* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 342 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
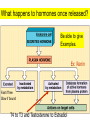
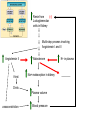
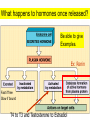
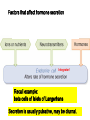
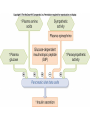
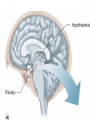
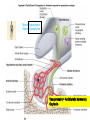
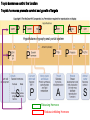
Monday, 15 September Chapter 11 The Endocrine System • • • • • • • • • Classes of hormones The adrenal gland Fates of hormones Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Control of hormone secretion Hormone interactions (permissive effects) Hypothalamus & Pituitary The story of Aunt Dot Endocrine disorders (lab) What happens to hormones once released? Be able to give Examples. Ex: Renin Fast if free Slow if bound T4 to T3 and Testosterone to Estradiol Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone Renin is released from kidney cells into bloodstream, its “target” in a plasma protein. Angiotensinogen from liver, a plasma protein Renin Angiotensin I Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) Angiotensin II Zona Glomerulosa of Adrenal Cortex Aldosterone Thirst Arterial smooth muscle … vasoconstriction…increase blood pressure Promotes Na+ retention in Kidney Renin from (-) Juxtaglomerular cells in Kidney Multi-step process involving Angiotensin I and II Angiotensin II thirst Aldosterone Na+ reabsorption in kidney Drink Plasma volume vasoconstriction Blood pressure K+ in plasma _______ What happens to hormones once released? Be able to give Examples. Ex: Renin Fast if free Slow if bound T4 to T3 and Testosterone to Estradiol Factors that affect hormone secretion Integrator! Recall example: beta cells of Islets of Langerhans Secretion is usually pulsative, may be diurnal. Fig. 11.08 Permissive effect Thyroid hormone stimulates production of beta-adrenergic receptors Questions so far? Fig. 11.12a Fig. 11.12b Neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis Vasopressin (= Antidiuretic hormone) Oxytocin Typical Blood Flow Artery – arteriole- capillary –venule- vein –heart Portal System Artery – arteriole- capillary –portal vessel – capillary –venule- vein –heart 1. Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system 2. Hepatic portal system 3. Vasculature of nephrons Tropic hormones control the function Trophic hormones promote survival and growth of targets P P P P A P Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system P P S P P P A Releasing Hormone Release-inhibiting Hormone P S