* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Associate the industry with the correct city or area
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
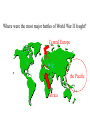
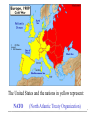
What were some causes of World War II? • Worldwide Depression • Massive unemployment •High debt owed by Germany: (reparations) • High inflation These conditions led to the rise of powerful leaders, called ____________________. dictators FASCISM a political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator and individual freedoms are denied World War II AXIS POWERS vs _______________ ALLIED POWERS _______________ • Italy (Benito Mussolini) • Japan (Tojo Hideki) • Germany (Adolf Hitler) •United States (FDR) •Great Britain (Winston Churchill) •Canada •France •U.S.S.R. (Joseph Stalin) Who were the leaders of these countries? Which ones were fascists? Give an example from World War II of: •AGGRESSION: Axis Powers invaded other Eastern European countries Japan invaded Manchuria •APPEASEMENT: The Munich Conference MAJOR EVENTS OF WORLD WAR II World War II began when: What happened to France? What happened to Britain? Germany invaded Poland. _____ USSR also invaded Poland. Germany invaded France, and captured Paris. Germany bombed London Battle of Britain during the ______________. The U.S. gave Britain war supplies & old naval ships in return for military bases in Bermuda & the Caribbean. Rising tension developed between the U.S. and Japan because of Japanese _______________ AGGRESSION in East Asia. What was the US policy at this time? First, we tried to remain in isolation. Then, we gave economic aid to the Allies. Finally, we were directly involved in the war, when… On December 7th, 1941, Japan attacked Pearl Harbor. “_________________________________,” a date which will live in infamy… said Franklin D. Roosevelt. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, United States declared war on __________. Japan the ______________ Then _________ Germany declared war on the United States. The result of the attack on Pearl Harbor was America entered World War II. 1. German air attack on London and other English cities: Battle of Britain 2. The turning point in the war in the Pacific, Japan lost 4 aircraft carriers: Battle of Midway 3. Allied invasion on the coast of Normandy, France which began the liberation of France from Nazi Germany: D-Day Turning Points in the War: 1. The Soviet Union defeated Germany at: Stalingrad. This was the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe. 2. Allied troops landed in Normandy, France on: D-Day. 3. The turning point of the war in the Pacific was the victory of the U.S. over Japan in the Battle of Midway. Where were the most major battles of World War II fought? Central Europe the Pacific Africa The need for workers temporarily broke down some racial barriers in hiring, but _______________ discrimination against African Americans continued: African American soldiers served in __________________ units. segregated How did the lives of some Japanese Americans change during World War II? • Many Japanese Americans (especially those living along the west coast) internment camps were placed in _____________________. • Many were treated with distrust & prejudice _________________________. • Some Japanese American men served gallantly in the armed forces ________________________________. How did the role of women change during World War II? • Women took jobs in ________________ defense plants during the war. •The model of the working woman was: Rosie the Riveter. How did Americans at home support the war? • Americans at home conserved & rationed resources. What finally brought an end to the Depression? America’s involvement in World War II. Factories & workers were needed to produce goods to win the war. Near the end of World War II, the U.S. developed a secret, new weapon: the atomic bomb The United States dropped atomic bombs on: Hiroshima Nagasaki _________________ and _______________. JAPAN Hitler and his Nazi Party believed: the Aryan race was supreme. The Holocaust • Anti-Semitism • ______ Aryan supremacy • A systematic attempt to ___________ exterminate all Jews in Europe by the Hitler’s Nazi Party • Tactics: - _________ boycott of Jewish stores - threats segregation - separation, or ___________ into ghettos - imprisonment, slave labor & death in ____________________ concentration camps • Liberation of the concentration camps by ____________. Allied Forces Following World War II, Americans prospered. WHY? America prospered because there was a rapid growth of the economy: Rationing was over! Businesses changed from producing war materials to consumer goods. Americans purchased goods on credit. The workforce shifted back to men, and most women returned to their families. Labor unions merged and became more powerful (AFL – CIO). Workers gained new benefits and higher wages. Technology boomed. A new generation of women entered the labor force. Rationing was over! Businesses changed from producing war materials to making consumer goods. Americans purchased goods on credit. The workforce shifted back to ______, men to their families and most women returned _______________. ____________ Labor unions merged and became more powerful. The union’s new name: Workers gained new _______ benefits and higher _________. wages Technology boomed! The Space Race • First artificial satellite: • Sputnik (USSR) • First man in space: • Yuri Gagarin(USSR) • First American in space: • John Glenn • First man to walk on the moon: • Neil Armstrong (USA) Industries benefiting from the new technologies: • Airline industry - JETS • Automobile industry & interstate highway system • Entertainment and news media • Exploration of SPACE • Satellite system – • Telecommunications • Computer industry • Internet The Space Program led to other industries, such as: pagers • cell phones • satellite dishes for television • a strong economy due to: healthy job market increased production of goods increased demand for American products greater investment in education interstate highway system “The Baby Boom” changing role of women (still expected to be at-home, but more & more were working) African American’s hopes for equal opportunities changes in the make-up of immigrants after 1965 The G.I. Bill for World War II veterans • educational benefits • housing opportunities • employment benefits United Nations The ______________________ was formed near the end of World War II to create an organization for the nations of the world to try to prevent future global wars. Proposed by George C. Marshall, ___________________________ the Marshall Plan provided Europe with financial aid to ______ rebuildEuropean economies and prevent the spread of___________. communism THE COLD WAR A state of tension between the US and the USSR without actual fighting. The SUPERpowers THE SOVIET UNION • totalitarian • communist • dictatorship THE UNITED STATES • democratic • capitalist • elected president The type of government under Joseph Stalin in the Soviet Union: COMMUNISM The United States and the nations in yellow represent: NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) _____________________________________________. The nations in red represent the Warsaw Pact (or: Soviet Union & its allies ). __________________________ West Germany: East Germany: became _____________ democratic remained ____________ communist & resumed self-government. under domination of the U.S.S.R. ____________________ Japan: • was occupied by American forces • soon adopted a democratic form of government • resumed self-government • became an ally of the United States The BERLIN WALL divided: East and West Berlin. What was America’s policy toward Communism during the Cold War? CONTAINMENT KOREAN WAR • South Korea & the United Nations resisted North Korean aggression. stalemate • The conflict ended in a_______________. The Cuban Missile Crisis •The Soviet Union placed missiles in Cuba. •President Kennedy ordered a blockade of Cuba. •The Soviets removed the missiles. America nearly went to war with the Soviet Union! THE VIETNAM WAR •The U.S. intervened to stop the spread of __________. communism •Americans were divided over this military involvement. •The conflict ended in a cease-fire and American troops withdrew. The idea that communism may spread throughout Southeast Asian countries like South Vietnam was called DOMINO THEORY the__________________________. Why were the Korean and Vietnam Wars fought? TO CONTAIN COMMUNISM What did President Reagan tell Soviet Premier Gorbachev to do? “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” The Collapse of Communism • began with the destruction of the Berlin Wall. • breakup of the USSR into independent countries. Why did communism fail in the Soviet Union? Because western influence (television) led to dissatisfaction with the Communist life style. What happened to the Soviet Union? The country was broken up into many independent countries. Jim Crow The __________________ laws: • made discrimination against African Americans legal • characterized by unequal opportunity in housing, work, education & government What were some effects of segregation on American society? - separate schools -separate public facilities (restrooms, drinking fountains, restaurants) - social isolation of the races Plessy v. Ferguson 1896 Supreme Court Case that stated “separate but equal” facilities was ok. What Supreme Court case ruling states that “separate but equal” facilities are not constitutional? • Brown v. Topeka Board of Education This Supreme Court case ordered the _______________ desegregation of schools. Who was denied a seat in front of the bus because she was not white? Rosa Parks What did Rosa Parks do? She refused to give up her seat & move to the back of the bus, The Montgomery Bus Boycott and that’s how the _________________________ began, when African Americans refused to ride the buses in Montgomery, Alabama. Who said, “I have a dream”? MARTIN LUTHER KING, Jr. What was his speech about? Racial equality What methods did Rev. King use to oppose segregation? Passive Resistance What were other actions taken in the struggle for equality? - organized protests - Freedom Riders - sit-ins and marches What organization helped African Americans during the Civil Rights Movement? NAACP = National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Civil Rights legislation Name two: • Civil Rights Act of 1964 • Voting Rights Act of 1965 How were women disadvantaged in the workplace? - discrimination in hiring -lower wages for women than men doing the same job What organization worked to improve women’s rights? N.O.W. = National Organization for Women The EQUAL RIGHTS ADMENDMENT failed to become a part of the Constitution, was introduced in Congress for 49 consecutive years, but it provided a focus on equal opportunity in employment forand women and finally passed both houses in 1972…. created a wider BUT rangeitofwas options and by advancement for women in business and public service. ratified only 35 states – 3 short of passing! Remember Remember AALLIICCEE PPAAUULL?! New laws forced colleges to give women equal athletic opportunities Since 1960, many Asian and Latin Americans have immigrated to the US. WHY? • to escape from poverty • to escape from political persecution • to seek greater economic & educational opportunities How did new technologies effect American life? • increased domestic and international travel for business & pleasure. • greater access to news & other information. • cheaper & more convenient means of communication. • greater access to heating & air conditioning. • decreased regional variations – why are Americans becoming more alike? Movies Television Radio Internet Computer games What are new challenges Americans face today? • Role of the US military to intervene in trouble spots around the world • Environmental issues • Global issues, such as trade, jobs, disease. GOOD LUCK!!!