* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Visibility Algorithms for Computer Graphics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
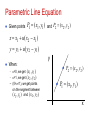
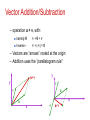
UBI 516 Advanced Computer Graphics Aydın Öztürk [email protected] http://www.ube.ege.edu.tr/~ozturk Mathematical Foundations Mathematical Foundations Hearn and Baker (A1 – A4) appendix gives good review I’ll give a brief, informal review of some of the mathematical tools we’ll employ – Geometry (2D, 3D) – Trigonometry – Vector spaces Points, vectors, and coordinates – Dot and cross products – Linear transforms and matrices – Complex numbers 2D Geometry Know your high school geometry: – Total angle around a circle is 360° or 2π radians – When two lines cross: Opposite angles are equivalent Angles along line sum to 180° – Similar triangles: All corresponding angles are equivalent Trigonometry Sine: “opposite over hypotenuse” Cosine: “adjacent over hypotenuse” Tangent: “opposite over adjacent” Unit circle definitions: – – – – sin () = y cos () = x tan () = y/x Etc… (x, y) Slope-intercept Line Equation Slope: m ( y - y1 ) / (x - x1 ) (y2 - y1 ) / (x2 - x1 ) Solve for y: y [( y2 - y1 ) / ( x2 - x1 )]x [-( y2 -y1 ) / ( x2 - x1 )]x1 y1 or: y = mx + b y P2 ( x2 , y2 ) P (x, y) P1 ( x1 , y1 ) x Parametric Line Equation Given points P1 ( x1 , y1 ) and P2 ( x2 , y2 ) x x1 u( x2 x1 ) y y1 u( y2 y1 ) y When: – u=0, we get ( x1 , y1 ) – u=1, we get ( x2 , y 2 ) – (0<u<1), we get points on the segment between ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) P2 ( x2 , y2 ) P1 ( x1 , y1 ) x Other helpful formulas ( x2 x1 ) 2 ( y2 y1 ) 2 Length = Midpoint P2 between P1 and P3 : x x3 y1 y3 P2 1 , 2 2 Two lines perpendicular if: M 1 1 / M 2 Cosine of the angle between them is 0. Coordinate Systems 2D systems Cartesian system Polar coordinates 3D systems Cartesian system 1) Right-handed 2) Left handed Cylindiric system Spherical system Coordinate Systems(cont.) Grasp z-axis with hand Roll fingers from positive x-axis towards positive y-axis Thumb points in direction of z-axis Y Y Z X X Left-handed coordinate system Z Right-handed coordinate system Points Points support these operations: – Point-point subtraction: Result is a vector pointing from P to Q – Vector-point addition: Q-P=v P+v=Q Q Result is a new point – Note that the addition of two points is not defined v P Vectors We commonly use vectors to represent: – Points in space (i.e., location) – Displacements from point to point – Direction (i.e., orientation) Vector Spaces Two types of elements: – Scalars (real numbers): a, b, g, d, … – Vectors (n-tuples): u, v, w, … Operations: – – – – – Addition Subtraction Dot Product Cross Product Norm Vector Addition/Subtraction – operation u + v, with: Identity 0 v+0=v Inverse v + (-v) = 0 – Vectors are “arrows” rooted at the origin – Addition uses the “parallelogram rule”: y u+v y v v u x u x -v u-v Scalar Multiplication – Scalar multiplication: Distributive rule: a(u + v) = a(u) + a(v) (a + b)u = au + bu – Scalar multiplication “streches” a vector, changing its length (magnitude) but not its direction Dot Product The dot product or, more generally, inner product of two vectors is a scalar: v1 • v2 = x1x2 + y1y2 + z1z2 (in 3D) Useful for many purposes – Computing the length (Euclidean Norm) of a vector: length(v) = ||v|| = sqrt(v • v) – Normalizing a vector, making it unit-length: v = v / ||v|| – Computing the angle between two vectors: u • v = ||u|| ||v|| cos(θ) – Checking two vectors for orthogonality u•v=0 u Dot Product Projecting one vector onto another – If v is a unit vector and we have another vector, w – We can project w perpendicularly onto v w v u – And the result, u, has length w • v u w cos(θ ) vw w ( v w v w Dot Product Is commutative – u•v=v•u Is distributive with respect to addition – u • (v + w) = u • v + u • w Cross Product The cross product or vector product of two vectors is a vector: v1 v2 ( y1z2 z1 y2 , z1x2 x1z2 , x1 y2 y1x2 ) The cross product of two vectors is orthogonal to both Right-hand rule dictates direction of cross product Cross Product Right Hand Rule See: http://www.phy.syr.edu/courses/video/RightHandRule/index2.html Orient your right hand such that your palm is at the beginning of A and your fingers point in the direction of A Twist your hand about the A-axis such that B extends perpendicularly from your palm As you curl your fingers to make a fist, your thumb will point in the direction of the cross product Cross Product Right Hand Rule See: http://www.phy.syr.edu/courses/video/RightHandRule/index2.html Orient your right hand such that your palm is at the beginning of A and your fingers point in the direction of A Twist your hand about the A-axis such that B extends perpendicularly from your palm As you curl your fingers to make a fist, your thumb will point in the direction of the cross product Cross Product Right Hand Rule See: http://www.phy.syr.edu/courses/video/RightHandRule/index2.html Orient your right hand such that your palm is at the beginning of A and your fingers point in the direction of A Twist your hand about the A-axis such that B extends perpendicularly from your palm As you curl your fingers to make a fist, your thumb will point in the direction of the cross product Cross Product Right Hand Rule See: http://www.phy.syr.edu/courses/video/RightHandRule/index2.html Orient your right hand such that your palm is at the beginning of A and your fingers point in the direction of A Twist your hand about the A-axis such that B extends perpendicularly from your palm As you curl your fingers to make a fist, your thumb will point in the direction of the cross product Cross Product Right Hand Rule See: http://www.phy.syr.edu/courses/video/RightHandRule/index2.html Orient your right hand such that your palm is at the beginning of A and your fingers point in the direction of A Twist your hand about the A-axis such that B extends perpendicularly from your palm As you curl your fingers to make a fist, your thumb will point in the direction of the cross product Triangle Arithmetic b Consider a triangle, (a, b, c) – a,b,c = (x,y,z) tuples a Surface area = sa = ½ * ||(b –a) X (c-a)|| Unit normal = (1/2sa) * (b-a) X (c-a) c Vector Spaces A linear combination of vectors results in a new vector: v = a1v1 + a2v2 + … + anvn If the only set of scalars such that a1v1 + a2v2 + … + anvn = 0 is a1 = a2 = … = a3 = 0 then we say the vectors are linearly independent The dimension of a space is the greatest number of linearly independent vectors possible in a vector set For a vector space of dimension n, any set of n linearly independent vectors form a basis Vector Spaces: Basis Vectors Given a basis for a vector space: – Each vector in the space is a unique linear combination of the basis vectors – The coordinates of a vector are the scalars from this linear combination – If basis vectors are orthogonal and unit length: Vectors comprise orthonormal basis – Best-known example: Cartesian coordinates – Note that a given vector v will have different coordinates for different bases Matrices Matrix addition Matrix multiplication Matrix tranpose Determinant of a matrix Matrix inverse Complex numbers A complex number z is an ordered pair of real numbers z = (x,y), x = Re(z), y = Im(z) Addition, substraction and scalar multiplication of complex numbers are carried out using the same rules as for two-dimensional vectors. Multiplication is defined as (x1 , y1 )(x2, y2) = (x1 x2 – y1 y2 , x1y2+ x2 y1) Complex numbers(cont.) Real numbers can be represented as x = (x, 0) It follows that (x1 , 0 )(x2 , 0) = (x1 x2 ,0) i = (0, 1) is called the imaginary unit. We note that i2 = (0, 1) (0, 1) = (-1, 0). Complex numbers(cont.) Using the rule for complex addition, we can write any complex number as the sum z = (x,0) + (0,y) = x + iy Which is the usual form used in practical applications. Complex numbers(cont.) The complex conjugate is defined as z̃ = x -iy Modulus or absolute value of a complex number is |z| = z z̃ = √ (x2 +y2) Division of of complex numbers: z1 z1 ~ z2 ~ z2 z1 z 2 Complex numbers(cont.) Polar coordinate representation z rCos riSin r (Cos iSin ) re i Complex numbers(cont.) Complex multiplication z1 z 2 r1r2 e i (1 2 ) r1 i (1 2 ) z1 / z 2 e r2 Conclusion Read Chapters 1 – 3 of OpenGL Programming Guide