* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War - JGIST
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
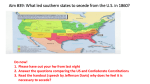
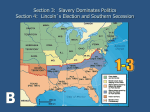
Civil War African American History Inevitable or Avoidable? Territorial Expansion disturbed the balance Six Decades of National Growth led to sectional strife American Nationalism tested Slave and Free Labor Economic Systems Review What was Southern Confederates goals in the war? ___________ refers to “enemy property” __________ an area that was successfully defended near the Mississippi by black soldiers against rebels. Review Part II Is War really necessary today? Did blacks have a right to get involved in this war? Why or Why not? ___________ hard-nosed southern racist, who eventually was elected as the President of the Confederate States of America Review III True/False; Lincoln’s initial position on slavery was that he supported it? True/False; General Order 11 was a threat by Lincoln to execute southern troops or confine them to hard labor? True/False; John C. Fremont, A union general was threatened by Lincoln to stop freeing slaves after the First Confiscation Act was passed Review Part IV First Confiscation Act stated that any_________ belonged to Confederacy and used in war effort could be seized. List the Four Border States: Why were they considered border states? True/False; The firing on Fort Pillow by the Confederates led to the beginning of the civil war. Crittenden Compromise 1861 Last minute compromise that recognized slavery in territories south of the 36 30’N latitude line. Lincoln rejected Horace Greeley, New York Tribune, proposed that the federal government allow seceding states to go in peace FIRE CRACKERS TO THE WAR Benjamin Butler, Union General “contraband” --enemy property and put them to work. Over a thousand runaways fled to Fortress Monroe. 1,000 plus runaway slaves fled to Fort Monroe. FIRE CRACKERS CONTINUED Aug. 6, 1861 First Confiscation Act was passed which stated that any property that belonged to Confederates that was used in the war effort could be seized by federal forces. John C. Freemont began to free slaves in Missouri: Why would Lincoln have a problem with this? FIRECRACKERS The Fort Pillow Massacre Nathan Bedford Forrest slaughtered black troops and their white commander William F. Bradford No one was ever punished during or after the war. founder of the Ku Klux Klan The New York City Draft Riot Poor, unskilled Irish workers, and other Northerns convinced by Democrats War was to benefit blacks white. For four days, city police could control and blacks were beaten and lynched. The Colored Orphaged was burned to the ground, businesses employing blacks and Protestant churches were destroyed Lincoln’s Position Believed secession was wrong Committed to stopping the expansion of slavery Emphasized his duty to enforce the laws of the United States Fort Sumter Occupied by Federal troops Confederates blocked the fort Lincoln promised to send food but no soldiers to re-supply Fort Sumter Jefferson Davis ordered General Beauregard to force a surrender of Fort Sumter When refused, Confederates fired upon Sumter Secession South Carolina seceded following Lincoln’s election Six other Lower South states followed After Fort Sumter, Upper South states (VA, NC, TN, and AK) seceded Border States: Missouri, Maryland, Kentucky, & Delaware Aims of the War South Defend their rights Protect their way of life Defend their families and property North Maintain the supremacy of the Constitution Preserve the Union Advantages North Greater Population Railroad Mileage Factories South Leadership Military Tactics Morale/Confidence The Issue of Slavery “If I could save the Union without freeing any slave, I would do it, and if I could save the Union by freeing all the slaves, I would do it.” -President Lincoln Lincoln’s Dilemma Lincoln personally opposed slavery Could not legally abolish it Concerned about the Border States Saw the importance of slave labor to the South’s war effort Ending slavery became a strategy for winning the war Emancipation Proclamation September 1862, Lincoln proclaimed that on January 1, 1863 slaves in the rebelling territories would be free. Slaves under Confederate control were to be set free Slaves under Union control were not set free Reaction Condemned and ignored in the South Debated heavily in the North Abolitionists believed Lincoln should end slavery Blacks assumed that with a Northern victory slavery would end Contraband Significance The war to preserve the Union now becomes a revolutionary struggle for the abolition of slavery. Black Soldiers Blacks were initially rejected July 1862 Congress authorized Lincoln to accept blacks 180,000 enlisted immediately Most were southerners 54th Massachusetts –Fort Wagner Blacks Roles during the War . Mary Elizabeth Bowser worked at the Confederate White House spy: Jeff. Davis Robert Smalls 23 yr old slave, served on the The Planter a Confederate supply ship. fifteen other slaves including the families of several crewmen and his own wife, daughter and son. Black Roles continued Harriet Tubman organized a spy ring in the South Carolina Second South Carolina Volunteer Regiment, organize an expedition that destroyed plantations and freed nearly 800 hundred slaves, many of whom joined the Union Army. Europe’s Reaction Perhaps the most significant reaction Proclamation ended any real chance of France and Great Britain intervening in the war (Antislavery/Abolitionism) The War for Constitutional Liberty; The War for Southern Independence; The Second American Revolution; The War for States' Rights; Mr. Lincoln's War; The War of the Southern Planters; The War of Rebellion; The Second War for Independence; The War to Suppress Yankee Arrogance; The Brothers' War; The War of Secession; The War Against Slavery; The War for Separation; The War for Abolition; The War of the Southrons; The War of the North and South; The Lost Cause; The War Between the States (Davis, 79). The title The War Between the States is