* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexual Motivation
Hookup culture wikipedia , lookup
Sexuality after spinal cord injury wikipedia , lookup
History of homosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual objectification wikipedia , lookup
Sexual slavery wikipedia , lookup
Sex-positive feminism wikipedia , lookup
Ages of consent in South America wikipedia , lookup
Ego-dystonic sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Sexual fluidity wikipedia , lookup
Sexological testing wikipedia , lookup
Sexual racism wikipedia , lookup
Age of consent wikipedia , lookup
Heterosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Exploitation of women in mass media wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dysfunction wikipedia , lookup
Sex and sexuality in speculative fiction wikipedia , lookup
Penile plethysmograph wikipedia , lookup
Body odour and sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Effects of pornography wikipedia , lookup
Sexual stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Sex in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Erotic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Age disparity in sexual relationships wikipedia , lookup
Rochdale child sex abuse ring wikipedia , lookup
Human mating strategies wikipedia , lookup
Lesbian sexual practices wikipedia , lookup
Human male sexuality wikipedia , lookup
History of human sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal hormones and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
Human sexual response cycle wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
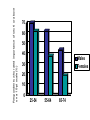
REPEAT AFTER ME • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • PINEAPPLE CLITORIS TEXTBOOK PENIS ORANGE VAGINAL LUBRICATION ORANGE WHO? CLITORAL ENGORGEMENT ORANGE YOU GLAD I DIDN’T SAY PENIS SEMEN WHEN EJACULATE IS THIS ERECTION OVER? Now… Sexual Motivation I. Sexual motivation: desire to have pleasurable erotic experiences A. Distinction between sexual desire and romantic love 1. Evolutionary roots vs. attachment 2. Distinct brain and hormonal mechanisms 3. Sexual desire linked to cognitive, behavior, and emotional processes B. Neuro-endocrine factors 1. Role of the brain (hypothalamus, pituitary gland) 2. Role of hormones from gonads and adrenal glands (androgens, estrogens) The Human Sexual Response: Physiologically Speaking… 1. Excitement phase: level of physical arousal usually rises rapidly • Which nervous system is at work? Vasocongestion: engorgement of blood vessels Males – penile erection and swollen testes Females – swelling and hardening of clitoris, expansion of vaginal lips, and vaginal lubrication 2. Plateau Phase: physiological arousal continues to build, but at a slower pace • Vasocongestion still underway, but may change due to time and amount of foreplay – Changes in male erections and amount of vaginal lubrication Men: secrete a bit of fluid at the tip of penis (contains sperm, but is not technically ejaculate) Women: tightening of vaginal entrance, clitoris withdraws under the clitoral hood 3. Orgasm phase: sexual arousal reaches peak intensity and is discharged in a series of muscular contractions that pulsate throughout pelvic area • Males: ejaculation of seminal fluid • Women: subjective (physical vs. psychological) • Women have a larger tendency to be multiorgasmic – able to experience more than one climax in a sexual pattern – Tend to engage in intercourse without experiencing orgasm • Men? – Climatic expectation – Tendency to be limited in orgasm experiences BUT WHY?!?! • Men experience a refractory period – Time following orgasm during which males are largely unresponsive to further stimulation (varies) • So what does the cycle look like, graphically speaking? C. Behavioral factors 1. Animals seek pleasure and repeat behaviors leading to it • (OC/reward stimulus) 2. Stimuli associated with sexual arousal become rewarding • • Animals and masturbation Humans and masturbation D. Socio-cultural factors 1. Society influences what is sexually attractive 2. All cultures have rules about acceptable sexual partners and practices E. Evolutionary factors 1. Sexual desire rooted in reproductive success 2. Cross-cultural consistencies in sexual partner preferences • Incest avoidance, waist-to-hip ratio 3. Sexuality is more loosely linked to reproduction in humans than in most animals • Complex aspect of identity, relationships, social life Parental investment • Refers to what each sex has to invest in terms of time, energy, survival risk, and forgone opportunities to produce and nurture offspring – Efforts required to guard eggs, build nests – What’s the human conclusion? males females Biological reality Evolutionary significance Behavioral outcome Reproduction involves minimum investment of time, energy, risk Maximize reproductive success by seeking more sexual partners with high reprod. potential ????? Reproduction involves substantial investment of time, energy, risk Maximize reproduction success by seeking Partners willing to invest material resources in your offspring ?????? Respondents who rated importance of sex 6 or above on a 10-pt scale (%) 70 60 50 40 30 Males Females 20 10 0 25-54 55-64 65-74 Gender Differences in Mate Preferences • Evolutionary theory of preferences = subconscious preferences – NOT CONSCIOUS STRATEGY Can women judge men’s mate potential in just one glance? • University of Chicago study Results • Women’s ratings of masculinity and actual testosterone levels correlated at .34 • Degree to which women rated male’s interest in infants correlated with male’s scores on interest inventory at .38 • Higher ratings of masculinity fostered higher estimates of short term mate potential • Conclusions: yes, women can meaningful inferences about male’s parental interest based on brief exposure to one photograph F. sexual orientation: enduring sexual attraction to people whose gender is the same (homosexual) or different from (heterosexual) oneself or to both (bisexual) 1. Strong evidence for prenatal and genetic influences 2. Development, nature, and fluidity of orientation differ between genders and individuals Sexuality as a spectrum • Desires vs. actions • Classifications and hard lines • “in the closet” vs. “out the closet” Outdated Behaviorist theories • Sexuality based on nurture – Disproved by lack of correlative evidence – No evidence linking parent’s sexual orientation to that of their children • Femininity in early males and masculinity in early females = transition to homosexual life – Totally false, sexual exploration prior to education – Conformity vs. nonconformity Biological Theories • 1990’s saw genetic predispositions – Twin studies • Today’s theory focuses on prenatal environment – Hormonal secretions during prenatal development in a critical period Socio-cultural factors • Studies have shown homosexuality in men vs. women can be different – Women and sexual plasticity Truth? • No one really knows – scientific and observational opinions fluctuate • Trends in research change over time • Nature vs. nurture debate continues… II. Pornography • Due to the internet, recent studies of young adults show that 87% of males and 31% of women have viewed pornography • 67% of males and 49% of females believed using porn was “acceptable way to express one’s sexuality” • Men are more likely to admit to find erotic materials enjoyable and arousing than women… why is that? Porn and Sex Crimes • Is there a correlation between increase in amount of pornography and increase in sex crimes in the US? • No. • During the last 15-20 years, internet porn has grown exponentially while rates of reported rapes have declined – Criticism… “reported” rapes • They do however ALTER attitudes that may influence sexual behavior – University students in a study were exposed to porn 3-6 times a week reported more liberal attitudes towards sex – Liberal attitudes about casual sex and multiple partners – Danish studies show self-perception of happiness in sex-life correlated to amount of porn (more porn, happier sex life) Sexual Aggression • Aggressive pornography has concerning correlations – Promotes myth that women enjoy being raped – Studies show increased aggressive behavior following the viewing of aggressive porn – “they asked for it” theory – Viewing aggressive pornography when already at high risk for sexual aggression may produce further sexual coercion Effects on Rape/Rape Identity • ¼ of young women in US may be victims of rape or attempted rape • Only a minority of rapes are committed by strangers • Date rape – 1 in 12 men admitted to either having forced a date into sex or having tried to do so – None of these men admitted to being a rapist