* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Dementia with Lewy bodies wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Restless legs syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Tourette syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish cognitive tempo wikipedia , lookup
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder controversies wikipedia , lookup
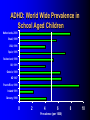
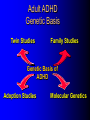
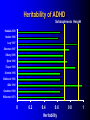
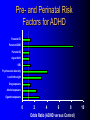
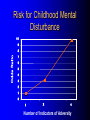
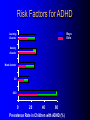
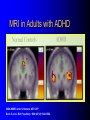
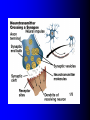
ADHD Overview Jeanette E. Cueva, M.D. Overview ADHD history Perception and reality Diagnosis in the US and UK Etiology ADHD in 1854: Fidgety Phil “Let me see if he is able to sit still for once at the table. Thus Popa bade Phil behave and Mama looked very grave But fidgety Phil, He won’t sit still…” http://www.fln.vcu.edu/struwwel/philipp_e.html History of ADHD Date Milestone 1902 Still: Description of ADHD symptoms 1937 Bradley: Benzadrine. Conceptualization of ADHD involved testing response to stimulants 1955 MPH 1960 Minimal Brain Dysfunction 1980 ADD – DSM-III; adults acknowledged 1987 ADHD – DSM-III R 1994 DSM-IV Erroneous Beliefs/Assumptions About ADHD Minor disorder if it even exists Affects almost solely males Has little impact beyond the classroom Disappears spontaneously after grade school Erroneous Beliefs/Assumptions About ADHD Overdiagnosed – Diagnosis made about any energetic or “different” child – Medication is only a form of chemical control Misdiagnosed in cases – Poor parenting – Rigid, misguided teachers Overtreated of by physicians who used powerful and potentially addicting drugs for a minor, temporary ailment Erroneous Beliefs/Assumptions About ADHD Produced a pattern of treatment in which clinicians did not use medications OR – – – – – Used low doses of medications (Only Monday through Friday) (Only during school hours) (Gave “drug holidays”) Stopped medications in adolescence Erroneous Beliefs vs Evidence Erroneous Beliefs/Assumptions Are False ADHD Evidence Exists to Invalidate Them Evidence In the beginning, the diagnosis of ADHD was unclear due to – Different names – Inconsistent nature of impairments – Feedback from 3rd parties (ie, children are poor historians) – Media controversy – Lack of validated diagnostic instruments But by 1998, the AMA called ADHD “…one of the best-researched disorders in medicine, and the overall data on its validity are far more compelling than for many medical conditions.” Goldman et al. JAMA 1998;279:1100. Controlled Studies of Medication in ADHD Stimulants 21 155 Antidepressants 12 3 Neuroleptics Antihypertensives N=6472 children, adolescents, and adults. Spencer et al. JAACAP 1996;35:409. ADHD: Diagnosis Based on coding systems DSM-IV and DSM-IV TR (www.behavenet.com/capsules/disorders/adhd.htm) – US 314.01 ADHD, Combined Type 314.00 ADHD, Predominantly Inattentive Type 314.01 ADHD, Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Type ICD 10 (www.mentalhealth.com/icd/p22-ch01.html) – EU/US F90 Hyperkinetic disorders F90.0 Disturbance of activity and attention F91.1 Hyperkinetic CD ADHD: Core Symptom Areas Inattention Impulsivity/Hyperactivity ADHD: DSM-IV Criteria Inattention Six or more of the following – manifested often Inattention to detail/makes careless mistakes Difficulty sustaining attention Seems not to listen Fails to finish tasks Difficulty organizing Avoids tasks requiring sustained attention Loses things Easily distracted Forgetful ADHD: DSM-IV Criteria Impulsivity/Hyperactivity Six or more of the following – manifested often Impulsivity – Blurts out answers before question is finished – Difficulty in awaiting turn – Interrupts or intrudes on others Difficulty organizing – Fidgets – Unable to stay seated – Inappropriate running/climbing – Difficulty in engaging in leisure activities quitely – On the go – Talks excessively ADHD: DSM-IV Diagnostic Criteria Symptom criteria must be met for past 6 months Some symptoms must be present before 7 years of age Some impairment from symptoms must be present in 2 or more settings Symptoms lead to significant impairment – Social, academic, or occupational Symptoms are not exclusionary due to other mental disorders ADHD: DSM-IV Subtypes ADHD predominately inattentive type – Criteria met for inattention but not for impulsivity/hyperactivity ADHD predominately hyperactivity/impulsivity type – Criteria met for impulsivity/hyperactivity – but not for inattention ADHD combined type – Criteria met for inattention and impulsivity/hyperactivity DSM IV Diagnosis: Clinical Subtypes Predominately inattentive – Easily distracted; not Predominately inattentive excessively hyperactive or impulsive Combined type – Predominent presentation; exhibits all three classical signs Predominately hyperactiveimpulsive – Extremely hyperactive and impulsive; not highly inattentive Combined type Predominately hyperactive-impulsive ADHD: ICD 10 Stresses HK disorders over “ADD” – Implies knowledge of psychological process and suggests anxious, preoccupied, or dreamy apathetic children – Inattention central feature Cardinal features of DSM-IV – Vague – Diagnostic guidelines descriptive Impairment DSM-IV-TR: ADHD symptoms must be consistently and persistently impairing in at least 2 areas of life functioning – Much more than personality traits and quirks – Must significantly impair major aspects of day- to-day life Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Text Revision. 2000. Impairment in ADHD Psychiatric comorbidity School failure Poor peer relationships Legal difficulties Smoking and substance abuse Accidents and injuries Family conflict Parent stress ADHD: Variations in symptoms Pervasiveness Frequency of Occurrence Degree of impairment DSM-IV-Defined ADHD Population (Paediatric 3-19 yrs) 2000 2005 2010 2000-5 Growth (%/Yr) 2005-10 Growth (%/Yr) United States 10,362,900 10,391,600 10,225,200 0.1 (0.3) Europe 9,795,600 9,396,600 8,900,300 (0.8) (1.1) France 2,185,100 2,133,200 2,082,000 (0.5) (0.5) Germany 2,581,500 2,471,300 2,270,800 (0.9) (1.7) Italy 1,637,200 1,565,200 1,480,300 (0.9) (1.1) Spain 1,222,700 1,108,200 1,052,800 (1.9) (1.0) United Kingdom 2,169,100 2,118,700 2,014,400 (0.5) (1.0) Japan 3,432,000 3,265,600 3,233,300 (1.0) (0.2) Major Market Total 23,590,500 23,053,800 22,358,800 (0.5) (0.6) Source: Decision Resources, “Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder”, December 2001 ADHD: World Wide Prevalence in School Aged Children Netherlands, 2000 Brazil, 1999 USA, 1996 Spain, 1995 Switzerland, 1998 UK, 1991 Ontario, 1989 NZ 1987 Puerto Rico, 1998 Ireland 1991 Gemany, 1990 0 2 4 6 Prevalence (per 1000) 8 10 Diagnosis & Treatment Rates of ADHD 12,000,000 10,000,000 8,000,000 Prevalence 6,000,000 Diagnosis 4,000,000 Treatment 2,000,000 0 USA Europe* Source: Decision Resources, “Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder”, December 2001 Japan *Europe = D,F,I,UK,E ADHD: Etiology ADHD is a heterogeneous behavioral disorder with multiple possible etiologies Genetic origins Neuroanatomic Neurochemical ADHD CNS insults Environmental factors Adult ADHD Genetic Basis Twin Studies Family Studies Genetic Basis of ADHD Adoption Studies Molecular Genetics Heritability of ADHD Schizophrenia Height Hudziak 2000 Nadder 1998 Levy 1997 Sherman 1997 Silberg 