* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Unit 10 Personality 2014-2015
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
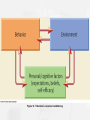
Personality unique make-up of consistent behavioral traits • Personality trait=durable way to behave in a variety of situations-what Trait Theories look at • Ex=honest, dependable, moody, friendly, etc… Factor Analysis factor analysis= Statistical correlation between traits that they cluster as a factor. For instance, conscientiousness is the cluster of traits (punctual, neat, diligent, for instance) Trait Theories • The Five-Factor Model /the Big Five (Costa and McCrea)(CANOE) – Extraversion (outgoing, friendly, upbeat) – Neuroticism (anxious, insecure, self conscious, hostile) – Openness to experience (curious, flexible, imaginative, artistic)-this trait determines political attitudes – Agreeableness (sympathetic, trusting, cooperative, straight forward) – Conscientiousness (diligent, disciplined, well organized, punctual, dependable) Freud on Development: Psychosexual Stages • Sexual = physical pleasure • Psychosexual stages –developmental periods with a sexual focus that leaves its mark on adult personality-formed by age 5 – Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital • Fixation = Excessive gratification or frustration, failure to move forward • Overemphasis on psychosexual needs during fixated stage • Old apple peels look gross Freud’s Five Stages • Oral Stage 0-1=Mouth as pleasure source; Key taskweaning from bottle; Fixation=excessive eating, smoking, etc.. • Anal 2-3=expelling/retaining feces; first attempt to regulate urges; punitive toilet training=hostility toward trainer or a group of people -all women; fixation=Anal retentive-controlling or Anal expulsive-messy • Phallic 4-5=genitals and self stimulation; Erotic energy focuses on the opposite sex parent (Oedipal Complex/Electra Complex) Penis envy-girls hostile toward mom who girl blames for the anatomy deficiency Resolve by identifying with same sex parent (Must resolve for sexual/gender identity personality is developed (Most Imp. Stage) Latency 6-12 • None-sexually repressed • Expand social contact beyond immediate family Genital – puberty and beyond • Focus is on the genitals again • Sexual energy channeled towards the opposite sex Psychodynamic Perspectives Freud’s psychoanalytic theory – Structure of personality • Id - Pleasure principle, instinctive component (unconscious-below surface) • Ego - Reality principle-seeks to delay gratification, tames the desires of the id-The Mediator • Superego =conscience or sensor – Morality-strives for moral perfectionemerges from the ego during Phallic Stage3-5 yrs. (below surface) Underdeveloped id=no impulses control (lie, steal, drugs) Psychodynamic Perspectives Levels of awareness/Consciousness • Conscious-what we are aware of at any given time (EGO) • Preconscious-info. just beneath the surface that can easily be retrieves (EGO) • Unconscious-thoughts, memories and desires below surface but have a GREAT influence on behavior (ID/SUPER EGO) • Freudian Slip/Dreams Psychodynamic Perspectives Freud’s psychoanalytic theory – Conflict between the id, ego and superego is routine-because id wants: Sex and Aggression-causes many conflicts because: These drives need to be routinely frustrated Psychodynamic Perspectives Anxiety, on the conscious level, results when 1. Id getting out of control 2. Superego getting out of control and causing guilt for the real or imagined transgression Anxiety is primary in Freud’s personality theory The result? • Defense Mechanisms-unconscious reactions that protect from unpleasant emotions, anxiety, and guilt Figure 12.3 Freud’s model of personality dynamics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Defense Mechanisms-Work Through Self Deception (protect from anxiety, desires, guilt) Rationalization-explain away failures or flaws Repression-burry painful thoughts/feelings in unconscious (don’t remember an event) Projection-see my own faults in others Displacement-substitute, safe target (yell at brother rather than teacher) Reaction formation-behave opposite of what you feel Regression-act immature Identification-bolster self-esteem through alliance with a person/group ( ex. Club or fraternity) Denial-refusing to believe painful realities (he’d never cheat on me) Sublimation-Sublimation channels the energy from impulses and into acceptable acts (sports, art, hobbies) Neo Freudians • Carl Jung • Alfred Adler • Karen Horney • Eric Erickson Less concerned with Libido=sexual desire Other Psychodynamic Theorists Carl Jung: Analytical Psychology • Unconscious had two layers: – 1. Personal unconscious-houses repressed or forgotten information/events – 2. collective unconscious-latent memories inherited from people’s ancestral past-we share this with the entire human race; seen in: Archetypes- are/symbols/literature/religion-similar between cultures since archetypes are shared by the whole human race (mandala or magic circle) – He