* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensory Physiology
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Macular degeneration wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
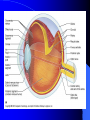
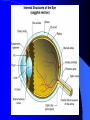
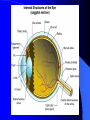
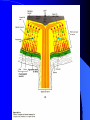
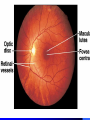
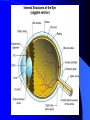
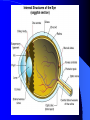
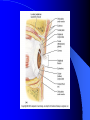
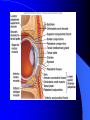
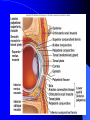
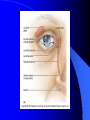
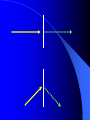
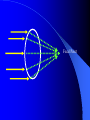
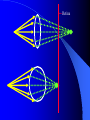
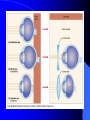
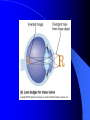
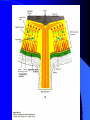
Vision Anatomy of the Eye Fibrous tunic – Sclera – Cornea Anatomy of the Eye Vascular tunic = Uvea – Choroid – Ciliary body – Iris – Pupil Anatomy of the Eye Nervous tunic = Retina & optic nerve – Outer pigmented layer – Nervous layer Photoreceptors Rods Cones Macula Fovea centralis Optic Nerve Optic disc Blind Spot Anatomy of the Eye – Miscellaneous structures Lens Anterior cavity – Aqueous humor Posterior cavity – Vitreous humor Anatomy – Accessory structures Eyelids = Palpebrae – – – – – – – Tarsal plate Meibomian glands Palpebral fissure Lateral commissure Medial commissure Caruncle Sebaceous ciliary glands Anatomy – Accessory structures Conjunctiva – Palpebral – Bulbar Anatomy – Accessory structures Lacrimal apparatus – Function – Lacrimal gland – Lacrimal puncta – Lacrimal canal – Nasolacrimal duct Vision Light Refraction Emmetropia = Normal vision, light rays focus on a single point called the Focal Point Focal Point Retina Vision Accommodation – For close vision – Pupils constrict – Eyeballs converge – Near point of vision Vision Eye movement controls Voluntary fixation (premotor area) Involuntary fixation (visual area) Vision Binocular vision Diplopia Strabismus Photoreceptors of Vision Rods – – – – – – – Rhodopsin is photopigment Numerous – about 120 million Sensitive to light Relative lack of color discrimination Peripheral retina in location Good for night vision, but poor detail Convergence Photoreceptors of Vision Cones Few – about 6 million Photopigments sensitive to differing wavelengths of light – 400 nm blue – 500 nm green – 600 nm red Photoreceptors of Vision Cones High level of illumination Not very sensitive to light See in color Precise detail Little convergence Mostly in center of retina, esp. fovea Neural Components of Vision Bipolar neurons Ganglion neurons Lateral inhibition – Horizontal cells – Amacrine cells Visual Acuity Snellen Eye Chart 20/20 Light/Dark Adaptation Photopigment concentration Pupillary light reflex – PNS constricts pupil – Direct – ipsilateral – Indirect = Consensual - contralateral Cones inhibit rods in bright light Visual Pathway Optic Nerve Optic Chiasma Optic tracts Thalamus – lateral geniculate body Occipital lobe of cerebral cortex