1996 Gjone 1996 Thapar 1995 Schmitz 1995 Edelbrock 1992 Gillis 1992 Goodman 1989 Willerman 1973 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 Heritability 0.8 1 ADHD: Etiology ADHD is a heterogeneous behavioral disorder with multiple possible etiologies Genetic origins Neuroanatomic Neurochemical ADHD CNS insults Environmental factors Pre- and Perinatal Risk Factors for ADHD Parental CD Parental ADHD Parental IQ Age at birth SES Psychosocial adversity Low birth weight Drug exposure Alcohol exposure Cigarette exposure 0 2 4 6 8 Odds Ratio (ADHD versus Control) 10 Indicator of Adversity Low social class Maternal psychopathology Paternal criminality Family conflict Placement outside the home Risk for Childhood Mental Disturbance 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 4 Number of Indicators of Adversity Rutters Indicators of Adversity and Risk for ADHD 5 Gender, parental ADHD 4 Maternal smoking during pregnancy 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 Number of Rutter’s Indicators ADHD: Diagnostic Considerations Inattention Impulsivity/Hyperactivity Risk Factors for ADHD Boys Girls Learning disorder Anxiety disorder Mood disorder CD ODD 0 20 40 60 Prevalence Rate in Children with ADHD (%) ADHD: Adult Common Comorbid Diagnosis Male Female Alcohol/drug dependency Anxiety disorder Mood disorder AntiSocial disorder 0 20 40 60 Life-time Prevalence Rates in Adults with ADHD (%) “It’s a guy thing.” Psychiatric Comorbidity Anxiety (34%) MD (20 to 30%) 7% 23% 7% 4% CD (8 – 20%) Non-comorbid (55%) 2% ADHD: Etiology ADHD is a heterogeneous behavioral disorder with multiple possible etiologies Genetic origins Neuroanatomic Neurochemical ADHD CNS insults Environmental factors Affected area of brain MRI in Adults with ADHD MGH-NMR Center & Harvard- MIT CITP Bush G, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;45(12):1542-1552. ADHD: Neurochemistry ADHD best understood by the interaction of multiple neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters most critical in ADHD – Norepinephrine (NE) – Dopamine (DA) Neurotransmitters Dopamine Norepinephrine OH OH CH2 CH2 NH2 OH OH CH NH2 OH Amphetamine CH2 CH CH CH3 NH2 Methylphenidate Pemoline O O COCH3 N O NH NH2 Probable Mechanism of Action of Methylphenidate Wilens and Spencer. Handbook of Substance Abuse: Neurobehavioral Pharmacology. 1998;501-513. Presynaptic Neuron Storage vesicle Cytoplasmic DA DA Transporter Synapse Methylphenidate inhibits The Mechanisms of Action of Amphetamine Wilens and Spencer. Handbook of Substance Abuse: Neurobehavioral Pharmacology. 1998;501-513. Presynaptic Neuron AMPH blocks uptake into vesicle AMPH diffuses into vesicle causing DA release into cytoplasm AMPH AMPH Storage vesicle Cytoplasmic DA AMPH is taken up into cell causing DA release into synapse DA Transporter Protein Synapse AMPH Inhibits Dopamine Neurotransmission Relative to ADHD Dopamine Nigrostriatal Pathway Enhances signal Improves attention – Focus – On-task behavior – On-task cognition Mesolimbic Pathway Substantia nigra Mesocortical Pathway Ventral tegmental area Solanto. Stimulant Drugs and ADHD. Oxford; 2001. Norepinephrine Neurotransmission Relative to ADHD Norepinephrine • Dampens noise • Executive operations • Increases inhibition Frontal Limbic Locus Ceruleus Solanto. Stimulant Drugs and ADHD. Oxford; 2001. Catecholaminergic Neurotransmission Relative to ADHD Dopamine Striatal - Prefrontal Enhances Signal Improves Attention – – – – – – Focus Vigilance Acquisition On-task behavior On-task cognitive Perception(?) Solanto. Stimulant Drugs and ADHD. Oxford; 2001. Norepinephrine Prefrontal Dampens Noise – Distractibility – Shifting Executive operations Increases Inhibition – Behavioral – Cognitive – Motoric Questions