* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensation and Perception
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
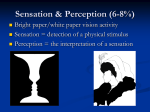
Sensation and Perception Unit 6 Lesson 1 Objectives Define sensation and perception and distinguish between them. Define thresholds and variables which affect measurements. Explain why psychophysics is the oldest field in psychology. Warm Up What are the 5 basic senses? Vision, Hearing, Taste, Smell, Touch Kinesthetic, Vestibular Sensation vs Perception Sensation The way sense receptors take in stimuli (chemical & electrical energy) and transmit it to our brain. Sensation vs Perception Transduction Sensory neurons convert physical energy into electrochemical signals that are carried to the brain. Sensation vs Perception Perception The way our brain interprets & organizes sensations to understand the world around us. Psychophysics Study of relationship between sensations and our perceptions of them. Thresholds Absolute Threshold Point at which something becomes noticeable to our senses. (Min amt to detect 50% time) Thresholds Just Noticeable Difference (JND) Weber’s Law Difference Threshold Amount of change needed for us to recognize a change has occurred. Larger or stronger a stimulus, the larger the change required for an observer to notice Signal Detection Theory Used to predict when signal is detected… Signal strength Experience Motivation Expectation Sensory Adaptation Decrease in sensitivity to unchanging stimulus. Varies for each sense