* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Photographers of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
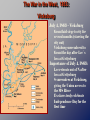
The Civil War (1861-1865) EU: The Civil War, begun as a limited struggle over the Union, eventually became a total war to end slavery and transform the nation. (Change over time – the goal of the war) The Great Emancipator? Assess the following claim: Lincoln has often been called “The Great Emancipator.” This is a misnomer. Many other actors were much more crucial to the emancipation of the slaves than Abraham Lincoln, who was reluctant and slow in coming to the decision and cautious and ineffectual in its execution. Further, the Emancipation Proclamation was not the revolutionary document that some historians claim. Events Prior to the War •November 6, 1860 – Lincoln elected President •December 20, 1860 South Carolina secedes from Union •February 8, 1861 Confederates States of America formed, Jefferson Davis – President •March 4, 1861 – Lincoln inauguration •April 12, 1861 – Fort Sumter attacked – Civil War begins! Fort Sumter – Charleston, South Carolina 3000 shell hits in 36 hour battle. Slave/Free States Population, 1861 Railroad Lines, 1860 Resources: North & the South The Union & Confederacy in 1861 Men Present for Duty in the Civil War The Leaders of the Confederacy Pres. Jefferson Davis VP Alexander Stevens The Confederate “White House” The Confederate Seal MOTTO “With God As Our Vindicator” A Northern View of Jeff Davis Overview of the North’s Civil War Strategy: “Anaconda ” Plan The “Anaconda” Plan Winfield Scott believed an effective "Blockade" of Southern ports, a strong thrust down the Mississippi Valley with a large force, and the establishment of a line of strong Federal positions there would isolate the disorganized Confederate nation "and bring it to terms." Lincoln’s Generals Winfield Scott Irwin McDowell George McClellan Joseph Hooker Ambrose Burnside Ulysses S. Grant George Meade George McClellan, Again! McClellan: I Can Do It All! South’s victory increased overconfidence (desertions increased, enlistments decreased) North’s defeat caused them to prepare for a long war General George McClellan given command of Army of the Potomac (main army in Washington D.C.) Great organizer & drillmaster, but too cautious (refused to move the army; always believed he was outnumbered) Lincoln ordered him to advance – Spring 1862 Peninsula Campaign 100,000 Union troops under McClellan advance to peninsula b/w James and York Rivers Lincoln pulled him away from Richmond to stop Stonewall The Confederate Generals “Stonewall” Jackson Nathan Bedford Forrest George Pickett Jeb Stuart James Longstreet Robert E. Lee The “new kid in town” – U.S. Grant February 1862 – Grant seizes Fort Henry and Fort Donelson in TN. April 6-7, 1862 “Total War” introduced by Grant: Battle at Shiloh Grant demands unconditional surrender Significance: Secured KY for Union Opened Tennessee line Opened route to GA The Battle of the Ironclads, March, 1862 The Monitor vs. the Merrimac Buy Your Way Out of Military Service War in the East: 1861-1862 Battle of Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” September 17, 1862 23,000 casualties Battle of Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” General Robert E Lee is stopped by McClellan, by days ends 26,000 are dead, wounded or missing. Lee Withdraws to VA. Lincoln restored McClellan to command of Northern Army Northern soldiers found a copy of Lee’s battle plans wrapped around 3 cigars dropped by a Confederate officer. *Preliminary Emancipation Proclamation is written. Emancipation in 1863 The Emancipation Proclamation Jan 1, 1863 The Southern View of Emancipation African-American Recruiting Poster The Famous 54th Massachusetts Black Troops Freeing Slaves Extensive Legislation Passed Without the South in Congress 1861 – Morrill Tariff Act 1862 – Homestead Act 1862 – Legal Tender Act 1862 – Morrill Land Grant Act -This gave each state 30,000 acres of public land for each Senator and Representative. These numbers were based on the census of 1860. The land was then to be sold and the money from the sale of the land was to be put in an endowment fund which would provide support for the colleges in each of the states. 1862 – Emancipation Proclamation (1/1/1863) 1863 – Pacific Railway Act The War in the West, 1863: Vicksburg July 4, 1863 – Vicksburg Grant laid siege to city for several months (starving the city out) Vicksburg surrendered to Grant the day after Lee’s loss at Gettysburg Importance of July 4, 1863: Lee retreats out of N after loss at Gettysburg S surrenders at Vicksburg, giving the Union access to the MS River Ex-slaves truly celebrate Independence Day for the first time The Road to Gettysburg: 1863 Lee marched into Pennsylvania – hoping strong victory in N would give strength to peace Dems in N & get BR or FR to help S July 1-3, 1863: GETTYSBURG Meade (92,000 men) took the good land Lee (76,000 men) attacked 3 day battle General George Pickett’s charge against Union lines driven back, breaking Confederate advance, forcing Lee to retreat As far North as South ever got Confederate peace delegation was rejected by Lincoln Last chance for Southern victory; final two years were fighting a lost cause TURNING POINT of the Civil War November 19, 1863 – Gettysburg Address delivered by Lincoln The North Initiates the Draft, 1863 Recruiting Irish Immigrants in NYC Recruiting Blacks in NYC NYC Draft Riots, (July 13-16, 1863) NYC Draft Riots, (July 13-16, 1863) A “Pogrom” Against Blacks The Progress of War: 1861-1865 Sherman’s “March to the Sea” through Georgia, 1864 1864 Election Pres. Lincoln (R) George McClellan (D) The Peace Movement: Copperheads Clement Vallandigham 1864 Copperhead Campaign Poster Presidential Election Results: 1864 Surrender at Appomattox April 9, 1865 Casualties on Both Sides Civil War Casualties in Comparison to Other Wars Ford’s Theater (April 14, 1865) The Assassin John Wilkes Booth The Assassination WANTED~~!! Now He Belongs to the Ages! The Execution