* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CD ch1-2 - Fairfield Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
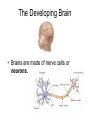
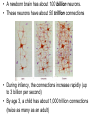
Studying Children Chapter 1-2 The Developing Brain • Brains are made of nerve cells or neurons. • A newborn brain has about 100 billion neurons. • These neurons have about 50 trillion connections • During infancy, the connections increase rapidly (up to 3 billion per second) • By age 3, a child has about 1,000 trillion connections (twice as many as an adult) • The first 3 years are optimal for learning. • As a child matures, many unused connections are lost. Brains develop in response to stimulation: activities that arouse a baby’s senses (sight, sound, touch, taste, smell) Stimulation can improve: • Curiosity • Attention span • Memory • Nervous system development Repetition helps to strengthen brain connections. Children who do not receive enough stimulation may develop learning problems. Theories About Development • Theorists provide insights about how children learn and develop – Some use experiments – Some cannot Not everyone agrees about how we should apply these findings. Sigmund Freud (1856 - 1939) • One of the first to study child development and recognize how much childhood affected adult life. • Believed that personality develops through a series of stages • Much of his work has since been found to be flawed. Jean Piaget (1896 - 1980) • First to study children scientifically • Focused on learning •Believed that children go through four stages of learning •Much of his work still applies today Erik Erikson (1902 - 1994) • Believed that personality develops through 8 stages • Thought that each stage included a crisis that must be resolved in order to move on •Believed that caregivers must know how to support children’s needs at each stage B. F. Skinner (1904 - 1990) • Believed that learning occurred because of positive and negative reinforcement (reward and punishment) What researchers have found • Although they did not always agree, they have given us much insight about how to nurture and educate children. • They have found that child development follows five general rules. 5 Characteristics of development 1. Development is similar for everyone Children go through the same stages in the same order (but not necessarily as the same speed) 2. Development builds upon earlier learning It follows a sequence or an order of steps 3. Development proceeds at an individual rate 4. The different areas of development are interrelated • • • • Physical Cognitive Social Emotional physical cognitive social emotional 5. Development is a lifelong process It never stops (although it slows down) Influences of Development • Heredity: the biological transfer of traits from parents to offspring • Environment: The people, places, and things that surround you Nature vs. Nurture (Heredity) HEREDITY (Environment) ENVIRONMENT You And how you respond to your environment Lifelong Growth and Development • Human Life Cycle: The stages that humans go through during life • Developmental Tasks: Challenges that must be met or skills to be acquired during each stage of life Development Beyond Childhood • • • • • • Adolescence Young Adulthood The Thirties Middle Age Late Adulthood Very Late Adulthood • Self-esteem: – Self-worth – The value that people place on themselves