* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homeostasis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
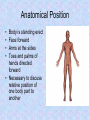
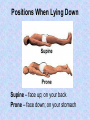
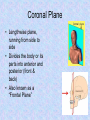
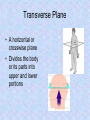
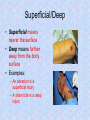
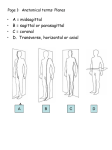
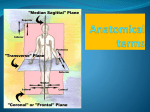
Homeostasis Staying (stasis) the Same (homeo) Warm up Mar. 7 • What is something we study in anatomy? • Why should you study how the body works? • What are two organs found in the body? Vocab. • • • • • • • Homeostasis Anatomical Position Supine Prone Sagittal Plane Transverse Plane Coronal Plane • Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment within an organism. – Body temperature stays around 98.6o no matter what the surrounding temperature – Helps make sure you are healthy Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position • • • • Body is standing erect Face forward Arms at the sides Toes and palms of hands directed forward • Necessary to discuss relative position of one body part to another Positions When Lying Down Supine – face up; on your back Prone – face down; on your stomach Body Planes Used to “cut” the body into smaller segments for study Sagittal Plane • Lengthwise plane, running from front to back • Divides the body into right and left portions • If the cut is exactly in the middle of the body, the division is a midsagittal plane. Coronal Plane • Lengthwise plane, running from side to side • Divides the body or its parts into anterior and posterior (front & back) • Also known as a “Frontal Plane” Transverse Plane • A horizontal or crosswise plane • Divides the body or its parts into upper and lower portions Essential Questions • • • What are the three planes of the body? What does it mean if the body is in homeostasis? Describe Anatomical position. Vocabulary • • • • Superior Inferior Anterior/Ventral Posterior/Dorsal Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Directional Terms • Used to describe the relative position of one body part to another body part Superior/Inferior • Superior means “toward the head”; upper or above • Inferior means “toward the feet”; lower or below • Determined by a transverse plane • Example: the lungs are located superior to the diaphragm, while the stomach is located inferior to it Anterior/Posterior • Anterior means “front” or “in front of” • Posterior means “back” or “in back of” • In humans, ventral (toward the belly) can be used instead of anterior, and dorsal (toward the back) can be used instead of posterior • Determined by coronal or frontal plane • Example: the nose is on the anterior surface while the shoulder blades are on the posterior surface Medial/Lateral • Medial means “toward the midline of the body” • Lateral means “toward the side of the body or away from its midline) • Determined by a sagittal plane • Example: the big toe is on the medial side of the foot while the little toe is on the lateral side; the heart is medial to the lungs Proximal/Distal • Proximal means “toward or nearest the trunk of the body” or “nearest the point of origin of one of its parts” • Distal means “away from or farthest from the trunk or the point of origin of a body part” • Determined by a sagittal plane • Example: The elbow is proximal to the hand; the hand is at the arm’s distal end Superficial/Deep • Superficial means nearer the surface • Deep means farther away from the body surface • Examples: – An abrasion is a superficial injury – A shark bite is a deep injury