* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solar System – Odds & Ends - Saint Paul Public Schools
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Eris (dwarf planet) wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
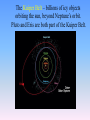
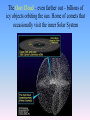
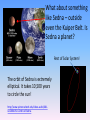
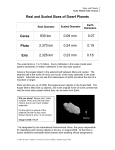
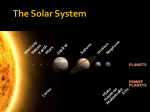
Solar System – Odds & Ends So what was that “retrograde motion” stuff all about? Why do the planets appear to move backwards sometimes? http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/allaboutmars/nightsky/nightsky04/ http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/astronomy/applets/Retro/frame.html It’s an ILLUSION caused by the earth “passing” other planets as we all orbit the sun. We would not see this if earth was at the center. Dwarf Planets Ceres – the largest object in the asteroid belt; 600 miles wide (photo) Eris and its moon 1500 miles wide (drawing) Pluto and its moon 1430 miles wide (drawing) The Kuiper Belt – billions of icy objects orbiting the sun, beyond Neptune’s orbit. Pluto and Eris are both part of the Kuiper Belt. The Oort Cloud – even farther out – billions of icy objects orbiting the sun. Home of comets that occasionally visit the inner Solar System What about something like Sedna – outside even the Kuiper Belt. Is Sedna a planet? Rest of Solar System! The orbit of Sedna is extremely elliptical. It takes 10,500 years to circle the sun! http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu/video-audio/681ssc2004-05v1-Orbit-of-Sedna What makes something a planet? Why did Pluto get kicked out? Possible definitions of “planet”: (from Mike Brown – discoverer of Eris, Quaoar, and Sedna - and the “killer” of Pluto - “www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/ ) 1) Purely historical: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto are planets. No scientific basis. 2) Historical plus: Mercury through Pluto are planets, as is any newly discovered object larger than Pluto. But why is Pluto’s size the cutoff? No scientific basis. Possible definitions of “planet”: 3) Gravitational rounding: Any object which is round and which directly orbits the sun is a planet. Scientifically based. Pluto would be a planet, but so would Ceres, Eris, Quaoar, Sedna, and perhaps a dozen other Kuiper belt objects. But what’s so special about roundness? Possible definitions of “planet”: 4) Population classification: If the object is a “solitary individual” it is a planet. If it’s part of a whole population of objects ranging in size, it is not. So: Ceres – just part of the asteroid belt. Pluto, Eris, Quaoar – just part of the Kuiper Belt Sedna – just part of the “inner Oort Cloud” (they think) But Mercury, Venus, Earth, etc……. No other objects anywhere near their size in their region of the solar system. They are definitely PLANETS. (This one seems pretty good, according to Mike Brown.) SO: Our Solar System has 8 planets and 3 “dwarf planets” (But why isn’t Sedna a dwarf planet then??)