* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Calcium Cycle
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
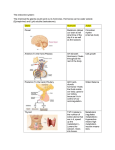
Calcium enters from biosphere in dust or from organisms Like phosphorous, there is no gaseous state so it does not stay in the atmosphere When animals die, the calcium in their bodies are decomposed and go into soil Water can carry calcium to or from soil through weathering When in the soil, calcium is in an insoluble form until it is broken down by microbes into a usable form Mineralization can store calcium in rocks Calcium can be returned from root leakage Calcium can be absorbed by plant roots When absorbed by plants, calcium is now in an organic state The calcium can continually be recycled between the plant roots and soil OR herbivores can eat the plants or drink the water and the calcium returns to the biosphere If the plant or animal dies, decomposers break down the organism and calcium is returned to water or soil Calcium is a mineral necessary for life In early life, calcium helps build strong bones and teeth Helps with muscle contraction and other body processes Plants need calcium to help in cell wall development and their metabolism; stronger cell walls protect from pathogens











![Poster ECE`14 PsedohipoPTH [Modo de compatibilidad]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007957322_1-13955f29e92676d795b568b8e6827da6-150x150.png)