* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Judaism
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on sin wikipedia , lookup
Jewish military history wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Pardes (Jewish exegesis) wikipedia , lookup
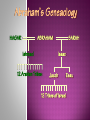
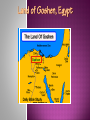
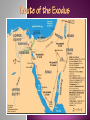
The religion of Judaism cannot be separated from the history of its people: A religion, a people/nation, a culture, and ethnicity Jews are those who experience their long and often difficult history as a continuing dialogue with God The founder was Abraham, but many consider Moses to be the founder as well. The God of Abraham was called El Shaddai The God of Moses was called YHWH (Yahweh)- “I am that I am” Another name for God used in the Old Testament was Elohim Look up the roots of the words El Shaddai, Elohim and YHWH. At least Two Paragraphs answering these questions: What do they mean ? Is there any connection to Allah? Judaism is a strongly earth focused religion. It is more concerned with this life than the afterlife- The main focus is that of ethics and doing God’s will. Judaism sees man as having free will and being constantly faced with the choice between good and evil Jewish path is one of loving God and trying to be like him God offered to share the divine law with 70 nations, but only the tribes of Israel answered the call to enter into a living covenant with their creator Jews still feel this call is open to all “Israel” refers to all who answer the call, who acknowledge and strive to obey the one God through teachings given to the patriarchs, Moses, and the prophets Tanakh- Jewish Scriptures stories end @2nd century BCE Talmud- Jewish Law and Lore compiled in 6th century CE Torah- whole body of Jewish teachings and law Pentateuch- 5 books of Moses Beginning of Tanakh, most sacred part of scriptures Most Hebrews were not truly monotheistic- many wavered back and forth w/ Old gods and animal spirits Canaanites were polytheistic Main idea in early Judaism: rejection of gods of surrounding peoples Israelites came to see themselves as having been chosen by a single divine patron: God was seen as a ruler: like a parent to children or sovereign to vassals Judaism resembles a family Names/Terms: “Hebrew” comes from the term habiru (term for low class, landless people) “Ibri” biblical word for Hebrew- Children of Eber “Israelites”- mixed ethnic stock- Hebrews, Aramaean, and Canaanite “Semite”- modern word applied to Jews, Arabs and others of Eastern Mediterranean origin (often used inaccurately as an ethnic designation) People who 1st became known as “Israelites” were the offspring of Israel (Jacob)- grandson of Abraham Early History: Stories from the Pentateuch Sweeping poetic creation of Heaven and earth by God in 6 days God is a transcendent Creator w/o origin, gender or form EC assignment: What happened on each of the 6 days? At least one FULL paragraph. Some creation accounts see YHWH as a supreme male deity, created all but woman; offshoot of Adam blames woman for all troubles in humanity not supported in Hebrew manuscripts This legend shows though how after being tempted and having strayed from God’s path= exile Theme repeats in Hebrew history People risk God’s displeasure every time they stray from God’s commandments OR Jewish people were spread throughout the world by God’s will, to be good citizens in whichever land they live, and spread God’s word. Way out of exile is through study and righteous living But.. people continually stray from God’s will Noah legend: all men wicked but him: God makes covenant with Noah catastrophic flood, but spares Noah and his family and two of all the creatures of the earth • God makes covenant- promises to never destroy the world by flood or interfere with the natural order 1900 BCE: left Ur (present day Iraq), rejects polytheism, “chooses” to worship one God, God “chooses” Abram and his followers. Canaan The “Promised Land” Abraham’s Journeys Abram promises to be loyal and obedient to God God will protect Abram, his descendants, will make a great nation Settle in the land of Israel Circumcise males on 8th day- sign of the living covenant Blood Promise to the one God Changes names to Abraham and Sarah Abraham fears he will not have a son (86 years old) (Wife Sarah 77) Genesis 16 “And Sarai Abram's wife took Hagar her maid the Egyptian, after Abram had dwelt ten years in the land of Canaan, and gave her to her husband Abram to be his wife.” Hagar bears Ishmael Sarah becomes jealous; casts out Hagar and Ishmael Ishmael- Father of Arabs: Muhammad said to be direct descendant Abraham 99 and 1st wife Sarah 90 have son Isaac Isaac- Father of Israelites Abraham tested- will sacrifice own son to prove loyalty to God God stops Abraham’s hand Pleased with his loyalty Rosh