* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
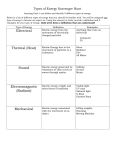
Chapter 4 – ENERGY Energy Energy—The ability to cause change and the ability to do WORK 9 Main forms of energy: – 1. Electrical: energy due to moving electrons – 2. Chemical: energy stored in bonds between atoms – 3. Thermal: energy from heat – 4. Radiant = Light: energy from the sun & light – 5. Nuclear: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom – 6. Sound: energy of vibrating sound waves – 7. Magnetic: energy of magnetism – 8. *Mechanical: Energy due to position and motion • Kinetic + Potential= Mechanical 9. Elastic potential Energy: Energy that is stored in something that stretches or compresses, such a rubber band or spring. Kinetic Energy • KE is energy of motion. • KE = 1×m×v2 2 • – m = mass (kg) – v = velocity (m/s) • SI Unit for Energy is Joule (J) –Joule = kgxm2/s2 (This is NOT an equation— just another way to write the unit) Calculating Kinetic Energy • What is the kinetic energy of a 44 kg cheetah running at 31 m/s? • KE = 1 m v2 • 2 • KE = https://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=AO117teuR2Q • Bill Nye Energy: • On the back of your paper: • Name as many examples of energy as you can from the video. • Name examples of energy changes in the video. • http://glencoe.mheducation.com/sites/007 8778360/student_view0/brainpop_movies. html# Forms of energy overview Potential Energy (PE) • PE is energy that is stored in an object. 4 types of PE: 1. Elastic PE – Energy due to a stretch (rubber band) or compression (spring) 2. Chemical PE – Energy in the bonds between atoms (foods & fuels) 3. Gravitational PE – Energy due to an elevated position – GPE = m×g×h • m = mass (kg) • g = gravity=9.8 m/s2 (on Earth) • h = height (m) 4. Nuclear energy: Energy stored in the nucleus of Calculating Potential Energy • A 65 kg rock climber ascends a cliff. What is the climber’s GPE 35 m above the base of the cliff? • GPE= • • Kinetic Energy Watch this BrainPOP animated movie explain how the energy of motion changes depending upon an object's speed and mass. Potential Energy In this BrainPOP movie, Tim and Moby show how potential energy changes depending upon an object's position and condition. https://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=AO117teuR2Q • Bill nye energy 22 min • Bozeman science KE PE • https://www.youtub e.com/watch?v=BS Wl_Zj-CZs Law of Conservation of Energy L.o.C.o. Energy-• Energy can not be created or destroyed, it just changes form. • • • • Rollercoaster mass and spring Circus physics: transforming energy 2 min. http://www.pbs.org/opb/circus/classroom/circ Mechanical Energy • Energy can be converted from Potential to Kinetic, but the total energy doesn’t change • Total Mechanical Energy = Kinetic + Potential • ME = KE + PE Nuclear Energy • There are two types of nuclear energy • Fission and Fusion • Both forms energy are stored as mass in the atoms of certain elements. This mass can be changed into energy under the proper conditions according to Albert Einstein's famous equation: • • nuclear fission http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/nvhe.sci.chemistry.fission/afission-chain-reaction/ nuclear fusion http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/phy03.sci.phys.matter.fusionbom b/fusion-the-hydrogen-bomb/ Fusion & Fission • Fusion atoms are "fused" together • In fusion lighter elements form heavier elements • Uses • Fission the 2nd form of nuclear energy • The exact opposite of fusion. • In fission atoms are broken apart. • In fission heavier elements form lighter elements. • Uses – Hydrogen Bomb – Nuclear Energy Plants – The middle of stars Rube Goldberg Unbelievable Rube Goldberg Machine - Google Video •