* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File road to civil war2
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
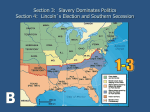
Sectionalism Issue: Should the price of Western land be High or Low? North: HIGH This would prevent northern workers from moving out west in search of land. South: LOW Low prices would make it easier to spread slavery and expand the cotton industry. Replace land worn out from farming. West: LOW Low prices would encourage people to come and settle the west. Sectionalism Issue: Should Workers be Free Men or Slaves? North: FREE South: SLAVE Workers should be free men and have the ability to select the occupation they are best suited for. Slave labor would be a threat to the working man Slave labor is necessary to do the hard work of producing cotton, The south’s “White Gold”. Owners argued that without slavery they would be unable to hire enough workers to harvest cotton West: FREE Workers in the west do not want slave labor in their section. Slave labor would steal jobs away from free whites. Sectionalism Issue: Should the U.S. have a High or Low protective tariff? North: HIGH South: LOW West: HIGH Tariffs would protect northern businesses by increasing the prices of foreign imports. This results in more people purchasing American-made goods. High U.S. tariffs would cause other nations to have higher taxes on Southern farm goods which would cut into their profits. Low tariffs would keep farming costs down. Money raised by the tariffs could be used to build roads and bridges which would allow farmers in the west to transport their raw materials to Northeastern factories. This would enable them to make more money. Sectionalism Issue: Should the U.S. make Internal Improvements (Bridges + Roads)? Yes or NO North: YES Better roads would allow them to sell their goods out in the west and receive raw materials from the West. South: NO West: YES Money spent would empty the treasury and would cause the government to raise taxes, resulting in more costs for Southern plantation owners. Better roads would allow western farmers to sell their goods to the northeast and increase access to manufactured goods from the Northeast. Sectionalism Issue: Should the U.S. increase the supply of money, ultimately causing inflation.? North: NO Northerners were often money lenders. Increasing the supply of money would lessen the value of each dollar that will be repaid on loans. South: YES Farmers were often in debt. Greater supply of money would enable them to inflate prices and pay off debts faster. West: YES More money in circulation would make it easier for Westerners to pay off their debts. Sectionalism: Loyalty to one’s sectional interests • 1. Who is the man in the cartoon? • 2. What are the different regions shown in the cartoon? • 3. What are the economic ways of life of each of these regions? • 4. What is happening to the man in the cartoon? The Bottom Line • As you can see the North and South differed on these five important issues. • This led to a power struggle between these two sections of the nation. • The section that controlled the federal government would be able to set economic policy that would affect the very livelihood of the other. • Political power became crucial to their economic interests. The Missouri Question - Northerners were against adding Missouri to the union as a slave state because it would disrupt the balance of power in Congress between slave and free states. Balance of Free and Slave States (1819) Original 13 States Illinois (1818) Indiana (1816) Alabama (1819) Mississippi (1817) Ohio (1803) Vermont (1791) Rhode Island Louisiana (1812) Tennessee (1796) Kentucky (1792) New York New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Maryland New Jersey Pennsylvania Free States Georgia Delaware Slave States Balance of Free and Slave States (1821) Missouri Compromise • Missouri was admitted to the union as a slave state, and Maine was admitted as a free state. Original 13 States Maine (1820) Illinois (1818) Indiana (1816) Ohio (1803) Missouri (1821) Alabama (1819) Mississippi (1817) Louisiana (1812) Vermont (1791) Rhode Island New York New Hampshire Tennessee (1796) Kentucky (1792) Virginia North Carolina