* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marine Policy - Chaparral Star Academy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
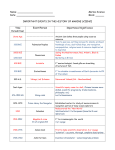
Marine Policy Introduction • Marine Policy is an academic field in which approaches from social science disciplines are applied to problems arising out of the human use of the oceans • Legal property rights of the ocean often differ from those found on land General Policy Areas • Environment; – Ocean/climate change, hypoxia, spills • Natural Resources – Fishery management, ocean minerals • Energy – Offshore oil, tidal power • Land Use – Coastal zone management, zoning, barrier beach protection • Waste Management – Waste disposal, marine debris, nuclear waste disposal General Policy Areas • Transportation – Shipping/ports, international rights of passage • Defense – Zoned training and testing areas, atomic zones • Foreign Policy – Legal geography, piracy, refugees, trades • Emergency Management – Weather prediction, hurricanes, harmful algal blooms • Science Policy – Funding for research, large-scale science programs UNCLOS • United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea • UNCLOS I (1956-58) – Geneva, Switzerland – Though it was considered successful, it left open the issue of breadth of territorial waters • UNCLOS II (1960) – Geneva, Switzerland UNCLOS • UNCLOS III (1973-1982) – Internal waters – Territorial Waters • 12 Nautical miles, – Contiguous zone • 12 more nm; customs, taxation, immigration, pollution – Exclusive Economic Zones • 200 nm, exploitation rights – Continental Shelf • To the edge of the continental margin/200 nm MARPOL Convention • International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (1973-78) • (Marine Pollution) • To minimize pollution of the seas; dumping, oil and exhaust pollution • To protect the environment by elimiating all pollution • Countries signed under MARPOL must follow all the requirements Conventions • IWC (International Whaling Commision)(1946) – Regulates the global sustainable taking of whales • IMO (International Maritime Organization) (1958) – International cooperation • Ramsar Convention (1971) – National initiatives to conserve wetlands • London Convention (1972) – First global standards to govern the dumping of wastes into the ocean Institutions • Important regional institutions for coastal and ocean management • UNEP (United Nations Environment Program) – Addresses coastal/marine environment problems • Man and the Biosphere Program – Nations working to solve environment problems – Establishing MPAs • The Great Lakes Program – Protection and management of the Great Lakes Marine Protected Areas • Areas of the ocean in which some or all of the natural and cultural resources are protected • 328 sites in the U.S. – 251 Federally managed • National Marine Sanctuaries (14 sites) • National Wildlife Refuge System (162 sites) • National Park Service/National Seashore (39 sites) • National Marine Fisheries Service (36 sites) • Marine Reserves Land Management • Coastal Zone Management Act – 1972 – Encourages coastal states to develop and implement coastal zone management plans (CZMPs) – U.S. National policy to preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, restore or enhance, the resources of the Nation’s coastal zone Pollution • Most pollution acts either; – Prohibit the dumping of materials known to be harmful – Specify the criteria under which other materials may be dumped (environmentally friendly substances) • The basic premise of each seems to be that land disposal is preferable to marine disposal Pollution • Point Source Pollution – These pollutants have easily determined starting points • Factories, sewage treatment pipes, dumping toxins, wastewater • Nonpoint Source Pollution – These pollutants have indirect beginnings • Oil, fertilizers, urban runoff, agricultural run off Pollution • Rivers and Harbors Act (1899) – A prohibition of dumping refuse into navigable US waters • Federal Water Pollution Control Act(1948) – (Clean Water Act) – Addresses point sources of municipal and industrial waste and spills of oil and hazardous materials • Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act (1972) – Ocean Dumping Act – Controls dumping of waste at sea, at-sea research, establishment of marine sanctuaries Pollution • Ocean Dumping Ban Act (1991) – Banned all sewage and industrial waste dumping in the U.S. offshore waters • Oceans Act of 2000 (2000) – Establishes a 16 member U.S. Commission on Ocean Policy – Undertake a thorough review of U.S. ocean and coastal programs and activities Marine Biodiversity • National Wildlife Refuge System – 1903 – Managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service – Lands and waters set aside to conserve America’s fish, wildlife, and plants – Protects the habitats of wildlife populations, and the wildlife Marine Biodiversity • National Estuarine Research Reserve System – 1972 – Protects coastal and estuarine habitats for long term research, water-quality monitoring, education, and coastal stewardship – 28 protected areas – Works in partnership with NOAA Marine Biodiversity • Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA) – 1972 – Prohibits the taking of marine mammals • Take: Hunting, killing, capture, harassment • Harassment: tormenting, annoying, disturbing it’s behavioral patterns – Migration, breathing, nursing, breeding, feeding, or sheltering – First act of Congress to call specifically for an ecosystem approach to natural resource management and conservation Marine Biodiversity • Endangered Species Act – 1973 – Administered by NOAA and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service – Designed to prevent any endangered species from becoming extinct because of human activities Marine Biodiversity • Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Act (MFCMA) – 1976 – The primary law governing marine fisheries management in the United States – Conservation of fishery resources – Amended several times in response to the continued overfishing of major stocks U.S. Senate Committees • Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation – Jurisdiction includes ocean and atmospheric policy, generally: NOAA, NASA, U.S. Coast Guard, MARAD, and Marine Mammal Commission programs • Committee on Environment and Public Works – Jurisdiction includes environmental protection U.S. Senate Committees • Committee on Energy and Natural Resources – Jurisdiction includes energy resource development • Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition, and Forestry – Jurisdiction includes: USDA Forest Service, Natural Resources Conservation Service programs