felt dreams contained messages from the unconscious Other Psychodynamic Theorists Carl Jung – First to describe Introversion/Extraversion – This was more valuable than his archetype theory • Introverts-preoccupied with the internal world of there own thoughts, feelings, experiences • Extraverts-interested in the external world of people and things Other Psychodynamic Theorists • Alfred Adler: Individual Psychology – Striving for superiority was the main goal of life, not sex – Striving for superiority=a universal drive to adapt , improve oneself, and master life’s challenges – It was inferiority typical of children that motivated children to acquire new skills/talents Other Psychodynamic Theorists Alfred Adler: Individual Psychology Felt we all have to work to overcome feelings of inferiority-a process called: – Compensation=efforts to overcome feelings of inferiority by developing one’s abilities – Inferiority complex=exaggerated feelings of weakness and inadequacy – not normal, results in: – overcompensation=people engage in this to hide these feelings from others/themselves; they engage in activities to make self superior to others, trappings of success( money, cars), status is what they go for rather than achievement – They worry about appearance more then reality Behavioral Perspectives • Skinner’s views –Operant Conditioning and response tendencies-they pay little attention to personality structure –Environmental determinismenvironment determines our behaviors Figure 12.6 Personality development and operant conditioning Behavioral Perspective • Bandura’s views (now called social- cognitive theory) or Social leaning theory Observational learning =(Imitation and Models) Reciprocal Determinism= 1.Thinking, 2. Behavior and the 3. Environment interact , and influence each other Self-efficacy (part of 1. Thinking) =one’s beliefs about one’s ability to perform behaviors that lead to expected outcomes (2 and 3 above) Perceptions of self-efficacy are subjective • High=feel confident and results in behavior • Low= opposite Figure 12.7 Bandura’s reciprocal conditioning Humanist Perspective on Personality • Humanism=emphasizes the unique qualities of humans, especially their freedom and potential for personal growth Humanistic Perspectives • Carl Rogers – Person Centered Theory-theory based on one construct: • Self-concept (beliefs about our own nature, unique qualities, and typical behavior) “I’m easygoing, shy, hard working…” • We distort this in our favor- it may not be in-line with our experience – Conditional/unconditional positive regard Conditional (love you if you please me)verses Unconditional Positive Regard (Rogers-Humanism) Incongruence=the degree of disparity between one’s self-concept and one’s actual experiences and We all have incongruences-Too much incongruence undermines one’s psychological well-being Humanistic Perspectives Carl Rogers Development of the Self: Unconditional love-congruence Conditional love incongruence- Distort more experiences to feel worthy of acceptance Defense Mechs. Protect inaccurate selfconcept Figure 12.9 Rogers’s view of personality structure Humanistic Perspectives Abraham Maslow “What a man can be, he must be.” – Self-actualization theory-felt drive is innate – Hierarchy of needs • The healthy personality= people who have continued self-growth Peter Sees Bees Everywhere Silly Physical, Safety/ Belonging, Esteem, Self Actualization Evaluating Humanistic Perspectives • criticized for overly optimistic view of human nature (Maslow had a hard time finding live people who had self-actualized). Biological Perspectives • Eysenk’s theory – All traits come from 3 higher order traits – Extraversion, neuroticism (anxious, tense, moody, low self-esteem), and psychoticism (egocentric, cold, impulsive, antisocial) Behavioral Genetics and Personality Determined by genes • Twin studies showed CANOE innate or had a high level of heredability Figure 12.14 Twin studies of personality Personality Tests • 2 Types 1. Self reporting inventories =most common personality tests = true false rating scale Example: MMPI (most widely used ) -14 subscales MMPI used to detect disorders MMPI Sub-Scales 2. Projective Tests • Respond to vague, ambiguous stimuli that reveal one’s needs, feelings and personality traits (which perspective would use this???) • Rorscharch-10 inkblots • TAT (Thematic Apperception Test) shown scenes and asked to tell what they see (Side fact from Motivation Unit-those high in achievement motive revealed on TAT) Cons of self-reporting scales • Social desirability bias • Response set-respond in a way that has nothing to do with the content (Yes or no to every question) Ink Blot Test TAT (Thematic Apperception Test) Pros-not transparent to subject Can show unconscious features Cons-not reliable/valid Thematic Apperception Test Other Concepts • Julian Rotter-Locus of Control impacts one’s personality External-others and events control my life and/ or my reactions Internal –I have control over life events and/ or my reactions