* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Anatomy & Physiology II
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
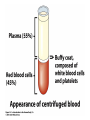
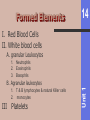
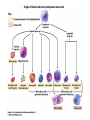
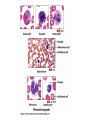
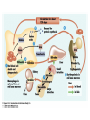
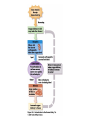
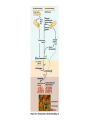
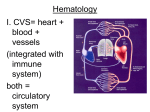
The Cardiovascular System: 14 Blood Unit 1 Chapter 14 • Transportation-hormones, gasses, nutrients, ions, heat • Regulation- pH, temperature, water balance in cells • Protection- clotting, white cells interferons, complement 14 Unit 1 Function • Connective tissue-Two parts • Plasma = soluble materials (~55%) • Formed Elements = cells (~45%) • Percent occupied by red blood cells (RBC) = hematocrit (Hct) • White blood cells (WBC) ~1% 14 Unit 1 Composition Figure 14.1a Figure 14.1b • ~91% water, 7% proteins, 1.5 % other solutes • Proteins: Albumin (54%)- osmosis and carriers; • Globulins (38%)- antibodies • Fibrinogen (7%)- clotting • Other: Electrolytes , nutrients, gases, hormones, vitamins & waste products 14 Unit 1 Plasma Formed Elements 14 I. Red Blood Cells II. White blood cells A. granular Leukocytes 1. Neutrophils 2. Eosinophils 3. Basophils 1. T & B lymphocytes & natural Killer cells 2. monocytes III Platelets Unit 1 B. Agranular leukocytes Formation of Blood Cells 14 • Called hemopoiesis • Just before birth and throughout life occurs in red bone marrow • Contains pluripotent stem cells • In response to specific hormones these develop through a series of changes to form all of the blood cells Unit 1 Figure 14.2a Figure 14.2b Erythrocytes (RBCs) 14 • Hemoglobin package- carries oxygen • Male has ~ 5.4 million cells/µl; Female has ~4.8 million • membrane, no nucleus, flexible structure • use glucose for ATP production to maintain ionic composition No mitochondria • Wear out fast- live ~120 days Unit 1 Also carries some CO2 RBC Cycling 14 • cleared by macrophages (liver & Spleen) • Fe- recycled in bone marrow • Heme bilirubin and excreted (bile) • Globin A.A. recycled. Unit 1 Carried in blood on transferrin Figure 14.3 RBC Synthesis 14 • called erythropoiesis • From stem cells: hemocytoblasts • Released as reticulocytes • • • • Production & destruction is balanced Low O2 delivery (hypoxia) erythropoietin release (EPO) from kidney Stimulates erythropoiesis Unit 1 Mature to erythrocytes in 1-2 days Figure 14.4 White Blood Cells 14 Neutrophil- first responders Monocytes macrophages (big eaters) Eosinophil- phagocitize antibody-antigen complexes Involved in suppressing allergic responses Basophil- intensify allergic reactions • Immune response: T-cells, B-cells& natural killer (NK) cells Unit 1 • Defenses: phagocytes, antibody production and antibacterial action • Phagocytes: WBC Life Span • • • • • Unit 1 5000-10,00 WBC /µl blood Limited number of bacteria can be eaten Life span is a few days During active infection may be hours Leukocytosis= increased WBC numbers response to stresses • Leukopenia = decreased WBC numbers 14 • Myeloid stem cells megakaryocytes 2000 -3000 fragments = platelets • Plug damaged blood vessels • Promote blood clotting • Life span 5-9 days 14 Unit 1 Platelets Hemostasis 14 • Hemostasis = stationary blood • 1. Vascular reactions (spasm) Response to damage Quick reduction of blood loss • 2. platelet plug formation • 3. blood clotting (coagulation) Series of chemical reactions involving clotting factors • Clotting in unbroken vessel= Unit 1 Become sticky when contact damaged vessel wall Coagulation 14 • Extrinsic pathway common steps tissue factor(TF) from damaged cells 1 • Intrinsic Pathway common steps • 1. prothrombinase which causes • 2. prothrombin thrombin causes • 3. fibrinogen fibrin clot Unit 1 Materials “intrinsic” to blood 1 • Clot pugs ruptured area • Gradually contracts (retraction) • Pulls sides of wound together • Fibroblasts replace connective tissue • epithelial cells repair lining 14 Unit 1 Clot Retraction & Vessel Repair • Fibrinolysis: dissolving of clot by activated plasmin enclosed in clot • Clots can be triggered by roughness on vessel wall = thrombosis • Loose clot = embolus and can block a small vessel = embolism 14 Unit 1 Control Mechanisms Figure 14.5 Blood Types 14 > 24 blood groups and > 100 different antigens • We will deal with ABO and Rh groups Unit 1 • Surface antigens- react with antibodies • Divided into groups based on antigens • • • • • Two antigens = A & B If have only A –type A If have only B –type B If neither then Type O Blood usually has antibodies that can react with antigens e.g. anti-A antibody or anti-B antibody • You don’t react with your own antigens Thus: type A has anti-B and vice versa 14 Unit 1 ABO Group Figure 14.6 • Antigen discovered in rhesus monkey • If have antigen- Rh+ • Normally don’t have antibodies • antibodies develop after the first exposure from transfusion 14 Unit 1 Rh Blood Group • If mismatched blood given antibodies bind to it and hemolyze cells • Type AB has no AB antibodies so can receive any ABO type blood called Universal recipients • Type O have neither antigen so can donate to any other ABO type called Universal donors • Misleading because of many other blood groups that must be matched 14 Unit 1 Transfusions