* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Scala (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Go (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Functional programming wikipedia , lookup
Programming language wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Stream processing wikipedia , lookup
Object-oriented programming wikipedia , lookup
Reactive programming wikipedia , lookup
Structured programming wikipedia , lookup
Java (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
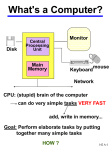
Introduction Chapter 1 1/22/15 & 1/26/15 Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, (c) Pearson Education - Prentice Hall, 2010 Announcements • Hard copy of first assignment is due. • Most of you already handed it in. • Next assignment is on the 119 website. • To work at home: – Only need to download Java & eclipse – Need to transfer program file to onyx • Could use mobaxterm *If you can't get into Engr 213 and 214, see the adminstrative assistants in MEC302J, the CS dept. Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Contents • An Overview of a Computer What Can a Computer Do? The Components of a Typical Computer • A Computing System’s Software The Programming Language Java Graphics • Writing, Compiling, and Running a Java Program Tools and Resources The Steps Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to … • Describe basic operations of a computer • State purpose of four major components of a computer • Distinguish between contents of a byte and address • Describe difference between machine language and high-level language Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Operations a Computer Does • • • • • • • Get data from outside world Save data Retrieve saved data Do mathematic operations +, -, /, * Compare values, =, <, > Manipulate data Display numbers, words, symbols, graphics Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Components of a Computer • Figure 1-1 Components of a typical computer Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 CPU • Central Processing Unit 7 7 Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 CPU • • • • Brain of the Computer Carries out instructions from programs Controls other parts of the computer Does arithmetic operations and compares values Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Other Components • Primary memory – Stores data and programs temporarily – volatile – Another name is RAM • Secondary memory – Long term storage – non-volatile – Hard disks and DVDs Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Other Components • Input – Get data from outside world – Keyboard, mouse, camera • Output – Send data to outside world – Monitor, speaker, printer Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Components of a Computer • Figure 1-2 Transfer data to, from computer memory Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Binary Data Data in the computer is stored as bits, or binary data. ON/OFF, electrical charge or no charge. Eight bits make a byte Enough to store a character, 'A', '#', '1' Data in Memory • Figure 1-3 Bytes in memory • Address and contents Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Computing System Software • Languages Machine language used in 1940s High-level languages developed, 1950s • Written program called source code • Translated to machine language • Done by compiler or interpreter programs • Other Software Operating system (a program) Application programs Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Java Programming Language • • • • • Developed by Sun Microsystems, 1995 Object oriented Platform independent Can run within Internet browser Can execute either locally (application) or remotely (applet) Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Java Programming Language • Figure 1-4 Steps of Java program to achieve platform independence Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Graphics • Both applications and applets can produce graphics • Application with graphical components called GUI (Graphical User Interface) • Classes support graphics programming Abstract Window Toolkit Swing Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Tools and Resources • Java Development Kit (JDK) • Text editor, e.g. notepad • Integrated Development (IDE) eclipse is an IDE Combines editor, compiler, Java Virtual Machine Also has other features, like a debugger. Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Steps • Figure 1-5 Steps involved in developing a Java program Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 Questions • What two major components of a computer? • What does the CPU do? • How does Java differ from other high-level languages? • What is the difference between a logic error and a syntax error? Imagine! Java: Programming Concepts in Context by Frank M. Carrano, © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall, 2010 For Next Week Take quiz one on Black Board. See questions 1, 2, 4, 5, 7 on page 13 before taking the quiz. There will be questions from Chapter 1 and over Linux and eclipse.