* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 7 Gravity and Space
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
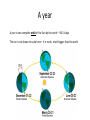
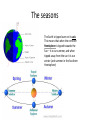
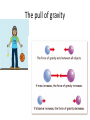
Year 7 Gravity and Space Sept 2011 Day and Night Rotating Earth day & night – PlanetObserver You tube video One day is one complete rotation of the earth around its axis A year A year is one complete orbit of the Sun by the earth – 365 ¼ days The sun is not drawn to scale here – it is much, much bigger than the earth The seasons The Earth is tipped over on its axis This means that when the northern Hemisphere is tipped towards the Sun – it is our summer, and when tipped away from the sun it is our winter (and summer in the Southern Hemisphere) The moon We see the Moon by reflected light from the sun -So We cannot see the part that is in shadow. This gives us the phases of the moon The moon takes approximately 28 days to go round the Earth once The solar system This is not to scale My Very Easy Method Just Speeds Up Naming (Planets Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto) Comets Asteroids Meteors Meteorites Asteroid belt Kuiper belt Moons Rings The planets Students do not have to remember planetary information. They need to remember the order of the planets and they need to know how to use data to find patterns and trends Past ideas about the universe Aristotle – everything went round the Earth Ptolemy's outstanding contribution was to develop a mathematical model of the Solar System which could be used to calculate planet positions. He put the Earth at the centre, but realized that the planets did not simply orbit the Earth Copernicus put the Sun at the centre, planets and stars orbit around Newton • Newton recognized that other planets had moons Current ideas about the universe We live on a small planet, orbiting a smallish star, towards the edge of a spiral galaxy of stars we call the Milky Way. There are billions of stars within the Milky way. There are billions and billions of galaxies, some bigger, some smaller than ours. A spiral galaxy – like our own This is a view of a tiny section of the sky showing hundreds of galaxies The expanding Universe The speed and direction of galaxies can be measured using light. It show that the Universe is expanding The Big Bang Theory If the universe is expanding now, it must have been smaller in the past So at the beginning it must have been very, very small and then expanded outwards very quickly – the big bang Aliens We have found planets orbiting other stars – they may have life on them, but that life will be adapted to the environment of that planet and may not be like us The pull of gravity Satellites To put a satellite into orbit Get it high above the atmosphere Give it forward thrust The satellite will get pulled down by gravity, but the Earth is round and curves away. The satellite will continue to fall towards the Earth, but never reach it. It will be in orbit. orbits