Massachusetts Connecticut South Carolina Maryland New Jersey Pennsylvania Free States Georgia Delaware Slave States • An imaginary line was drawn across the southern border of Missouri at the latitude 36 30'N. 36 , 30’ • Slavery was allowed in the part of the Louisiana Purchase south of the 36 , 30'N. • Slavery was banned north of 36 , 30'N, except for Missouri. Sectionalism – loyalty to a state or section rather than to the whole country. Free States Original 13 States California (1850) Wisconsin (1848) Iowa (1846) Michigan (1837) Maine (1820) Texas (1845) Florida (1845) Arkansas (1836) Missouri (1821) Illinois (1818) Alabama (1819) Indiana (1816) Mississippi (1817) Ohio (1803) Louisiana (1812) Vermont (1791) Tennessee (1796) Rhode Island Kentucky (1792) New York Virginia New Hampshire North Carolina Massachusetts South Carolina Connecticut Maryland New Jersey Georgia Pennsylvania Delaware Slave States Compromise of 1850 I. California became a free state. II. The rest of the Mexican Cession was divided into two parts; Utah (UT) and New Mexico (NM). * people in UT and NM used popular sovereignty (a vote of the people) to decide on the slavery issue III. The slave trade ended in Washington, D.C. IV. The Fugitive Slave Law was passed. Compromise of 1850 The Fugitive Slave Law • All Americans, by law, were required to help catch runaway slaves. • You could be fined and/or imprisoned for helping a runaway slave. • This law infuriated northerners! Cazenovia, MA, Fugitive Slave Law Convention held on 21 and 22 August 1850; Frederick Douglass is seated at the right side of the table. Uncle Tom’s Cabin 1852 Sold 300,000 copies in the first year. 2 million in a decade! Impact of Uncle Tom’s Cabin • The book portrays slavery from a slave’s perspective. • Broke down the stereotype that slaves were a sub-human, animal-like race. • Showed slaves as caring people with the same feelings and emotions as whites. • Convinced many in the North that slavery was evil and must be abolished. • Southerners call the book a “pack of lies” and become more determined to defend slavery. Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811 – 1896) So this is the lady who started the Civil War. -- Abraham Lincoln Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854 Kansas-Nebraska Act II. The people of each territory voted on whether or not to allow slavery. (popular sovereignty) * The Kansas-Nebraska Act violated the Missouri Compromise. Both territories were north of 36 , 30’ N and should NOT have been allowed to have slaves. Birth of the Republican Party, 1854 ß In response to the passage of the KansasNebraska Act, the Republican party was formed. ß Party platform: ßFree Labor ßFree Soil ßFree Men ßOpposed the expansion of slavery into the territories of the west. “Bleeding Kansas” Border “Ruffians” (pro-slavery Missourians) * In 1856, an abolitionist named John Brown murdered five proslavery men. * Over 200 people died in the fighting that followed. The abolitionist John Brown lived in Osawatomie, Kansas Territory. Brown and his sons were responsible for the brutal murder of several proslavery men near Pottawatomie, Kansas. The men were called out of their homes at night and hacked to death with swords. This was just one of many incidents that earned Kansas Territory the name of "Bleeding Kansas.” “Bleeding Kansas” Before the vote on slavery: • Northerners crossed the border to keep KS a free state. • Southerners crossed the border to make KS a slave state. • Both sides claimed victory on the vote! Kansas became a free state in 1861 “The Crime Against Kansas” Sen. Charles Sumner (R-MA) Congr. Preston Brooks (D-SC) On May 19, 1856, Senator Charles Sumner, a Massachusetts antislavery Republican, was attacked by Congressmen Preston Brooks. Sumner was speaking out against ProSlavery senators and Brooks took exception. Dred Scott v. Sanford, 1857 Dred Scott Decision - FACTS: • Dred Scott was a slave from Missouri. (MO) Dred Scott Dred Scott Decision - FACTS: • Scott and his owner moved to Wisconsin for four years. Dred Scott Dred Scott Decision - FACTS: • Scott’s owner died after returning to Missouri. Dred Scott Dred Scott Decision - FACTS: * Scott sued for his freedom. He claimed that he should be a free man since he