* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gym instructor - AS Physical Education OCR
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
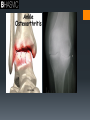
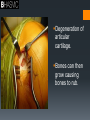
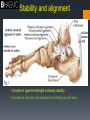
Joints Anatomy and Physiology Synovial Joint Structure Feature Ligament Synovial Fluid Articular Cartilage Joint Capsule Structure Function p20 Feature Structure Function Ligament Band of fibrous tissue Connect bone to bone Synovial Fluid Slippery fluid – egg-white consistency; in joint capsule Reduce friction between articular surfaces in joint Articular Cartilage Glass-smooth cartilage; spongy and covers ends of bones in joint Absorb shock and prevents friction between ends of bones Joint Capsule Tough fibrous tissue – 2 layers with fibrous capsule lying outside the synovial membrane Fibrous capsule helps to strengthen the joint, synovial membrane lines the joint and secretes synovial fluid Osteoarthritis Degeneration of articular cartilage. Bones can then grow causing bones to rub. “So why are we trying to encourage the next generation to take part in sport if it’s so bad for us?” WHY DO IT? Development of knowledge Page 39 of books Using your understanding of osteoarthritis complete the table on benefits of physical activity as well as the negative elements that may be involved in participation in physical activity linked to osteoarthritis. Positive of Physical activity Negative of physical activity. Stability and alignment Increase in ligament strength increases stability. Increase in exercise will increase surrounding muscle tone. Movement patterns Booklet task TYPES OF SYNOVIAL JOINT (Freely Movable) Joints and movements. Each pair has a joint that they need to describe. Actions that take place at the joint Type of joint/ name of the joint Sporting example relating to movement. Bones that are articulating (moving) Rotation Pivot joint Turning your head when swimming front crawl. Atlas and Axis Pairs Wrist Elbow Shoulder Spine Hip Knee Ankle I’ll allocate one and then you pick another. Put them on your paper and then place them on the board. Make sure we can read it. Movement patterns Movements have a start & finish point – identify these to help you analyse the movement occurring in a picture. FLEXION EXTENSION CIRCUMDUCTION When a limb bends. The angle at the joint gets smaller. To FLEX biceps, you BEND your arm! Biceps are therefore FLEXORS, as they bend the arm. Hamstrings are FLEXORS. When a joint or limb is straightened. The triceps straighten the arm. The quadriceps straighten the leg. They are EXTENSORS. When one end of the bone or limb stays in place, and they other moves in a circle. Circling action as in bowling. ROTATION ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Turning head side to side is rotation (top 2 vertebrae). Whole body can rotate about an imaginary axis (line) – during spin or somersault. Wrist rotates due to pivot joint at elbow (screwdriver action). Limbs move towards the centre line of the body. Both legs and arms do this during the narrowing phase of a star jump. You ADD together (bring limbs together) Movement of limbs away from the centre line of the body. You ABDUCT someone away from somewhere. The outward phase of a star jump. PRONATION The inward (medial) roll of the foot and in particular the heel and arch which occurs naturally at the heel strike as a cushioning mechanism. motion of rotating towards the prone position SUPINATION The feet don't roll inward enough ‘Sole UP’! S..UP..ination To turn or rotate so the palm is facing up. HORIZONTAL / SHOULDER FLEXION Moving arm forwards in horizontal plane HORIZONTAL / SHOULDER EXTENSION PLANTARFLEXION DORSI-FLEXION Returning arm to the abducted position Lateral movement away from the midline of the body in a horizontal plane Hyperextending the ankle joint so toes point downwards is the movement which increases the approximate 90 degree angle between the front part of the foot and the shin Bending ankle so that the toes are raised LATERAL FLEXION Bending body sideways (frontal plane) LATERAL EXTENSION Returning body to anatomical position PROTRACTION • Moving the scapula away from the spinal column Scapula moves towards the spinal column Depression Movement of shoulder girdle from an elevated position to the anatomical position (inferior movement) Elevation Superior movement of the shoulder girdle Anatomical terminology Anterior or ventral: Toward the front of the body Posterior or dorsal: Toward the back of the body Anatomical terminology A part above another part Superior: Inferior: Medial: A part below another part Toward the midline (median plane) of the body Lateral: Away from the midline of the body; toward the sides Superficial Near the surface Deep Below the surface 10 mark Question Critically evaluate the impact of physical activity and participation in lifelong physical activity on bones and joints. Plan for essay Look at all the points possible. Note the key points Make reference to physical activity as this is the subject qualifier. Note the command word (evaluate) depth or both sides. White boards plan as a group. Homework Completion of the booklet up to muscle pairings.