* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eye and Ear - smithlhhsb121
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
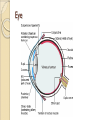
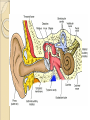
Eye and Ear Eye The eye is covered in a tough layer of connective tissue called the sclera ◦ This is covered by a mucous membrane called the conjunctiva Becomes clear in front of the eyes, called cornea Next inner layer is the choroid ◦ Turns into ciliary body, then iris (gives the eye its colour) ◦ Iris can change size, regulate amount of light ◦ The hole it makes is the pupil Innermost layer is retina ◦ Made of neurons and photoreceptors (clustered in the back) In centre of front is lens Flexible, focuses light entering eye Shape controlled by ciliary bodies ◦ Ciliary bodies contract, compressing lens, focus on near objects ◦ When the relax, lens lengthens, focus on distance objects Light passes through clear fluid called vitreous humour ◦ Fluid supplied by ciliary bodies Light strikes two types of photoreceptors, rods or cones ◦ Rods detect intensity ◦ Cones detect colour (three types) Rods more around perimeter, cones in center The cluster of cone cells at centre of vision is called fovea Information is processed and sent through optic nerve The nerve leaves a sort of “optic bald spot” This is the optic disc, aka blind spot Visual cortex (posterior of cerebrum) fills in the blanks, so we normally don’t see it Ear Broken into three sections: outer, middle, and inner Outer Ear Only two structures Actual “ear” that we see is the pinna Opens to a tube called auditory cannal Both are designed to collect logitudinal compression and rarefaction waves Middle Ear Contains three bones (smallest in the body) All three - malleus, incus, and stapes (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) transmit the vibrational waves to the oval window, a membrane connected to the inner ear Also in middle is a opening to the pharynx called the Eustachian tube Regulates pressure affecting tympanic membrane Inner Ear Actual center where sound waves are processed Has fluid filled chambers called semicircular canals, responsible for spatial orientation The cochlea is the hearing centre Connected to auditory nerve, which relays info to auditory complex in cerebrum