* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8 Life Functions
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition transition wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
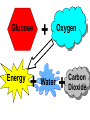
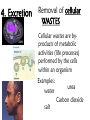
Do Now: Imagine you are a new cast member on the show “Survivor” ….according to the rules you are allowed to bring three items of your choice. What would you bring and why? What is Biology ? • The study of Living Things • Bio = life logy = knowledge (study of) How to Study Biology ? • So many new words ! – know some common prefix and suffix – eg. photosynthesis • photo = light • synthesis = to combine together • ∴ to combine some elements together by using the energy from sunlight Organism Any living thing that carries out life processes Ex. Plants, humans, bacteria, mold Life Processes/ Life functions Activities that are carried out by an organism that enable it to survive. 8 Life Functions 1. Nutrition 2. Respiration 5. Regulation 7. Growth 3. Transport 4. Excretion 6. Reproduction** 8. Synthesis DO NOW: • List the life functions and Describe a system or structure in your body that performs or assists you to perform this process. 1. Nutrition The process in which food is obtained and processed (modified) into nutrients, for Energy Growth and Repair. Four Steps 1. Ingestion - The process of taking in food 2. Digestion -Process of breaking down food into nutrients 3. Absorption -Process of nutrients being absorbed into the bloodstream from the digestive system 4. Egestion -Process of removing solid wastes (undigested food) in the form of feces 2. Respiration The process in which chemical energy is released from the organic material (nutrients) found within the organism ___________ with the help of inorganic substances (oxygen) ____________. Glucose Energy + + Water Oxygen + Carbon Dioxide Two types of Nutrition Heterotrophic nutrition = organism cannot make it’s own food • Example – animals Autotrophic nutrition = organisms make their own food PLANTS= photosynthesis Nutrition involves these activities by which organisms …. 1. Remove cellular waste products 2. Obtain and process materials needed for other life activities 3. Exchange gases with their environment 4. Absorb and circulate materials Respiration is best described as a process by which…. 1. 2. 3. 4. Necessary nutrients are circulated Hydrogen is used to synthesis glucose Metabolic wastes are absorbed Chemical energy is converted into a usable form The absorption of fluids by various cells of the body is part of life function known as 1. 2. 3. 4. Excretion Transport Respiration Growth 3. Transport Movement of materials through the body & within a cell 4. Excretion Removal of cellular WASTES Cellular wastes are byproducts of metabolic activities (life processes) performed by the cells within an organism Examples: water salt urea Carbon dioxide 5. Regulation The process in which all of the organism's life activities are controlled and coordinated to maintain equilibrium 6.Reproduction • Production of new individuals • As an individual, a living thing doesn’t have to reproduce for individual survival BUT must in order to have species survival 7. Growth Process in which there is an increase in cell number NOT size (cell division) AIM: How does our metabolism enable us to live? 8 Life Functions 1. Nutrition 2. Respiration 5. Regulation 7. Growth 3. Circulation 4. Excretion 6. Reproduction** 8. Synthesis 8. Synthesis The process in which the body naturally creates substances by combining small molecules to create larger molecules. Is the set of chemical reactions (life processes) that occur in living organisms in order to maintain life Specific proteins in the body control metabolism. Metabolism is a constant process that begins when we're conceived and ends when we die. It is a vital process for all life forms. If metabolism stops, a living thing dies. refers to the body's ability to regulate its internal physiology to maintain stability in response to fluctuations in the outside environment Balanced internal environment A.D.A.M. Homeostasis • Constant Balance, Steady State or Dynamic Equilibrium • Ability of an organism to “maintains it’s internal environment while responding to external environmental factors – Temp increase or decrease – Starve a fever feed a cold! Which process removes the process of urea in the blood stream of humans? 1. 2. 3. 4. Excretion Egestion Digestion Synthesis Organisms that obtain and ingest organic molecules for their nutrition are classified as 1. 2. 3. 4. autotrophs producers algae heterotrophs Which process includes all three? 1. 2. 3. 4. Synthesis Metabolism Excretion Nutrition Homeostatic regulation of the body Is made possible through coordination of all body systems. This coordination is achieved mainly by… 1. Respiratory and reproductive systems 2. Skeletal and excretory systems 3. Nervous and endocrine systems 4. Circulatory and digestive systems Which situation is not an example of the maintenance of a dynamic equilibrium in an organism? 1. Guard cells contribute to the regulation of water content in a geranium plant. 2. Water passes into an animal cell causing it to swell. 3. The release of insulin lowers the blood sugar level in a human after eating a big meal. 4. A runner perspires while running a race on a hot summer day. How does metabolism enable us to live? THE END