Hashanah (sept) and Eid al Adha (nov) Abraham’s Geneaology HAGAR ABRAHAM Ishmael SARAH Isaac 12 Arabian Tribes Jacob Esau 12 Tribes of Israel Jacob received the name “Israel” after wrestling with an angel Israel- “One who struggles with God” Research the 4 wives of Jacob. Who were they? Why did Jacob have 4 wives? What role do they play in Jewish History? Dinah was the one daughter of Jacob. Who was she? What is known about her life? Sold into slavery by jealous brothers Rose to become Pharaoh’s chief advisor for helping the Egyptians to prepare for famine Brought family down from the famine in Canaan to the land of Goshen in Egypt (1740 BCE) Israelites lived for 430 years in Egypt until led out of Egypt by Moses Land of Goshen, Egypt Pharaoh ordered midwives to kill all Hebrew baby boys Pharaoh had dreamed of a leader from the Hebrews who would destroy him Moses: son of the tribe of Levimother hid him away for 3 months Basket/Nile river Pharaoh’s daughter found him and raised him as her own. Moses : “to draw” Sister Miriam approached the Queen and offered a wet nurse for the child Grew up as Egyptian prince discovered heritage killed an Egyptian overseer fled Pharaoh’s wrath lived with and married into desert tribe on Sinai Peninsula for 40 years Zipporah- his wife Burning Bush- God speaks directly to Moses Moses was chosen by God to free the Hebrew’s very conflicted how to free them and lead them back to Canaan? Moses goes back to Egypt; brother Aaron spoke for Moses. Chapters of Exodus tell of the Miracles God performed. Each miracle more impressive than the last, but Pharaoh’s magicians seemed to match them Final miracle- Killing of all the 1st born in the land- Israelites spared this fate by marking their doors with blood of a lamb- so that the Angel of Death would Pass Over them. Passover holiday- remembers this event. Research the 10 miracles/plagues of Egypt Name and describe each; take into account how these plagues would have affected the people of Egypt @1450 BCE Pharaoh frees the Hebrews. Red Sea incident Reed Sea? Translation error? travel to Mt Sinai to reestablish the covenant btwn God and his people Route of the Exodus God gave the people a set of rules through Moses: Ten Commandments Set of social norms Prescribed religious feasts Detailed instructions for the holy ark- Ark of the Covenant- keep stone tablets on which God inscribes the commandments A new Covenant with Yahweh Mount Sinai St. Catherine’s Monastery at Mount Sinai 40 days on the mountain: people became impatient Wanted a God they could see- melted down gold jewelry and cast it into the form of a golden calf- Idol worship- strictly forbidden! Moses smashed the stone tables and destroyed the idolordered the Levites to slay the 3000 who had strayed from YHWH Moses again went back up on Mt Sinai and received tables Aaron and sons became priests constructed the Ark and went to Canaan w/ the word of the Lord with them Wandered 40 years/ long sojourn in the wildernessmetaphor for spiritual search- faith is continually tested by difficulties Even in the wilderness, God did not abandon them. Manna and water, protection from enemies 1410-1050 BCE of Israel Jews settle in the land There they divide into 12 tribes each of which is led by a judge. Merge with people who lived there, often strayed from YHWH, worship other gods, idols/ easy prey for other tribes 1050-933 BCE Saul, 1st King of Israel unites the 12 tribes David, 2nd King: chosen by prophet Samuel: anointed with oil, God’s choice, Israel’s greatest king made several alliances, defeated several nations, captured city of Jerusalem and made it his capital, wanted permanent place for Ark. King David’s Empire Solomon’s Kingdom • Solomon, 3rd King: Constructed the Holy Temple. permanent place for Ark, place for offerings, God was said to have blessed the Temple, Central place for sacrifice for Israelites Recreation of Ancient Jerusalem King Solomon’s Temple Floor Plan The First Temple Inside the Temple Tabernacle The Arc of the Covenant The Temple Mount, Jerusalem Today Solomon’s Temple Wall: The “Wailing” Wall After Solomon’s death the kingdom was divided into the Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah Kingdom of Israel: 10 northern tribes/independent of Jerusalem and dynasty of David Kingdom of Judah: continued allegiance to House of David and kept Jerusalem as its capital Prophets: Early ones, like Elijah- spoke out against idolatry, later ones spoke out against social injustice and moral corruption Prophets speak God’s words- not necessarily to predict the future but to keep people on the path Offer “corrections” EC assignment: research two Prophets from the Torah; Summarize their lives and their message 586 BCE- Babylonians conquer the and destroy the Temple Many taken to Babylonia became known as Jews (from Judah), build new places of worship-synagogues 