* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eustachian tube
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Speed of sound wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
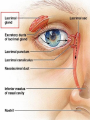
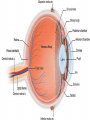
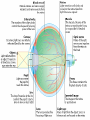
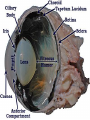
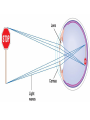
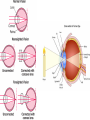
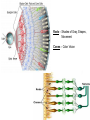
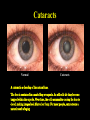
Eustachian tube - a canal that links the middle ear with the throat area. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure between the outer ear and the middle ear. Having the same pressure allows for the proper transfer of sound waves. The eustachian tube is lined with mucous, just like the inside of the nose and throat How we hear! 1. When a sound is made outside the outer ear, the sound waves, or vibrations, travel down the external auditory canal and strike the eardrum (tympanic membrane). 2. The eardrum vibrates. 3. The vibrations are then passed to three tiny bones in the middle ear called the ossicles. 4. The ossicles amplify the sound and send the sound waves to the inner ear and into the fluid filled hearing organ (cochlea). 5. Once the sound waves reach the inner ear, they are converted into electrical impulses which the auditory nerve sends to the brain. 6. The brain then translates these electrical impulses as sound Hearing Loss Home • 50 refrigerator • 50 - 60 electric toothbrush • 50 - 75 washing machine • 50 - 75 air conditioner • 50 - 80 electric shaver • 55 coffee percolator • 55 - 70 dishwasher • 60 sewing machine • 60 - 85 vacuum cleaner • 60 - 95 hair dryer • 65 - 80 alarm clock • 70 TV audio • 70 - 80 coffee grinder • 70 - 95 garbage disposal • 75 - 85 flush toilet • 80 pop-up toaster • 80 doorbell • 80 ringing telephone • 80 whistling kettle • 80 - 90 food mixer or processor • 80 - 90 blender • 80 - 95 garbage disposal • 110 baby crying • 110 squeaky toy held close to the ear • 135 noisy squeeze toys Recreation • 40 quiet residential area • 70 freeway traffic • 85 heavy traffic, noisy restaurant • 90 truck, shouted conversation • 95 - 110 motorcycle • 100 snowmobile • 100 school dance, boom box • 110 disco • 110 busy video arcade • 110 symphony concert • 110 car horn • 110 -120 rock concert • 112 personal cassette player on high • 117 football game (stadium) • 120 band concert • 125 auto stereo (factory installed) • 130 stock car races • 143 bicycle horn • 150 firecracker • 156 capgun • 157 balloon pop • 162 fireworks (at 3 feet) • 163 rifle • 166 handgun • 170 shotgun Noise above 85 dBA over time, will cause hearing loss Rods – Shades of Gray, Shapes, Movement Cones – Color Vision Cataracts Normal Cataracts A cataract is a clouding of the natural lens. The lens is contained in a sealed bag or capsule. As old cells die they become trapped within the capsule. Over time, the cells accumulate causing the lens to cloud, making images look blurred or fuzzy. For most people, cataracts are a natural result of aging. Astigmatism Astigmatism means that the cornea is oval like a football instead of spherical like a basketball. Most astigmatic corneas have two curves – a steeper curve and a flatter curve. This causes light to focus on more than one point in the eye, resulting in blurred vision at distance or near. Astigmatism often occurs along with nearsightedness (Myopia) or farsightedness (Hyperopia).