* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
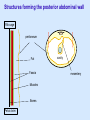
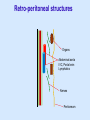
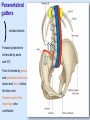
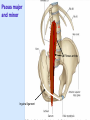
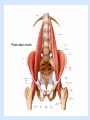
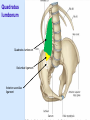
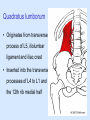
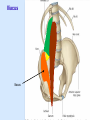
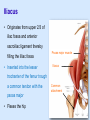
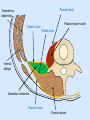
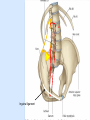
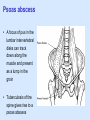
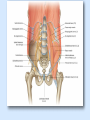
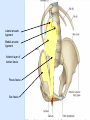
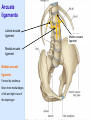
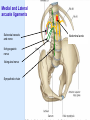
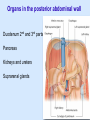
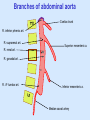
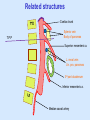
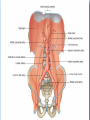
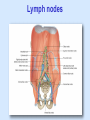
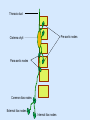
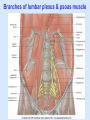
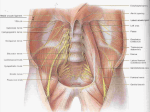
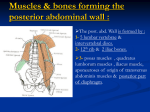
Posterior abdominal wall Sanjaya Adikari Department of Anatomy Objectives Describe the arrangement of muscles and fascia in the posterior abdominal wall Describe the structures found in the posterior abdominal wall Describe the posterior abdominal viscera Contents of abdominal cavity Contents removed Posterior abdominal wall • A musculoskeletal wall between the lower border of the rib cage and the pelvic brim • Marks the posterior boundary of the abdominal cavity • Anteriorly lie the retroperitoneal organs and the parietal peritoneum • Posteriorly lie muscles, fascia and the lumbar spine Structures forming the posterior abdominal wall Rib cage peritoneum Fat Fascia Muscles Bones Pelvic brim cavity mesentery Retro-peritoneal structures Organs Abdominal aorta IVC, Portal vein Lymphatics Nerves Peritoneum Paravertebral gutters lumbar lordosis Forward projection is enhanced by aorta and IVC Floor is formed by psoas and quadratus lumborum above and iliacus below the iliac crest Posterior part of the diaphragm also contributes Psoas major and minor L1 Fibrous arches Inguinal ligament Psoas major muscle Psoas major • Originates from bodies of T12 to L5, intervertebral disks and the medial end of transverse processors • Inserted into the lesser trochanter of the femur • Part above the medial arcuate ligament lies in the thoracic cavity • Flexes the hip and laterally flexes the lumbar spine • Both muscles acting together flexes the trunk Quadratus lumborum Quadratus lumborum Iliolumbar ligament Anterior sacroiliac ligament Quadratus lumborum • Originates from transverse process of L5, iliolumbar ligament and iliac crest • Inserted into the transverse processes of L4 to L1 and the 12th rib medial half Iliacus Iliacus Iliacus • Originates from upper 2/3 of iliac fossa and anterior sacroiliac ligament thereby filling the illiac fossa • Inserted into the lesser Psoas major muscle Iliacus trochanter of the femur trough a common tendon with the psoas major • Flexes the hip Common attachment Fascia of the posterior abdominal wall • Psoas fascia • Iliac fascia • Lumbar part of the thoracolumbar fascia Psoas fascia • Thick fascial sheath surrounding the psoas muscle • Arises as the muscle enters the abdominal cavity under the medial arcuate ligament • Ends at the pelvic brim as the muscle leaves the abdomen inferior to the inguinal ligament (does not extend into the thigh) Thoracolumbar fascia • Extends from the back of sacrum to the neck • Binds erector spinae to vertebral column and encloses the quadratus lumborum • Very strong in the lumbar region • Laterally it gives origin to internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles • Its lumbar part medially splits into three layers Posoas fascia Transversus abdominis Posoas major muscle Anterior layer Middle layer Internal oblique Quadratus lumborum Posterior layer Erector spinae L1 Inguinal ligament Psoas abscess • A focus of pus in the lumbar intervertebral disks can track down along the muscle and present as a lump in the groin • Tuberculosis of the spine gives rise to a psoas abscess Skeleton of the posterior abdominal wall include A. Ischium B. 11th rib C. 12th vertebra D. Sacrum E. Intervertebral disks Correct: B, C, D, E Muscles of the posterior abdominal wall include A. Iliopsoas B. Erector spinae C. Quadratus lumborum D. Diaphragm E. Transversus abdominis Correct: A, C, D Lateral arcuate ligament Medial arcuate ligament Anterior layer of lumbar fascia Psoas fascia Iliac fascia Arcuate ligaments L1 Lateral arcuate ligament Medial arcuate ligament Median arcuate ligament Formed by tendinous fibres from medial edges of left and right crura of the diaphragm Median arcuate ligament Medial and Lateral arcuate ligaments Subcostal vessels and nerve Iliohypogastric nerve Ilioinguinal nerve Sympathetic chain Abdominal aorta Organs in the posterior abdominal wall Duodenum 2nd and 3rd parts Pancreas Kidneys and ureters Suprarenal glands Vessels • Aorta and its branches • Inferior vena cava and its tributaries • Portal vein and its tributaries • Lymphatics and lymph nodes Branches of abdominal aorta Main branches are in three categories • Single ventral arteries to gut and its derivatives – Coeliac trunk, superior and inferior mesenteric • Paired arteries to other viscera – Suprarenal, renal, gonadal • Paired arteries to body wall – Inferior phrenic, lumbar Branches of abdominal aorta Coeliac trunk R. inferior phrenic art. R. suprarenal art. Superior mesenteric a. R. renal art. R. gonadal art. R. 4th lumbar art. Inferior mesenteric a. Median sacral artery Related structures Coeliac trunk T.P.P Splenic vein Body of pancreas Superior mesenteric a. L. renal vein Un. pro. pancreas 3rd part duodenum Inferior mesenteric a. Median sacral artery Lymph nodes Lymphatics follow arteries • Single ventral arteries Pre-aortic nodes • Paired arteries to other viscera Para-aortic nodes • Paired arteries to body wall Lymph nodes Thoracic duct Pre-aortic nodes Cisterna chyli Para-aortic nodes Common iliac nodes External iliac nodes Internal iliac nodes Lumbar plexus 1st – 4th lumbar spinal segments Embeded in the psoas Branches related laterally, medially or anteriorly to psoas Branches of lumbar plexus & psoas muscle