* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Colonization of the Moon wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
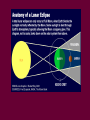
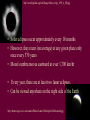
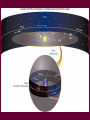
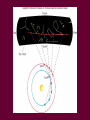
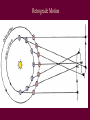
Survey of the Universe Tom Burbine [email protected] Moon, Planets, and Stars • All celestial objects appear to rise in the east and set in the west Moon • Besides the Sun, the Moon is the brightest object in the sky • The Moon reflects light from the Sun • Light areas are called highlands • Dark areas are called maria (huge impact basins filled with lava) http://sos.noaa.gov/datasets/solar_system/moon.html Cycle • The Moon’s changes in the sky follow a 29.5 day cycle • This is why each month has approximately 30 days Phases of the Moon29.5 day cycle http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lunar-Phase-Diagram.png Color of lunar eclipse • The Moon does not completely disappear because of the refraction of sunlight by the Earth’s atmosphere • If the Earth had no atmosphere, the Moon would be completely dark during an eclipse. • The red color arises because sunlight reaching the Moon must pass through the Earth’s atmosphere, where it is scattered. • Shorter wavelengths are more likely to be scattered by the small particles. By the time the light has passed through the atmosphere, the longer wavelengths dominate. This resulting light reflected from the Moon we perceive as red. Solar eclipse http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Solar_eclips_1999_4_NR.jpg • Solar eclipses occur approximately every 18 months • However, they recur (on average) at any given place only once every 370 years • Moon's umbra moves eastward at over 1,700 km/hr • Every year, there are at least two lunar eclipses. • Can be viewed anywhere on the night side of the Earth http://home.cogeco.ca/~astrosarnia/Photos/Lunar%20eclipse%20binocular.jpg http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cresource.dspexpguide&resourceid=556 Eclipses Moon is tilted at an angle of 5 degrees to Earth’s orbit Solar eclipse of July 22, 2009 • Lasted a maximum of 6 minutes and 39 seconds off the coast of Southeast Asia http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f2/Solar_eclipse_animate_%282009-Jul-22%29.gif http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Solar_eclipse_22_July_2009_taken_by_Lutfar_Rahman_Nirjhar_from_Bangladesh.jpg Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010 • Occurred over the Southern Pacific Ocean • Very remote • Seen over French Polynesia, the Cook Islands, and Easter Island Models • When you have a model of how something works, you should be able to predict what will happen • If observations do not fit the model, either the observations or the model is wrong • The ancient astronomers wanted to predict the positions of planets in the sky What did the ancients think • That the Earth was the center of the universe (geocentric model) • That the celestial sphere was rotating around the Earth • However, there was two observations that caused problems with this idea – Apparent retrograde motion – Inability to detect stellar parallax Greek model Motion of planets • Planets always appear to rise in the east and set in the west • But planets usually move from west to east past the stars • The exception is retrograde motion Figure 2.6 Figure 2.7 Apparent Retrograde Motion = “backward” motion Ptolemy’s (100-170 AD) Model of the Universe epicycle Occam’s Razor • The principle that generally recommends selecting the hypothesis that makes the fewest new assumptions Retrograde Motion Any Questions?