lived in a free territory (WI) for four years. Dred Scott SUPREME COURT DECISIONS: Q: Was Scott a U.S. citizen with the right to sue? A: NO Q: Did living in a free territory make Scott a free man? A: NO Q: Did Congress have the right to outlaw slavery in any territory? A: NO RESULTS: • Dred Scott was not given his freedom. • The Missouri Compromise was found to be unconstitutional. •Southerners viewed the decision as a victory and refused to accept any limitations on slavery in the territories Open to slavery through popular sovereignty (Compromise of 1850) Missouri Compromise line is declared unconstitutional (Dred Scott Decision) Open to slavery through popular sovereignty (KS-NE Act) The Lincoln-Douglas (Illinois Senate) Debates, 1858 A House divided against itself, cannot stand. Lincoln – Douglas Debates In 1858, Abraham Lincoln challenged incumbent Stephen Douglas for his seat in the Senate. (Incumbent – the holder of an office or position) Abraham Lincoln (left) and Stephen Douglas (right) Lincoln – Douglas Debates Stephen Douglas: • Lincoln was wrong for wanting to limit the expansion of slavery. • If Lincoln tried to end slavery, the U.S. could face a civil war. • Douglas believed that each territory should be able to decide on its’ own whether or not to allow slavery by using popular sovereignty. Lincoln – Douglas Debates Abraham Lincoln: • Lincoln believed that slavery was evil and should be kept out of the territories. • Lincoln believed that African Americans were guaranteed “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness”, as stated in the Declaration of Independence. Lincoln – Douglas Debates Results: • Douglas won the election by a slim margin. • However, Lincoln became well known throughout the nation. Lincoln-Douglas Debates: Video (2:13) John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry, 1859 John Brown’s Raid: • In 1859, John Brown and his followers seized a federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia. •Part of a bigger plan to start a national slave rebellion. John Brown in August, 1859. Engine house at Harpers Ferry. Marines storm the engine house. • Brown was caught and sentenced to death by hanging. Brown as a wounded prisoner after his capture. Brown being carried from court to prison. "Now, if it is deemed necessary that I should forfeit my life for the furtherance of the ends of justice, and mingle my blood further with the blood of millions in this slave country whose rights are disregarded by wicked, cruel, and unjust enactments, I say, let it be done." --John Brown, statement at his sentencing on Nov. 2, 1859 Last Moments of John Brown (painting by Thomas Hovenden) The hanging of John Brown. John Brown: Madman, Hero or Martyr? Mural in the Kansas Capitol building by John Steuart Curry (20c) √ Abraham Lincoln Republican Stephen A. Douglas Northern Democrat 1860 Presidential Election John Bell Constitutional Union John C. Breckinridge Southern Democrat 1860 Election: A Nation Coming Apart?! Republican Party Platform in 1860 ß Non-extension of slavery [for the Free-Soilers. Free Homesteads for Farmers. ß Protective tariff [for the No. Industrialists]. ß No abridgment of rights for immigrants [a disappointment for the “Know-Nothings”]. ß Government aid to build a Pacific RR [for the Northwest]. ß Internal improvements [for the West] at federal expense. 1860 Election Results Election of 1860: Main Candidates Abraham Lincoln (Republican) John Breckinridge (Southern Democrat) Stephen Douglas (Northern Democrat) John Bell (Constitutional Union) * Lincoln won the election. Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860 Secession: • In response to Lincoln’s victory, the southern states seceded from the Union in 1861, forming the Confederate States of America. Original Confederate flag Eventual Confederate flag Fort Sumter • Fort Sumter, South Carolina, was important because it guarded Charleston harbor • Therefore, the Confederates attacked, defeating the Union soldiers. * The Civil War had now begun! Bombardment of Fort Sumter, Charleston Harbor 12 and 13, 1861 April Fort Sumter, S.C., April 4, 1861, under the Confederate flag. Civil War: Union v. Confederacy • Jefferson Davis was named the president of the Confederacy.