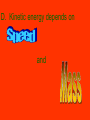* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Sci. 5-1 What is Energy? Pages 116-123 A. Energy- is the ability to do work and work is the transfer of energy B. Both energy and work are expressed in Joules (J). C. Kinetic Energy- the energy of motion. D. Kinetic energy depends on and E.Speed has a greater impact on kinetic energy than does mass because speed is squared. F. Kinetic Energy formula m = mass v= speed KE=mv 2 2 G. Potential Energy- the energy an object has because of its position or shape. It has energy because work has been already done to it. H. Gravitational Potential Energy happens when something has been lifted. GPE = weight x height Newtons x meters Which is the same as work W=Fxd I. Mechanical Energy- the total energy of motion and position of an object. 1)Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy 2) When potential energy increases, kinetic energy decreases. J. Six forms of energy are thermal, chemical, electrical, sound, light, and nuclear. 1) Thermal Energy (heat) – all matter has particles in constant motion. The hotter the object then the faster the particles move. 2) Chemical Energy- the energy of a compound that changes as its atoms rearrange to form a new compound 3) Electrical Energy- the energy of moving electrons. Electrons are negatively charged particles of an atom. 4) Sound Energy- caused by an object’s vibrations. The object vibrates which causes the air to vibrate which causes your eardrum to vibrate and you hear sound. 5) Light Energy- produced by vibrations of electrically charged particles, NOT ALL light can be seen. 6) Nuclear Energy- produced by an atom’s nucleus splitting or when two nuclei join together.