538 BCE a new Babylonian King: King Cyrus allows Jews to return to Judah and rebuild the Temple Temple completed in 515, central symbol to the scattered Jewish people. Many Jews Kingdom of Judah chose to remain in Babylon very profitable city, not much in Jerusalem Israelites in Captivity In the 400s the priestly Class under Ezra began to edit and revise the Pentateuch 430 BCE Ezra began reading for hours- the scrolls in public- setting the precedent to read and study them (sacred covenant) New ideas blended with early Jewish thoughts as more Jews were exposed to Persians, Greeks and Romans Concepts of Satan, angels, reward or punishment in afterlife Resurrection of body on Day of Judgment are thought by many to have been introduced by Zoroaster’s. (Persians) 322- 164 BCE King Antiochus and the Greeks: Tried to force Greek ways upon Jewish peoples. Abolished the Torah as Jewish law Burned copies of Torah Killed families with Circumcised sons Built an altar to Zeus in Temple of Jerusalem Sacrificed a hog on the altar Goes against Mosaic law against eating /touching dead pigs as unclean Under the leadership of the Hasmoneans (particularly Judah Maccabee) the Judeans successfully revolt against Antiochus This established a new independent Kingdom once again called Israel. Btwn 164 BCE and 63 BCE Hasmonean Family ruled Israel family of priests This only lasted 100 years- conquered by the Romans in 63 BCE (Pompey) Last independent Jewish nation until 1948 CE 3 Sects of Jews formed 1. Sadducees priests, wealthy business people, conservatives intent on preserving the letter of the law 2. Pharisees liberal citizens from all classes, wanted to study how Torah could apply to everyday life 3. Essenes thought the priesthood was corrupt. Very strict in interpretation, set up a fortified compound at Qumran (near the Dead Sea). Leader “Teacher of Righteousness” priest/reformer- name not uttered Their library found in 1947 (Dead Sea Scrolls) Essenes emphasized discipline, communal living, obedience, study and preparation for Day of Judgment Under Roman rule Messiah idea began to grow- a man who would rescue his people from suffering. Prophet Daniel in Babylon exile days had spoken of a man who would come and save his people. By 1st century CE this Messiah would set up Jewish sovereignty over the land of Israel again. All nations would then recognize that Israel’s God was the God of all the world. This messianic time would 1st be preceded by a time of great oppression and wickedness Many felt Jesus was the Messiah, his followers became the 1st Christians Most Jews saw Jesus as a radical who did not fulfill prophecy Zealots: Romans Jewish resistance fighters who fought the 66-73 CE Revolt fails miserably, Romans destroy the 2nd Temple. Only foundation stones remain. Temple has never been rebuilt- foundation stones are Western Wall- a place of Jewish pilgrimage and prayer The Temple Mount, Jerusalem Today Solomon’s Temple Wall: The “Wailing” Wall By 135 CE Jews were forbidden to read the Torah, observe Sabbath or circumcise sons None allowed to enter Jerusalem On anniversary of destruction of the Temple, the Romans would allow Jews to go to the remaining wall. had to pay to enter city Judea renamed Palestine- after ancient Philistines Judaism no longer has a physical heart or geographic center. Judaism could have died after the of the Temple 2nd destruction people spread throughout Mediterranean and Western Asia Two reasons for survival of ideas: 1. Rabbis- Jewish teacher today spiritual leader of Jewish congregation Kept Jewish law and lore alive 2. Christians also survived and carried on a lot of Jewish ideas Both groups have kept teaching of Tanakh alive, both use Hebrew Bible as a foundation document Rabbis: teachers, religious decision makers, creators of prayers No longer priests for Temple sacrifices Substitute for animal sacrifice was prayer and ethical behavior W/O Temple- tight knit communities of Jews became very Synagogues (house of assembly) Torah read, worship together, praying to God Minyan: ten adult males had to be present for community worship All learn basics of Torah Only men allowed formal study originally only male rabbis Literacy highly valued for men Jews sometimes only ones who knew how to read Centering the religion in books and teachings replaced a geographic center, has unified the people with common law, language and practices American By 1880, @ 250,000 Jews had immigrated to the US Judaism: More in the 1920s Mainly from Eastern Europe Anti Semitism in Germany and Russia Today US has 2nd largest Jewish Population in the world Israel: 5.3 million US: 5.2 million World wide: 13.2 million Zionism: The Jewish movement to establish a politically viable, internationally recognized Jewish state in the Biblical land of Israel Late 1800s Rise of Anti Semitism in Western Europe encouraged immigration EC assignment: Dreyfus Affair: Two Paragraphs British support for Jewish settlement in Palestine after WWI Also supported a continued Palestinian state Part of the cause of continued conflict today 1948 United Nations creates a modern Israel 1. Daily Study of the Torah: Boys education must include knowledge of Hebrew More girls included today Keeps the Word alive 2. Daily prayer and observance of commandments 3. Circumcism 4. Sabbath: Sundown to sundown ( Fri-Sat) Reading the Torah 5. Kosher: Ritually acceptable meats Warm blooded animals with cloven hooves that eat greens Cows, goats, sheep.. Only if prepared by Jewish Slaughterer Sharp knife Traditional cuts Drain blood Meats must be soaked in water and drained before cooking Try to avoid eating blood Poultry is kosher; not birds of prey Shellfish is NOT Kosher Meat and Milk cannot be eaten together Separate dishes maintained for preparation and serving Eggs, meat, milk, organs of forbidden animals cannot be eaten Fruits and vegetables are permitted Must be checked for bugs Wine made by non-Jews NOT Kosher 6. Morning Prayer: Before opening eyes and at bedtime Should offer at least 100 prayers/benedictions a day Thank God for restoring the soul Before eating bread, drinking wine, upon seeing the ocean…. etc… “Blessed are you, Oh God, Ruler of the Heaven, who gives us bread” Hands must be washed before reciting blessings 3 prayer services are chanted daily in Synagogue 7. T’filllin: Small leather boxes on forehead or upper right arm Prayers/verses 8. Talit: Fringed Prayer Shawl Fringes are reminders of God’s commands 9. Coming of Age Bar/Bat Mitzvah Religious instruction Learning to read and pronounce Hebrew Read a portion of the Torah Recite a passage from book of Prophets Celebrate and party!!! Spiritual new year begins with High Holy Days 1. Rosh Hashanah: New Year’s Day Celebrated on the 1st two days of the 7th month A time of spiritual renewal @ the fall equinox 30 days prior to Rosh Hashanah Each morning synagogue service brings blowing of the Shofar To remind people that they stand before God At the service on the eve of Rosh Hashanah, a prayer is recited asking: • that all humanity will remember what God has done • that there will be honor and joy for God’s People and • that the righteous will triumph while all wickedness vanishes like smoke • Ten Days of Awe follow R. H. People are encouraged to change inwardly look at mistakes of the past year Ask forgiveness from any you have wronged http://www.history.com/videos/ask-a-rabbirosh-hashanah#ask-a-rabbi-rosh-hashanah 2. Yom Kippur Completes the High Holy Days Day of repentance and forgiveness Renewal of the sacred covenant with God in a spirit of atonement and cleansing Celebration of When Jews regained access to Temple Burned for 8 Judah Maccabee declared this to be a time of remembrance and prayer Found only one jar of oil undefiled Still sacred and blessed by a priest Was only enough for one day/night the victory of the Maccabee Rebellion Now a gift giving time http://www.history.com/videos/ask-a-rabbi-roshhashanah#ask-a-rabbi-hanukkah Celebrates the liberation from bondage in Egypt and the spring time renewal Beginning of Passover Seder Dinner Eating of unleavened bread and bitter herbs http://www.history.com/videos/ask-a-rabbi-roshhashanah#history-of-passover Holocaust Memorial Day 5. April 30/May 1 Close to date of Warsaw uprising Orthodox Judaism: Stand by the Hebrew Bible as the Revealed Word of God and the Talmud as the Legitimate Law Bound by Tradition Very Family oriented Ex: Hasidic Jews Growing in #, esp in Israel Reform Judaism: began in the 19th Century Germany as an attempt to modernize Religion applied to today; not an ancient practice Open ended, evolving religion Making it more modern could help it survive Choirs added to services Sabbath was shortened and translated into Vernacular Conservative Judaism: Largest group in the US Traditional in interpretation of the Law But restructure and modernize to keep it alive Reconstruction Judaism: Rejects the idea that Jewish People were specially chosen by God An exclusionist idea They see it as they chose to be a people of God New prayer book More respect given to women and gentiles Women accepted fully in synagogue participation Messianic Judaism: Accept that Jesus was the Messiah Keep to traditional Jewish Calendar, holidays and practices Growing in number Judaism as a whole is shrinking Over 50% of Western Jews marry non-Jews Being counted as minyan Emphasizing the importance of women in the Torah How women shaped the stories Becoming cantors and rabbis More gender neutral texts Original Hebrew scripture describes God as formless; neither male nor female essence More accepted today than ever before in history Less fear about the unknown More people researching Judaism Continues to influence Christianity and Islam