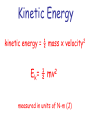* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
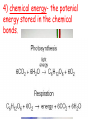
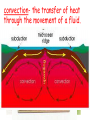
Energy energy- the ability to do work or cause change. (Remember- work can only occur if something moves!) Types of Energy 1) kinetic- energy of an object in motion 2) potential- the energy of an object’s position or shape. Kinetic Energy kinetic energy = ½ mass x velocity2 Ek= ½ mv2 measured in units of N-m (J) Potential Energy Gravitational Potenital = Energy weight x height Ep = w x h measured in units of N-m (J) Forms of Energy 1) mechanical energy- the energy of the position or motion of an object. 2) thermal energy- the total potential and kinetic energy of particles in an object. 3) electrical energy- the energy of electric charges. 4) chemical energy- the potenial energy stored in the chemical bonds. 5) nuclear energy- the potenial energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. 6) electromagnetic energy- the energy of light and other forms of radiation. Energy Transformations Kinetic to Potential click (most common) Multiple Transformations click convection- the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid. conduction- the transfer of heat from one particle of matter to another. radiation- the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed.