* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiography and Arteriography
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
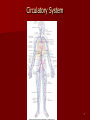
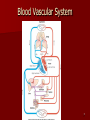
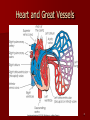
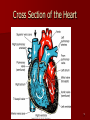
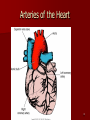
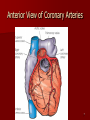
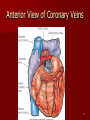
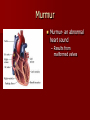
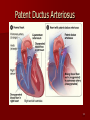
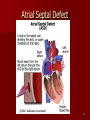
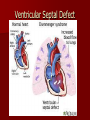
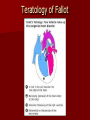
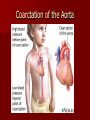
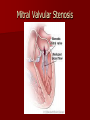
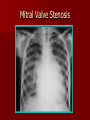
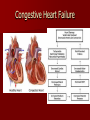
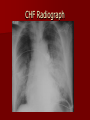
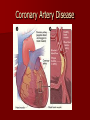
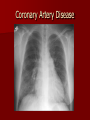
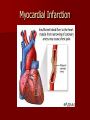
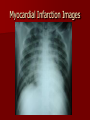
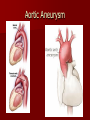
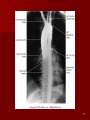
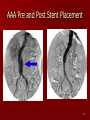
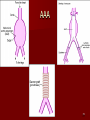
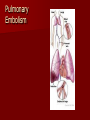
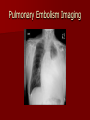
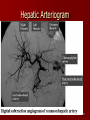
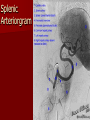
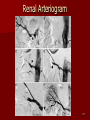
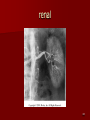
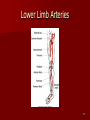
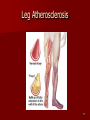
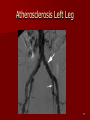
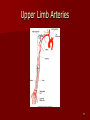
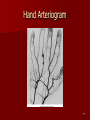
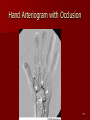
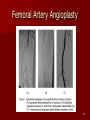
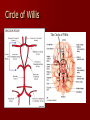
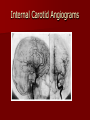
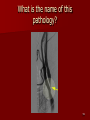
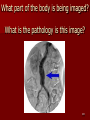
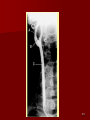
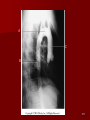
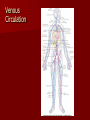
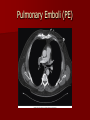
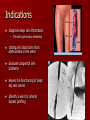
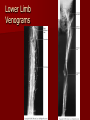
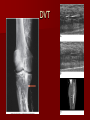
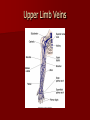
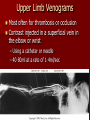
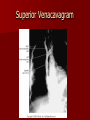
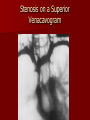
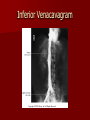
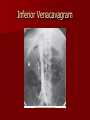
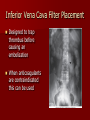
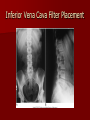
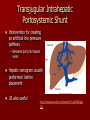
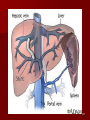
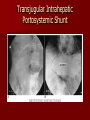
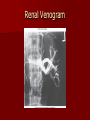
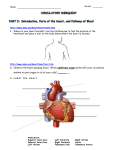
Circulatory and Cardiovascular Systems Spring 2013 Circulatory System 2 Blood Vascular System 3 Heart and Great Vessels 4 Cross Section of the Heart 5 Arteries of the Heart 6 Anterior View of Coronary Arteries 7 Anterior View of Coronary Veins 8 Pathologies Congenital Heart Diseases – – – – – Murmur Patent Ductus Arteriosus Arterial Septal Defects Ventricular Septal Defects Teratology of Fallot Valvular heart disease – Valvular Stenosis – Congestive Heart Failure Degenerative diseases – CAD – Atherosclerosis Myocardial infarction Aortic aneurysm Pulmonary Embolism 9 Murmur Murmur- an abnormal heart sound – Results from malformed valves Patent Ductus Arteriosus 11 Atrial Septal Defect 12 Ventricular Septal Defect Teratology of Fallot Coarctation of the Aorta Valvular Disease 16 Mitral Valvular Stenosis Mitral Valve Stenosis Congestive Heart Failure CHF Radiograph Coronary Artery Disease Coronary Artery Disease Myocardial Infarction Myocardial Infarction Images Aortic Aneurysm Aortic Aneurysm Imaging Aortogram 27 28 AORTOGRAM 29 Abdominal Aortoraphy 30 Abdominal Angiography 31 AAA Pre and Post Stent Placement 32 33 Abdominal Stent 34 AAA 35 Pulmonary Embolism Pulmonary Embolism Imaging Angiography Arteriography and Aortograms SPRING 2013 Angiography Is the general term that describes the radiologic examination of vascular structures within the body after the introduction of an iodinated contrast medium or gas Types of Angiographic Procedures 40 41 Angiography Team Radiologist CIT (Radiologic Technologist) – Sometimes more than one Other specialists (if needed) Nurse Anesthesiologist (if needed) 42 Indications Verify the presence of tumors – Clots – Thrombus – Embolus – Blood supply to tumors Internal bleeding – Possible anemia Occlusions Aneurysms Heart disease Stenosis – Can be caused form atherosclerosis 43 Contraindications Previous severe reaction to contrast Impaired renal function Impaired blood clotting factors Inability to undergo surgical procedure 44 Contrast Media Iodinated contrast media is used – Can produce nausea & an uncomfortable burning sensation – Allergic reactions Severe: anaphylactic shock – Shock, rapid shallow breathing, high pulse rate & ALOC Mild: Hives or slight difficulty breathing 45 What is this? 46 47 Angiographic Trays and Sterile Supplies 48 Other Supplies for Angiography 49 Needles Vascular access needles Size based on external diameter of needle Allows for appropriate Guidewires matching – So internal diameter must also be known 50 Guidewires Used as a platform over which a catheter is to be advanced Once positioned guidewire is fixed and catheter is advanced until it meets the tip of the guidwire Mostly constructed on stainless steel & coated with Teflon 51 Introducer Sheaths Short catheters used when multiple catheters will be used Placed in lieu of a catheter 52 Catheters 53 54 DSA A subtraction mask is taken before contrast injected Each of digitized image is from the mask Images acquired form – 1 image every 2-3 sec – Up to 30 images per sec 55 Three Dimensional (3-D) Intraarterial Angiography 56 What Method is this? 57 Catherization: Selinger Technique 58 Selinger Technique Catheters and Guidewires 59 Radiation Protection PT is protected by no less than 2.5 mm of Aluminum Beam restriction Avoidance of repeat exposure Cardinal rules – Time – Distance – Shielding 60 Stent Placement http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http:// www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/images/stent_rest enosis.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/h ealth/dci/Diseases/stents/stents_all.html&usg=_ _xDlbsaX9JhuYbpVojLcz19aprI=&h=513&w=450&sz=59&hl=en&start=20&tb nid=vWwqaG-RNW7MM:&tbnh=131&tbnw=115&prev=/images%3Fq %3Dabdominal%2Bstents%26gbv%3D2%26hl %3Den 61 Pulmonary Circulation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D3ZDJ gFDdk0 http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=0jznS5psypI 62 Pulmonary Arteriogram 63 Celiac Ateriogram Celian artery carries blood from stomach to duodenum, liver, spleen and pancreas Approx at level T12 64 Hepatic Arteriogram 65 Splenic Arteriorgram 66 Renal Arteriogram 67 renal 68 69 70 71 Lower Limb Arteries 72 73 Leg Atherosclerosis 74 Atherosclerosis Left Leg 75 Upper Limb Arteries 76 Upper Extremity Anatomy 77 Brachial and Axillary Arteriogram 78 Hand Arteriogram 79 Hand Arteriogram with Occlusion 80 81 Balloon Angioplasty 82 83 Balloon Angioplasty Procedure 84 Femoral Artery Angioplasty 85 Placing a Stent after Angioplasty with Balloon 86 Intravascular Stents 87 Cerebral Angiography Indications • Aneurysms • Arteriovenous Malformations • Tumors • Athersclerotic Lesions • Stenotic lesions Circle of Willis Circulation Time Cerebral circulation Carotid artery to jugular vein (3 seconds) With contrast – 4.13 seconds Certain pathologies shorten or delay time – AVM’s shorten time – Arterial vasospasm delays time Equipment Bi-plane imaging – Film – DSA Automatic Injector Carotid Angiogram Internal Carotid Angiograms Internal Carotid Angiogram Vertebral Arteries Angiogram Vertebral Artery Angiogram Let’s Review What is the name of this Procedure? What is it done for? 98 What is the name of this pathology? 99 What part of the body is being imaged? What is the pathology is this image? 100 101 What is this method callled? 102 A C B 103 Venography 2013 Venous Circulation What is Venography? Vein study using x-ray and contrast media – Fluoroscopy and still images One of the most accurate tests for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) Most commonly done in legs for DVT Thrombosis and Embolism Intravascular clot Commonly in veins more than arteries 3 factors – Where blood is slow – Change in the wall of vessels – Change in the blood itself Thrombus that becomes detached from the vessel wall Can easily flow to heart causing PE Severity depends on location of embolism Pulmonary Embolism Occurs when a clot forms or becomes lodged in the pulmonary artery Most