* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood Typing
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
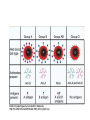
Blood Typing Blood Groups • Karl Landsteiner in the 1900’s discovered blood typing. ABO Blood Groups • Based on 2 Antigens (agglutinogens) • 4 blood types: A, B, AB, O • Blood antigens are genetically coded located on the surface of RBC membrane • Antigen found on RBC corresponds to blood type. Blood Groups • TYPE –A –B – AB –O ANTIGEN PRESENT A B AB Neither A nor B Blood Groups • Antibodies are called agglutinins they develop after birth in the plasma • You will have the antibody for the antigen that is NOT present. • If you have A blood you have the A antigen on your RBC you will develop the B antibody Antibody • TYPE • • • • A B AB O ANTIGEN A B AB neither ANTIBODY anti B anti A neither anti A antiB BLOOD TYPE O A B AB PERCENTAGE 45% 40% 11% 4% • A reaction outside the body between antigens and antibodies result in agglutination which means the blood cells clump together. • A reaction within the body between antigens and antibodies results in hemolysis which means the red cells burst Rh Factors • 1946 Landsteiner, Levine and Weiner did research on the rhesus monkey and developed the Rh factor • Three genes code for the antigen on red cells- C, D, E • Blood Types based on Rh • Rh positive means the Rh antigen is present on the RBC (+) • Rh negative means the Rh antigen is not present on the RBC (-) • Rh negative people that receive Rh positive blood can have the immune system develop Rh antibodies that will remain in the blood Erythroblastosis Fetalis • Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn • A Rh negative mom may be exposed to an Rh antigen from the blood of a Rh positive baby during pregnancy or birth. • If Rh + cell enters Rh- mom the mother’s immune system will respond and produce antibodies against the Rh positive blood antigen • In pregnancies thereafter Rh antibody may cause the placenta and cause RBC hemolysis in fetus. The baby will be anemic and very ill. • This can be avoided by giving a Rh- mom antibodies in the form of a RhoGam shot within 72 hours after delivery of every Rh+ child Blood Typing • Blood typing is when blood samples are tested with known antiseras that contain known antibodies O+ A+ B+ AB+ B+ o- Cross Matching • Cross matching is where typing the donor’s RBC’s are mixed with the recipients serum to check for compatibility before a blood transfusion • http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/m edicine/landsteiner/ • Go to this website and type some blood