* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
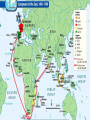
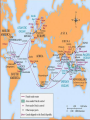
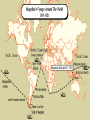
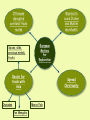
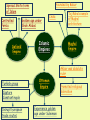
• 4/21 Focus: – Soon after European powers had established direct trading links with Asia, they sought to gain more permanent control there • Important Terms: • Imperialism • Do Now: – Which Portuguese explorer established a direct trade route with India? • Imperialism – The domination by one country of the political and/or economic life of another country – Europeans countries competed with each other to gain colonies in Asia, Africa, and the Americas • • Took control of Indian trade network from Muslims in the early 1500’s – Dominated trade in the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia • Seized the port of Malacca in Southeast Asia – Was an important Arab trading city – Gave Portuguese control of spice trade between Europe and Asia • Portugal was a powerful sea power but could not conquer large territories on land – Portuguese leaders, merchants and missionaries created resentment among many in Southeast Asia • Intolerant polices of Governor Alfonso de Albuquerque • Destruction of Hindu Temples • Massacre of Muslims – Led to the decline of Portuguese power in the Indian Ocean in the late 1500’s • First European nation to challenge Portugal for control of Asian spice trade – The Dutch East India Company • Trading company formed by group of wealthy Dutch merchants • Regulated trade between Holland and other parts of the world • • Seized Malacca from the Portuguese in 1641 • Created less resentment among Asian populations than Portuguese by being more tolerant of different beliefs – Allowed them to establish closer ties with local leaders • Dutch came to dominant the spice trade • Gained colonies in Southeast Asia in the 1500’s – Financed Magellan's circumnavigation of the globe • Magellan claimed the Philippine Islands for Spain in 1521 – Gave Spain a base to trade with China and spread Christianity to East Asia • • Decline of the Mughal Empire allowed France and England to gain influence in India • British East India Company made alliances with local rulers and created an army of Indian troops • Known as sepoys • pushed French out of their trading posts • England became the real power in India • 4/22 Focus: – Europeans had met with much resistance in their efforts to open the East trade. Expansion to the West in the Americas would be much more successful • Do Now: – What was the difference between the way the Portuguese dealt with people in Asia and the way the Dutch dealt with people in Asia? • Chinese restricted foreign trade during the Ming and Qing dynasties – Thought European goods were inferior – Limited trade to port of Macao • Matteo Ricci – Jesuit priest who was welcomed by the Ming in China – Shared European knowledge of arts and science – Ming were not interested in Christianity • Portuguese traders and missionaries came to Japan in the 16th century • Tokugawa Shogunate feared foreign influences and conversion of people to Christianity – Began persecuting Christians – Issued Edict of 1635 closing Japan to Europeans • Japanese not allowed to travel to other countries Exploration • China sends Zheng He on voyages of exploration to India, Middle East, and East Africa • Portuguese establish trading outposts throughout Asia & gain control of Asian spice trade (early 1500’s) • Dutch take control of Asian Spice trade from Portuguese • Europeans sail to China and Japan in search of more trade Isolation • China stops voyages of exploration in 1433 • Starting in the 1500’s the Chinese restrict trade with foreigners • Japan outlaws Christianity in 1612 • Japan beings closed country policy and remains isolated from Europe for 200 years Ottomans disrupted overland trade routes Spices, silks, precious metals, fruits Wanted to avoid Italian and Muslim merchants European Motives for Exploration Desire for trade with Asia Crusades Spread Christianity Marco Polo Pax Mongolia Founded by Babur Spread Shiite form of Islam Controlled Persia Golden age under Shah Abbas Safavid Empire India Islamic Empires Taj Mahal example of Mughal architecture Mughal Empire Akbar was absolute ruler Turkish group Capture Constantinople Disrupt European trade routes Ottoman Empire Experience golden age under Suleiman Promoted religious toleration Scientific Revolution • Heliocentric theory challenges geocentric theory • Copernicus • Math and observation support heliocentric theory • Galileo, Keppler, Newton • Scientific method develops • Bacon & Descartes New approach to solving problems and thinking about the world developed based on observation, experimentation, and challeinging traditional ideas • What was the reaction of the Chinese and Japanese to the presence of Europeans in Asia?