* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Feynman Problem-Solving Algorithm: (1)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
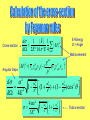
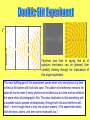
• Feynman Rules • Feynman Diagrams • Feynman Parametrization • Feynman Gauge • Feynman Cut-off • Feynman Propagator • Feynman Path integral • Feynman Parton Model • …. Feynman invented the language of modern particle physics – Feynman diagrams and covariant Feynman rules Sin-Itiro Tomonaga Julian Schwinger Richard P. Feynman "for their fundamental work in quantum electrodynamics, with deepploughing consequences for the physics of elementary particles“ What I am going to tell you about is what we teach our physics students in the third or fourth year of graduate school... It is my task to convince you not to turn away because you don't understand it. You see my physics students don't understand it... That is because I don't understand it. Nobody does. QED, The Strange Theory of Light and Matter, (London, 1990) 9. To those who do not know mathematics it is difficult to get across a real feeling as to the beauty, the deepest beauty, of nature ... If you want to learn about nature, to appreciate nature, it is necessary to understand the language that she speaks in. The Character of Physical Law Emitted photon Emitted electron (absorbed positron) Absorbed photon Flying photon g i 2 p v “I took the observation that positrons could electron simplyAbsorbed be represented as (emitted electronspositron) going from the future to the past in a back section of their world lines” R.Feynman, Nobel Lecture v Flying Electron Flying Positron p̂ m p̂ m i p m i 2 2 i p 2 m 2 i Interaction between electron, positrons and photons Absorption of a photon by an electron e Emission of a photon by an electron e e e Annihilation e All physical processes in Quantum Electrodynamics can be constructed from these elements like LEGO structures Amplitudes of probability = M Probability = |M|2 Compton Scattering Mueller Scattering p v ( pˆ m) v p 2 m2 p Annihilation p g v v (i 2 )v v p Electrons (e-) and positrons (e+) collide at accelerators at very high energy and produce a pair of muons (μ+ μ-) LEP Accelerator v=0. 999 999 999 987 c N Flux Number of events Cross-section Cross-section Angular Deps d 1 |k| 1 2 | M | 2 2 d 2 E 16 E 4 spin E=Energy Ω = Angle Matrix element g 2 2 | M | | v v (i 2 )v v | p d m2 1 E2 2 d 4E 2 (1 4 2 m2 1 E2 2 3E ) (1 ) cos E2 E2 m2 1 m2 2 m 1 2 E2 2 Total x-section Area view of the Large Hadron Collider (CERN) 27 km ring If I could explain it to the average person, I wouldn't have been worth the Nobel Prize. R.Feynman "The electron does anything it likes," he said. "It just goes in any direction at any speed, forward or backward in time, however it likes, and then you add up the amplitudes and it gives you the wavefunction." I said to him, "You're crazy." But he wasn't. Freeman J.Dyson, 1983 Feynman was fond of saying that all of quantum mechanics can be gleaned from carefully thinking through the implications of this single experiment. The most baffling part of this experiment comes when only one photon at a time is fired at the barrier with both slits open. The pattern of interference remains the same as can be seen if many photons are emitted one at a time and recorded on the same sheet of photographic film. The clear implication is that something with a wavelike nature passes simultaneously through both slits and interferes with itself — even though there is only one photon present. (The experiment works with electrons, atoms, and even some molecules too.) “I don't know why this is - it remains a mystery, but it was something I `learned from experience. There is always another way to say the same thing that doesn't look at all like the way you said it before. I don't know what the reason for this is. I think it is somehow a representation of the simplicity of nature”. . R.Feynman The most beautiful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and all science. He to whom this emotion is a stranger, who can no longer pause to wonder and stand rapt in awe, is as good as dead: his eyes are closed. A. Einstein I learned very early the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something. Some people say, "How can you live without knowing?" I do not know what they mean. I always live without knowing. That is easy. How you get to know is what I want to know. The Feynman Problem-Solving Algorithm: (1) write down the problem; (2) think very hard; (3) write down the answer. If it turns out there is a simple ultimate law which explains everything, so be it — that would be very nice to discover. If it turns out it's like an onion with millions of layers... then that's the way it is. R.Feynman No problem is too small or too trivial if we can really do something about it. The worthwhile problems are the ones you can really solve or help solve, the ones you can really contribute something to. The wonderful thing about science is that it's alive. Physics isn't the most important thing. Love is. He is by all odds the most brilliant young physicist here, and everyone knows this. J.Oppenheimer on Feynman's status among the physicists at Los Alamos.