* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FINISH COPYING THIS INTO YOUR NOTES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
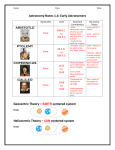
FINISH COPYING THIS INTO YOUR NOTES 22.1 Early Astronomy The Birth of Modern Astronomy Nicolaus Copernicus • a Polish Astronomer Copernicus concluded that Earth is a planet He theorized that the Sun was at the center of the Universe, and that the Earth and other planets revolved around it. STILL WRONG The Copernican Model of the Universe It did 3 things • It explained the motions of the planets. • It took the Earth out of it’s spot as the center of the universe. • it expanded the size of the Universe. 22.1 Early Astronomy The Birth of Modern Astronomy Tycho Brahe • Tycho Brahe designed and built instruments to measure the locations of the heavenly bodies. did not accept Copernicus’ model of the universe. He attempted to combine it with the Ptolemaic model. He proposed that the five known planets revolved around the sun, which, along with those planets, revolved around the earth each year. The stars, then, revolved around the Earth, which was immobile. Tycho Brahe’s first contributions to astronomy was the detection and correction of several errors in the standard astronomical tables. 22.1 Early Astronomy The Birth of Modern Astronomy Johannes Kepler • Kepler discovered three laws of planetary motion: 1. Orbits of the planets are elliptical. 2. Planets revolve around the sun at varying speed. 3. There is a proportional relationship between a planet’s orbital period and its distance to the sun. 22.1 Early Astronomy The Birth of Modern Astronomy Johannes Kepler • An ellipse is an oval-shaped path. • An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between Earth and the sun; it is about 150 million kilometers. Planet Revolution 22.1 Early Astronomy The Birth of Modern Astronomy Galileo Galilei • Galileo’s most important contributions were his descriptions of the behavior of moving objects. • He developed his own telescope and made important discoveries: 1. Four satellites, or moons, orbit Jupiter. 2. Planets are circular disks, not just points of light. 3. Venus has phases just like the moon. 4. The moon’s surface is not smooth. 5. The sun has sunspots, or dark regions. The Solar System Model Evolves 22.1 Early Astronomy The Birth of Modern Astronomy Sir Isaac Newton • Although others had theorized the existence of gravitational force, Newton was the first to formulate and test the law of universal gravitation. Universal Gravitation •There is a gravitational force acting between any two objects in the universe. Gravitational force decreases with distance. • The greater the mass of an object, the greater is its gravitational force. • We don't fall towards the people next to us because they are much less massive than Earth. But the Sun is more massive than Earth. Why don't we fall to the Sun? • It is much farther away. As the distance between two objects gets larger, the gravitational force between them gets smaller.