* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Survey of A&P/Chapter 8 Special senses
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
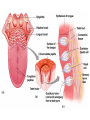
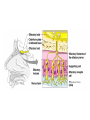
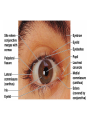
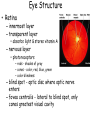
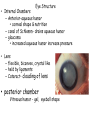
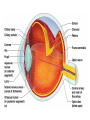
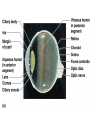
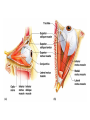
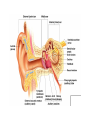
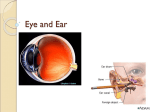
Chapter 8 Special Senses Chemical Senses • Taste Reception • Taste Buds – Repair in 7-10 days have 10,000 – gustatory cells • respond to chemical dissolved in saliva – papillae • peglike projections • Primary Taste Sensations – – – – sweet- tip of tongue sour- sides of tongue salty- tip of tongue bitter - base of tongue Chemical Senses – Gustatory pathways • facial nerve (VII) • glossopharyngeal (IX) • vagus nerve (X) – saliva – taste adaptations - 1-5 minutes – tactile: texture, temperature and irritation (pain) – olfaction plays a part in taste perception 80% Chemical Senses • Olfaction - smell closely tied to emotion – olfactory cells - neurons – olfactory nerve – olfactory hairs – olfactory cells secrete mucus – mucus is constantly replaced – chemoreceptors which detect: 30 - 1000 chemicals Chemical Senses • Primary Odors – seven • • • • • • • camphoraceous - alcohol ketones musky floral peppermint like etheral - ethers pungent - stinging putrid - rotten • Smells associated w/ danger – sympathetic nervous Changes • Ansomias – loss of smell – age, cold, allergies, smoking, head injuries – low levels of Zinc • Sensitivity & Adaptation – adapt to unchanging stimulus • Pain Receptors – irritants, harmful The Eye & Vision • Accessory Structures – orbital cavities • location of the eyes • fat & bone – eyebrows • • • • protect the eyes shade them prevent infiltration of perspiration prevent objects contacting them from above The Eye & Vision • Accessory Structures – eyelids & eyelashes • protection • lubricate w/ glands (oily secretion) – conjunctiva • membranes edge of cornea to eyelid • conjunctivitis is pink eye – lacrimal apparatus - tears • dilute salt solution • antibodies • lysozyme - enzyme kills bacteria – extrinsic muscles move eyeball • Fibrous tunic Eye Structure – anterior portion • cornea - transparent • nerves, no blood vessels – posterior portion • sclera - outermost protects • thick, white connective tissue • Vascular tunic (uvea) – choroid • pigments that absorb light (middle layer) dark purple – ciliary body • muscles move lens – iris • pigmented smooth muscles change size of pupil – pupil - opening Eye Structure • Retina – innermost layer – transparent layer • absorbs light & stores vitamin A – nervous layer • photoreceptors – rods - shades of gray – cones - color, red, blue, green – color blindness – blind spot - optic disc where optic nerve enters – fovea centralis - lateral to blind spot, only cones greatest visual cavity Eye Structure • Internal Chambers – Anterior-aqueous humor • corneal shape & nutrition – canal of Schlemm- drains aqueous humor – glaucoma • increased aqueous humor increase pressure • Lens – flexible, biconvex, crystal like – held by ligaments – Cataract- clouding of lens • posterior chamber Vitreous humor - gel, eyeball shape Physiology of Vision • Light Energy – electromagnetic spectrum- wavelengths • color: cones • Dark and light : rods • Focusing Processes – refraction • bending of light – myopia • nearsighted, eyeball too long, cornea curved – hypertrophy • farsighted, flat lens, eyeball too short – astigmatism • unequal curvatures in lens or cornea • blurry vision Physiology of Vision • Focusing of Processes – lens accommodation • focus close or far – pupil constriction • for close vision • for bright light – eye convergence • close objects Physiology of Vision • Photoreception – visual pigments • light absorption • choroid coat - deep purple – excitation of rods • shades of gray – excitation of cones • all cones ---> white color Physiology of Vision • Light and Dark Reception – into light - faster – into dark - slower 20-30 minutes – night blindness • rods function decreased, Vitamin A deficiency • Visual Pathways – optic nerve – occipital lobe – cerebrum • Binocular Vision – eyes anterior – depth perception 3 dimensional vision The Ear • Structure – outer ear • • • • • auricle capture sounds shell shaped external auditory canal ceruminous glands - make ear wax tympanic membrane - eardrum The Ear • Structure – middle ear • infections otitis media • air filled cavity • bones – ossicles transmit vibrations – hammer ---> anvil ---> stirrup • oval window • eustachian tube to throat “auditory” The Ear • Structure – inner ear • labyrinth – – – – maze of bony chambers into temporal filled w/ fluid vestibule pull of gravity sacs • semicircular canal – equilibrium • cochlea – spiral shaped – organ of corti - receptors – for hearing - hairs Physiology of the Ear • Sound waves – frequency – amplitude • Outer and middle ear – reception – increase & decrease sound • Cochlea – organ of hearing • sound ---> cochlear nerve ---> temporal lobe • Pitch transmission – frequency specific hairs • Loudness transmission – amplitude – more hairs stimulated Homeostasis Imbalances • Deafness – conduction deafness - hearing aid – sensorineural deafness • loud noise • damage organ of corti • Tinnitus – ringing in ears, clicking • Meniere’s Syndrome – arteriosclerosis – cranial nerve fluid pressure & “howling” • Motion Sickness – sensory input