synthesis RRREGNTS SUMMARY 1. All living things share certain characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. 2. The way living things carry out these processes may be different. 3. Non-living things lack the metabolic processes that maintain homeostasis. Metabolism - the total of all 8 life processes. When a person states he has high or low metabolism this is what they are talking about. It is the combination of all the life functions working together. R R R E G N T S = METABOLISM Is the body maintaining internal balance. When all the life processes are occurring normally, it is maintaining homeostasis. If a body is not in homeostasis then FEEDBACK MECHANINSMS kick in Examples: Body Temperature Sweating –cools body Shivering- heats the body Sugar Levels- ◦ Pancreas produces hormone called Insulinmaintains glucose (sugar) levels A Virus is an exception. It cannot carry out all the life processes. To stay alive a virus must invade the cell of a living organism. It needs a Host cell to stay alive. LET’S PRACTICE : People who study biology are concerned with 1. everything on earth 2. all living things 3. only animals 4. only plants LET’S PRACTICE : The removal of cellular waste from an organism is called 1. excretion 2. nutrition 3. transport 4. respiration LET’S PRACTICE : The energy present in food molecules is released by the process of 1. nutrition 2. excretion 3. digestion 4. respiration LET’S PRACTICE : Making complex substances from simpler ones is 1. regulation 2. digestion 3. synthesis 4. reproduction LET’S PRACTICE : The stability of an organism's internal environment is called 1. homeostasis 2. metabolism 3. synthesis 4. respiration