* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Texas and the Civil War
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
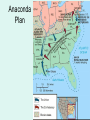
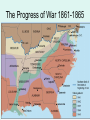
Chapter 15 Section 2 Texans Go To War In its declaration of secession, Texas stated that it intended to go to war to preserve a southern way of life that made racial distinctions, in part, by maintaining blacks in a condition of servitude. Civil War Begins • The Civil War begins in April 1861 at Fort Sumpter in Charleston Harbor, South Carolina • Confederate forces fire on a Union fort in the harbor and war begins • Beauregard vs. Anderson – Friends yet enemies Many Texans Become Soldiers • Thousands of Texans like other Southerners joined the Confederate army immediately. • In April 1862, the Confederate Congress passed the Conscription Act which required men of a certain age to serve in the Confederate military • German American settlers objected to fighting against the Union. The two highest-ranking Texans in the Confederate army were Albert Sidney Johnston and John Bell Hood. Most Texans Support the South • After the war began, most Texans who previously had been against secession now supported the Confederacy. • James W. Throckmorton, who had voted against secession, realized that he could not fight against Texas. • About 60,000 Texans joined the armed forces of the Confederacy. 5TH TEXAS VOLUNTEER INFANTRY, CO. K Some Texans Aid the Union • About 2,000 Texas Unionists, including 50 African-Americans, took up arms for the Union. Mexican-Americans served on both sides of the war. • Many Texas Unionists who did not want to fight on either side left Texas. Major Battles of the Civil War Chapter 15 Section 2 Americans Expect a Short War • Union and Confederate Advantages: A. Union advantages in war: 1) soldiers 3) food 2) factories 4) railroads B. Confederate advantages in war: 1) cotton profits 3) generals 2) motivation to fight Strategies • Union strategy to conquer South • Anaconda Plan (plan intended to): 1) blockade Southern ports 2) divide Southern states in half (at MS River) 3) capture Richmond, Confederate capital • Confederate strategy 1) defend the Confederate states 2) invade Northern states if opportunity arises Union “Anaconda” Plan • 1. Capture Richmond, Virginia – Capital of Confederacy • 2. Blockade Southern ports – Prevent trade with other countries • 3. Capture the Mississippi River – Cut Confederacy in half – Cut off trade routes from New Orleans and Texas Anaconda Plan Texas-Mexico Trade Routes Texas was economically important to the Confederacy because the Confederacy was able to conduct foreign trade through Mexico by way of Texas. The Progress of War 1861-1865 Ft Sumter • April 12, 1861 • Charleston Harbor – Charleston, S.C. • Union surrendered the fort Significance of Ft. Sumter • Led to the secession of Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina • First military action of the war • This is the start of the Civil War! First Battle of Bull Run • July 21, 1861 • Manassas, Virginia (also called “1st Manassas”) – 30 miles from Washington, D.C. • Confederates won the battle, but failed to chase the Union army • 4,700 killed/wounded/captured (K/W/C) Significance of Bull Run • First major battle of the war • Confederate victory; Morale boost for the South. • War would not go exactly as either side expected-people thought the war would be over in a few days Battle of Shiloh • April 6-7, 1862 • Pittsburg Landing, Tennessee – near Shiloh Church • Confederates drove Union back the first day, but Union won the battle the second day • 24,000 K/W/C Significance of Shiloh • Texas General Albert Sidney Johnston killed. – Considered one of South’s best Generals – Fought at Battle of San Jacinto • Showed that this would be a long and bloody war • Showed the determination and skill of Ulysses S. Grant Battle of Antietam • September 17, 1862 • Bloodiest single day of the Civil War • Bloodiest single day battle in American History! • Battle is a Standoff = no side wins • 28,000 killed (more WC) Battle of Gettysburg • July 1 - 3, 1863 • Gettysburg, Pennsylvania • R.E. Lee led Confederate forces into the North. Union army defeated the confederates in a costly 3 day battle • 46,000 K/W/C • Bloodiest battle of the entire Civil War Significance of Gettysburg • Turning point of the war • Confederate invasion of the North failed • Huge morale defeat for the South • Combined with the defeat at Vicksburg the next day, the South was never able to recover. Vicksburg • May 18 - July 4, 1863 • Vicksburg, Mississippi – on Mississippi River • Confederates surrender after 47 day Union siege of the city • 36,000 K/W/C Significance of Vicksburg • Ulysses S. Grant took control of the Mississippi River • Split the confederacy in half and cut off important trade routes through New Orleans and Texas Texans on the Attack • The Confederacy’s first objective was to overtake Union garrisons and supplies • Texas launched a preventative strike on Union Forces in New Mexico • The New Mexico Campaign failed and was abandoned in July 1862 Battle of Galveston • Union ships blockaded Texas ports. • Cotton was transported through Mexico and sent to Europe in exchange for war supplies. • In October 1862 Union forces attacked and captured Galveston. • Texas Confederate forces retook Galveston in January 1863. Texans Defend Sabine Pass • Confederate soldiers defeated Union forces at Sabine Pass. • Dick Dowling and the Davis Guards played a major role by capturing 350 soldiers and two boats. • The Battle of Sabine Pass was an important Confederate victory, foiling the Union’s major campaign against Texas. "There is no parallel in ancient or modern warfare to the victory of Dowling and his men at Sabine Pass considering the great odds against which they had to contend" Jefferson Davis The Battle of Sabine Pass September 8, 1663 In the fall of 1863, Confederate forces under the command of Lt. Richard Dowling turned back a much larger Union invasion force at the battle of Sabine Pass. Forces Battle over Brownsville • Hoping to cut off the overland supply line, the Union focused on Brownsville. • In November 1863 Confederate troops drove back a Union attack on Brownsville. Red River and Beyond • Union forces captured New Orleans. • With 25,000 troops, they moved toward East Texas. • A smaller Confederate army met the Union forces 25 miles from the Texas border in one of the bloodiest campaigns. Red River and Beyond • Hood’s Texas Brigade and Terry’s Texas Rangers served bravely • Terry’s Texas Rangers served in more battles than any other cavalry regiment in the Civil War. • General Robert E. Lee called Hood’s men his “finest soldiers.” Battle of Palmito Ranch • General Robert E. Lee surrendered to General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Courthouse in Virginia on April 9, 1865. • The last land battle of the Civil War took place on May 13, 1865, at Palmito Ranch, near Brownsville. • Texans learned from their prisoners that Lee had surrendered a month earlier. Milton Holland – Medal of Honor • Texan - Union soldier • Won Medal of Honor • Fifth U.S. Colored Troops in Athens, Ohio • Son of Bird Holland (TX Secretary of State before Civil War) • Possible slave to Bird’s half brother Colonel Santos Benavides –Confederate • Led may Mexican American Confederate Soldiers • Supported Lamar during Mexican American War • Supported South due to close principles to his beliefs in regionalism • Arranged safe passage of Tx cotton along Rio Grande to Matamoras while Union occupied Massacre at Nueces