* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hematology - science4warriors
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
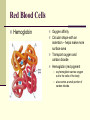
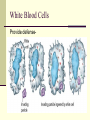
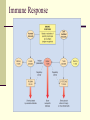
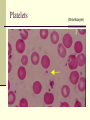
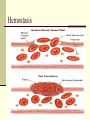
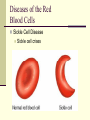
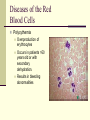
Blood Chapter Hematology The Study of Blood and Blood-Forming Organs Includes study of blood disorders: Red blood cell disorders White blood cell disorders Platelet disorders Coagulation problems Components of Blood RBCs, WBCs, Platelets and Plasma Plasma Plasma Plasma Water 90–92% by volume Proteins Albumins: thicken the blood Globulins: antibodies Fibrinogen: clotting factors Serum – plasma minus its clotting factors, RBC’s, and WBC’s Plasma What does plasma do? Acts as the primary means of transport Plays a role in clotting Acts a buffer Provides a source of energy Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Red Blood Cells Hemoglobin Oxygen affinity Circular shape with an indention – helps make more surface area Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide Hemoglobin (red pigment oxyhemoglobin carries oxygen out to the cells of the body also carries a small portion of carbon dioxide White blood cells (leukocytes) White Blood Cells Provide defense- White Blood Cells White Blood Cell Catagories: 1. Granulocytes Basophil Neutrophil Eosinophil 2. Lymphocytes 3. Monocytes White Blood Cells Immunity Subpopulation of lymphocytes known as T cells and B cells T cells develop cellular immunity. B cells produce humoral immunity. Immune Response Platelets (thrombocyte) Damaged cells release certain clotting factors into the plasma – forming prothrombin activator Platelets become sticky at the point of injury and soon accumulate near the opening in the broken blood vessel, forming a soft, temporary platelet plug Prothrombin converts to thrombin which reacts with fibrinogen to form a fibrous gel called fibrin – looks like a tangle of fine threads that catch RBC’s Hemostasis The combined 3 mechanisms that work to prevent or control blood loss. Hemostasis Controlling Blood Loss Vascular spasms Platelet plugs Stable fibrin blood clots Hemostasis Hemostasis Fibrinolysis Thrombosis Fibrinolytics In your squads, discuss how medications affect clot formation. Lab Work Blood Collection and Values Lab Work Purple Top CBC- Complete Blood Count Used for Hematology: RBC: 3.8-5.6 M/uL WBC: 3.8-11 K/mm3 Neutrophils: 50-81% Bands: 1-5% Lymphocytes: 1444% Monocytes: 2-6% Eosinophils: 1-5% Basophils: 0-1% Purple Top CBC- Complete Blood Count Hbg (hemaglobin): 11-18 g/dL Hct (hematocrit): 34-54% Platelets: 150-450x10-3/dL CBCs In your squad, discuss what you have learned about CBCs. Blood Typing Blood Products and Blood Typing Blood Types Antigens A, B, AB, O Universal donors Universal recipients Rh factor Diseases of the Red Blood Cells Anemias Sickle Cell Disease Polycythemia Diseases of the Red Blood Cells Anemias Anemia is a sign, not a separate disease process. Signs and symptoms may not be present until the body is stressed. Differentiate chronic anemia from acute episode. Diseases of the Red Blood Cells Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell crises Diseases of the Red Blood Cells Polycythemia Overproduction of erythrocytes Occurs in patients >50 years old or with secondary dehydration. Results in bleeding abnormalities Diseases of the White Blood Cells Leukopenia/Neutropenia Leukocytosis Leukemia Lymphomas Diseases of the White Blood Cells Leukopenia/Neutropenia Too few white blood cells or neutrophils. Leukocytosis An increase in the number of circulating white blood cells, often due to infection. Diseases of the White Blood Cells Leukemia Cancer of hematopoietic cells Initial presentation Acutely ill, fatigued, febrile and weak, anemic Often have a secondary infection Diseases of the White Blood Cells Lymphomas Cancers of the lymphatic system Presentation Swelling of the lymph nodes Fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss, fatigue, and pururitis Diseases of the Platelets Thrombocytosis An abnormal increase in the number of platelets Thrombocytopenia An abnormal decrease in the number of platelets Blood Clotting Abnormalities Hemophilia