* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lower limb Neurovasculature
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
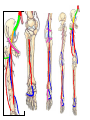
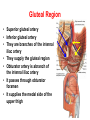
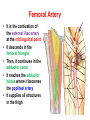
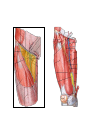
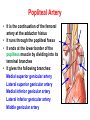
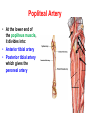
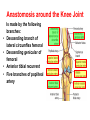
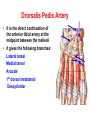
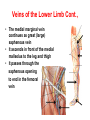
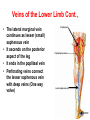
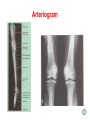
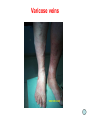
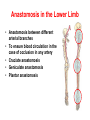
Blood Vessels of lower limb Objectives • Describe topography of major vessels • Illustrate clinical relevance of vascular anatomy Blood Vessels of lower limb They include the following: • Femoral, popliteal, obturator, gluteal, tibials and their branches • Great and small saphenous veins and their tributaries • Deep veins (Femoral, popliteal, tibials) Gluteal Region • Superior gluteal artery • Inferior gluteal artery • They are branches of the internal iliac artery • They supply the gluteal region • Obturator artery is abranch of the internal iliac artery • It passes through obturator foramen • It supplies the medal side of the upper thigh Femoral Artery • It is the contiuation of the external iliac artery at the mid inguinal point • It descends in the femoral triangle • Then, it continues in the adductor canal • It reaches the adductor hiatus where it becomes the popliteal artery • It supplies all structures in the thigh Femoral Artery In the femoral triangle, it gives the following branches: Superficial circumflex iliac artery Superficial epigastric artery External pudendal artery Deep artery of the thigh Muscular branches Deep Artery of the Thigh • • • • It is the main artery of the thigh It gives the following branches Medial circumflex femoral artery Lateral circumflex femoral artery which gives a descending branch • Perforating arteries Popliteal Artery • It is the continuation of the femoral artery at the adductor hiatus • It runs through the popliteal fossa • It ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle by dividing into its terminal branches • It gives the following branches: Medial superior genicular artery Lateral superior genicular artery Medial inferior genicular artery Lateral inferior genicular artery Middle genicular artery Popliteal Artery • At the lower end of the popliteus muscle, it divides into: • Anterior tibial artery • Posterior tibial artery which gives the peroneal artery Anastomosis around the Knee Joint • • • • Is made by the following branches: Descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral Descending genicular of femoral Anterior tibial recurrent Five branches of popliteal artery Anterior Tibial Artery • It is one of the two terminal branches of the popliteal artery • It supplies all structures in the anterior compartment of the leg and perforating branches to lateral compartment • It ends at the midpoint between the malleoli • It continues as Drorsalis Pedis Artery • It gives anterior medial and lateral malleolar branches Posterior Tibial Artery • It is one of the two terminal branches of the popliteal artery • It supplies all structures in the posterior and lateral compartment of the leg • It runs behind and inferior to lateral malleolus • It then divides into Medial and Lateral plantar branches • It gives the following branches: Peroneal artery which gives lateral malleolar and calcaneal branches Drorsalis Pedis Artery • It is the direct continuation of the anterior tibial artery at the midpoint between the malleoli • It gives the following branches: Lateral tarsal Medial tarsal Arcuate 1st dorsal metatarsal Deep plantar Plantar Arteries • The posterior tibial artery divides into: Lateral plantar Medial plantar artery which gives the first plantar metatarsal artery Deep plantar arch is formed by the deep plantar branch of dorsalis pedis artery and lateral plantar artery Anastomosis around the Ankle Joint Is formed by the following branches: • Calcanean branches of posterior tibial and peroneal arteries • Medial and lateral malleolar branches of anterior tibial artery • Malleolar branches of posterior tibial and peroneal arteries • Veins of the Lower Limb • Deep veins accompany arteries of the lower limb internal to the deep fascia • Superficial veins are not accompanied by arteries in the subcutaneous tissue • Deep veins of the foot are drained to the dorsal venous arch • Medial and lateral marginal veins emerge from the sides of the arch Veins of the Lower Limb Cont., • The medial marginal vein continues as great (large) saphenous vein • It ascends in front of the medial malleolus to the leg and thigh • It passes through the saphenous opening to end in the femoral vein Veins of the Lower Limb Cont., • The lateral marginal vein continues as lesser (small) saphenous vein • It ascends on the posterior aspect of the leg • It ends in the popliteal vein • Perforating veins connect the lesser saphenous vein with deep veins (One way valve) Lower limb Vasculature Applied anatomy • • • • • • Surface anatomy Arteriography and veinography Varicose veins Obstructive vasculopathy Arterial pulse Deep vein thrombosis Surface Anatomy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Femoral Profunda Popliteal Posterior tibial Peroneal Medial plantar Lateral plantar Anterior tibial Dorsalis pedis Veins Arteriogram Varicose veins Arterial pulse Lymphatics Anastomosis in the Lower Limb • Anastomosis between different arterial branches • To ensure blood circulation in the case of occlusion in any artery • Cruciate anastomosis • Geniculate anastomosis • Plantar anastomosis