* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Iliopsoas Abscesses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
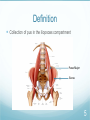
Iliopsoas Abscesses Jeremy Lynch 1 Case 66 year old female former secretary 6 month history of increasing right loin and hip pain Recently saw an orthopaedic surgeon who ascribed the hip symptoms to age For past 2 days: Severe exacerbation of pain Fever Nausea 2 Examination Pyrexial Tachycardic BP: 100/72 Swelling, and tenderness localized at the right side at the back of waist Most comfortable with right hip in flexion Extension especially painful 3 Investigations Raised WCCs, CRP, mild anaemia CXR/AXR: nil of note Ultrasound pelvis/abdomen: nil of note CT shows: hypodense lesion causing enlargement of the psoas muscle Diagnosis of psoas abscess made Treated with CT guided drainage 4 Definition Collection of pus in the iliopsoas compartment Psoas Major Iliacus 5 Aetiology 1. Primary: haematogenous spread of bacteria from distant source 2. Secondary: inflammatory/infectious process nearby Growing in frequency with growing use of CT scanning 6 Primary Causes Haematogenous spread of bacteria Risk Factors Diabetes mellitus AIDS Renal Failure Immunosuppression IV drug abuse Older patients 7 Secondary Causes Inflammatory/infectious process System Cause Gastrointestinal Crohns, Diverticulitis, Appendicitis, Colorectal Cancer Genitourinary UTI, Cancer, Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotrypsy Muskuloskeletal Verterbral osteomyelitis, Septic arthritis, Infected sacroilitis Vascular Infected AAA, Femoral catheterization Miscellaneous Endocarditis, IUD 8 Epidemiology 9 Clinical Features Fever Limp Back Pain 10 Examination 11 Investigations Bloods CRP/ESR FBC Cultures Radiological Plain films Ultrasound CT/MRI 12 Management Antibiotics CT Drainage 1984 first attempted Wael, 2008: 41 adults Problem of recurrence: 15% in Wael study Surgical Drainage: Significant morbidity 13 Message Diagnosis is difficult and often delayed Diagnosed more frequently now due to CT Dangerous if untreated Thorough clinical examination can suggest Repeated imaging often needed to confirm 14 References Mallick, Thoufeeq, Rajendran. Iliopsoas Abscesses. Postgrad Med J. 2004. 80:459-462 M. Cantasdemir, B. Kara, D. Cebi, N. D. Selcuk and F. Numan. Psoas abscess rarely requires surgical intervention. The American Journal of Surgery. 2003. 58:811 Ricci, M.A., Rose, F.B., Meyer, K.K. Pyogenic psoas abscess: Worldwide variations in etiology. World Journal of Surgery. 1986. 10:834 15