commonly thrombus originates in the lower limbs and migrates Can lead to resp distress, heart failure or cardiogenic shock Symptoms are acute: – Sudden coughing – SOB – Chest pain Pulmonary Emboli (PE) Indications Diagnose deep vein thrombosis – Prevent pulmonary embolism Distinguish blood clots from obstructions in the veins Evaluate congenital vein problems Assess the functioning of deep leg vein valves Identify a vein for arterial bypass grafting Risk Factors and Complications Previous thrombosis Dilution of the contrast dye in the lower limb Difficulty accessing the veins due to: – Obesity – Severe swelling (edema) – Inflammation in the cells ( cellulitis ) Contraindications Bleeding disorders Allergy to iodine CHF Severe pulmonary hypertension Prior to Procedure Fast or drink only clear fluids for four hours before the test Thorough PT history obtained Informed consent If you are nervous about the test, your doctor may give you a sedative. During Procedure PT will lie on a tilting x-ray table Area of interest will be shaved and cleaned Local anesthetic Catheter will be inserted. – A small incision may be made in that area as well Explanation of Procedure: Legs The catheter is inserted into PT vein – (usually a vein in the foot) Contrast is slowly injected. A tight band may be tied around your ankle and upper thigh – or your lower body may be tilted – Fluoro and/or x-ray images taken The procedure takes about 30 - 45 minutes Post Procedure Rest and avoid strenuous activity Increase fluid intake Stop bleeding with pressure – Call DR if it won’t stop bleeding Observe for signs of infection PT will be sore for a few days Resume normal activity 24 hours after procedure Possible Post Procedure Complications Infection at the injection site Tissue damage Phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) Allergic reactions to the contrast dye Congestive heart failure Acute renal insufficiency Venous thrombosis in a healthy leg Dislodging a clot, perhaps resulting in pulmonary embolus or other complications Lower Limb Veins Lower Limb Venograms To rule out thrombosis of the deep veins of the leg – Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) Contrast media injected in superficial veins of the foot with a needle Lower Limb Venograms DVT Inferior Venacavagram Primarily to rule out thrombus or occlusion Catheter inserted into femoral vein and positioned inside the common iliac vein or inferior aspect of inferior vena cava Contrast injected at 20 ml/sec for total of 40ml Upper Limb Veins Upper Limb Venograms Most often for thrombosis or occlusion Contrast injected in a superficial vein in the elbow or wrist – Using a catheter or needle – 40-80ml at a rate of 1-4ml/sec Superior Venacavagram Primarily done to rule out thrombus or occlusion Needle or catheter is introduced into antecubital fossa – Catheter is positioned in the axillary or subclavian vein and contrast is injected – 30-50ml at 10-15ml/sec X-rays should include: – – – – Brachicephalic vein Subclavian vein Superior vena cava RT Atrium Superior Venacavagram Stenosis on a Superior Venacavogram Inferior Venacavagram Inferior Venacavagram Inferior Vena Cava Filters Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement Designed to trap thrombus before causing an embolization When anticoagulants are contraindicated this can be used Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement Hepatic Venogram Performed to rule out stenosis or thrombus of the hepatic veins Obtain pressure measurements of the veins inside the liver Usually catheter enters jugular vein or upper limb veins Hepatic Venogram Portal Venogram Portal System http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=4aGNqmWOuEo&feature=relat ed Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Intervention for creating an artificial low-pressure pathway – Between portal & hepatic veins Hepatic venogram usually preformed before placement US also useful http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pGA6KUgq 7AI 139 Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Renal Venogram Rule out thrombosis of renal vein Renal vein catheterized to take blood – Measure the production of renin – Catheter insertion site: femoral vein Contrast injected 8ml/sec for 16ml total – 2 images per second for 4 seconds Renal Venogram