* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Visual Process & Implications of Visual Disabilities
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
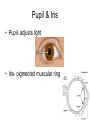
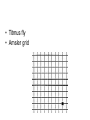
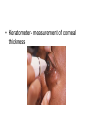
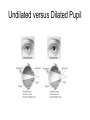
CLINICAL PERSPECTIVES STRUCTURES AROUND THE GLOBE Orbit- provides a safe place for the eyeball eyelids- closes light off of eye, protects, distributes tears tears- lubricates & protects lacrimal system- distributes tears conjunctiva- covers sclera and inner surface of eyelids orbital septum- bone covering top of orbit eyebrow- covers orbital septum, protects eye from sweat • Photos courtesy of the National Eye Institute • [email protected] Extraocular Muscles • Superior & Inferior Recti • Medial & Lateral Recti • Superior & Inferior Obliques Eyelids & eyelashes • meibomian glands- oil glands Conjunctiva • sclera- white fibrous covering of eyeball • limbus- point where sclera and cornea meet Lacrimal Apparatus • puncta- inner margin of the upper & lower lids • caniliculi- passages to sacs & ducts • lacrimal sac- contains some tears • nasolacrimal duct- drains tears into nose Eye Divided Into Two Parts • Anterior Segment – aqueous humor – pupil – Iris – lens • Posterior Segment – vitreous humor – retina – optic nerve Cornea • clear, avascular window of the eye, most refractive power Anterior Segment • • • • • aqueous humor trabecular meshwork canal of Schlemm ciliary process lens Pupil & Iris • Pupil- adjusts light • Iris- pigmented muscular ring Structures In the Globe • 3 Main Structures: – protective outer layer – vascular inner layer – sensory retina Vascular Inner Layer • Uveal tract • Ciliary body • Choroid Sensory Layer • Central Retina – Macula & fovea contain mostly cones – Optic disk • Peripheral Retina – Contains mostly rods Transmission of Visible Information to the Brain • Light energy from environment to chemical energy in retina to electrical energy in optic nerve & synapses to chemical energy in nerve cells Relationship of Sight to Vision • Images from eye structures must be interpreted in the visual cortex for sight to occur • The eyes and associated structures must be normal in structure & function. • The neurological pathways from the retina & optic nerve to the visual cortex must be in tact. • The brain must be capable of interpreting the information received. MEDICAL EYE REPORT • • • • • • • • Name Sex Age Family Medical Hx General Medical Hx Surgical Hx Medications Ophthalmic complaint Eye Care Professionals • Optometric technicians, ophthalmic technicians • Vision Rehabilitation practitioner • Teacher of Visually Impaired • D.O.- doctor of optometry, doctor of ophthalmology, low vision specialist • M.D.- ophthalmologist • Specialist- did fellowship in specialty, FACS • optician VISUAL ACUITIES • Autorefractor • Lensometer • Snellen chart (distance) • Checking distance each eye using an occluder • Jaeger near vision chart • Ishihara- color vision charts • Titmus fly • Amsler grid External Examination • LLL- Lids, lens, lacrimal system CAUSES & FUNCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS OF VISUAL IMPAIRMENT • PERL- Pupils equal & reactive to light • • MM- Muscular motility • Eye Muscle Balance Cornea & Anterior Segment • Ophthane- numbs eye • Midriatic- dilates pupil • Cycloplegic- relaxes lens • Tonometer- measures pressure – FP- finger pressure – Air puff – Contact • Keratometer- measurement of corneal thickness • Goniometer- measures angle of anterior segment (risk factors for glaucoma) • Slit lamp • Direct ophthalmoscope Undilated versus Dilated Pupil • Indirect ophthalmoscope Normal Fundus • Phoropter Functional & Visual Efficiency Testing • Behavioral • Electrophysiological • Subjective Behavioral • OKN (optokinetic nystagmus)- cortical • PLT (preferential looking test)- Teller acuities • Chromatic luminance- contrast sensitivity • Tracking a toy or light Electrophysiological • Fundus photos & OCT • VER- visual evoked response- visual pathways, cortical function • ERG- electroretinogram (cone & rod function) • EOG- electrooculogram (measures charge & potentials of eyes) Subjective • Acuity – – – – • • • • Lea charts Snellen Tumbling E Amsler grid CSF- contrast sensitivity function Flicker fusion macular & foveal function Color- Ishihara & Farnsworth Visual fields – Confrontation – Ganzfeld globe – computerized Visual Efficiency Testing • ISAVE • Program to Improve Visual Efficency (Barraga) • Conditions That Result In Low Visual Acuity Ocular Muscle Disorders- • eyes that are not in proper alignment Strabismus & Amblyopia amblyopia- a reduction in visual acuity due to non-use of the eye • tropia- marked deviation of an eye • esotropia- turning in of one or both eyes • exotropia- turning out of one or both eyes • hypertropia- turning up of one or both eyes • hypotropia- turning down of one or both eyes • phoria- tendency of eye to deviate, particularly when fatigued or fusion broken Nystagmus • Involuntary, rhythmical repeated movement of one or both eyes in a horizontal, vertical or pendular motion – null point- point of least nystagmus & best vision – pendular nystagmus- up-and-down movements of equal speed, amplitude & duration – jerk nystagmus- slower movement in one direction