* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
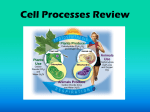
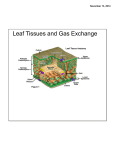
Start a Warm UP Page for our new unit PLANTS Title AND put today’s date on your paper 1. Write down 3 facts you KNOW about plants 2. Write down 1 thing you WANT TO KNOW about plants 3. Finish up Vocabulary and sentences 4. Make up tests!!! Plants belong to the Plantae Kingdom. There are two large categories of plants: 1. Vascular plants or tracheophytes – ◦ flowers, trees and grasses. 2. Non-vascular plants or Bryophytes, ◦ moss Tracheophytes - have tissues called xylem and phloem Xylem - tissues that transport water Phloem – tissues that transport food Xylem and the phloem are called vascular tissue. Vascular plants have roots, stems and leaves. Bryophytes have no roots, leaves or stems. Moss and liverworts belong to this group. They are flowerless plants that grow in clumps. They don't have roots. Instead they have thin root like growths called rhizoids that help anchor the plant. Because they don't have roots and stems to transport water, mosses and liverworts dry out very quickly. They are usually found in moist habitats. The only place they don't grow is in salt water. How Do Plants Obtain and Store Energy from the Environment? •Plants are: complex multicellular organisms that cannot move their bodies to change location. •Multicellular - made of more than one cell. •Plants have a rigid cell wall Ever notice how tough tree bark is? Or how tough a fresh leaf is even when you step on it? That’s because trees are made of plant cells. A plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall. It protects the parts of the cell. The cell wall also gives the plant cell a fixed shape. Inside the cell wall is a cell membrane, just like in animal cells. But animal cells do not have cell walls. Most animal tissue is not as tough as plant tissue. Vascular plants have some adaptations that help them survive. They are covered with a waxy layer or cuticle that holds in water They have stomata or pores that help them take in and let out gasses like carbon dioxide and oxygen. Their roots take up water and nutrients from the soil and anchor them to the soil. Stems move water and nutrients to the plant's leaves Leaves capture the sunlight the plant needs for photosynthesis. Leaves are also where transpiration occurs Transpiration the process in plants by which water is taken up by the roots and released as water vapor through stomata in the leaves Stomata look like tiny mouths on the surface of a leaf. They are so small that they can only be seen with a microscope. Stomata open and close to let carbon dioxide enter the leaf. The leaf uses light energy to combine the gas from the air and water from the ground to make food. During this process, oxygen is made by the plant. Stomata open again to release the oxygen. Thanks to the stomata, we have fresh air to breathe! All living things need to take in energy. Plants obtain energy through photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis - process of using light energy from the sun, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and water to produce glucose. 1. 2. Plants get their energy directly from the sun. Plants absorb soil nutrients they need through their roots 1. 2. Animals obtain energy by eating plants or other animals Many animals make their homes in plants Plants are not alive, because they cannot move around and all living things are able to move. • Plants really are living organisms! Not every living thing can move. • Plants do respond to their environment. The tendrils of some kinds of vines respond to touch by curling. This allows the vine to grab onto objects for support. 1. Tropism ◦ Plants respond to sunlight by bending in its direction. ◦ The roots of plants grow downwards in response to gravity. Plants do not have nervous systems There are numerous kinds of plants. Conifers - pine trees - bear their seeds in cones and have sharp needle-like leaves. Flowering plants - bear their seeds in fruits. Ferns- use spores to reproduce rather than seeds. Mosses - which do not have roots, stems or leaves. All living things are made of cells Cells - tiny, microscopic building blocks of all living things. EACH CELL IS A SEPARATE LIVING THING. ◦ Some organisms only have one cell. ◦ Most organisms have millions of cells just like you. The living things you can see are made of more than one cell. They are multi-cellular. ◦ Humans are multi-cellular. ◦ Plants are multi-cellular Plant cells contain chloroplasts Chloroplasts - organelles that use the sun’s energy, carbon dioxide, and water to produce a sugar called glucose during photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contains chlorophyll. ◦ Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Photosynthesis - occurs primarily in a plant’s leaves. ◦ Leaves collect sunlight and absorb carbon dioxide, ◦ Leaves release oxygen and water vapor. (Transpirtaion_ Photosynthesis can also occur in other plant structures. Structure - a part of an organism; also refers to the way parts are put together Vascular Plants have a definite structure. They have leaves, stem, and roots. However - Remember - some plants don’t have leaves! Bryophytes Lichens, fungi, mosses, liverworts, slime-molds, algae Many plants have special adaptations that help to protect them from being eaten. Some plants defend themselves with sharp thorns, prickles, or spines. Thorns are branches or stems that end in sharp points. Prickles, found on rose stems, are protuberances from the epidermis of the stem. Spines are found on the leaves of plants, especially cacti. Some plants, like poison ivy, produce toxins which can make a herbivore sick or even kill it. Other plants, such as the sensitive plant, close their leaves when touched. This is known as thigmotropism. The closed leaves appear dead and therefore unappetizing to the plant eater. Plants are an essential part of the carbon cycle VIDEO – take notes!!!!!!! 1. Plants on land AND plants in the ocean take carbon dioxide out of the air 2. Carbon dioxide is a molecule made of 2 carbon atoms &1 oxygen atom 3. Without carbon dioxide and photosynthesis there would be no life on earth 4. Plants incorporate carbon dioxide into their bodies 5. A plant leaf is like a sugar factory 6. Sunlight makes the factory work 7. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through the stomata 8. Stomata are located on the bottom side of the leaf pores on the surface of a plant that allow gases to move into and out of the plant (related word: stoma) Gases in the air move in and out of a plant’s leaves through stomata. 9. Water is a molecule made up of 2 hydrogen atoms & 1 oxygen atom 10. Water enters plants through the roots, travels up the stems (Xylem ) and into the leaves 11. Carbon dioxide is broken down by energy (sunlight) 12. It is reassembled as sugar (glucose) 13. GLUCOSE is the building block of LIFE 14. IN plants - SUGAR (glucose) is burned, oxygen is given off 15. WE BREATHE IN oxygen and WE EAT plants and other animals