* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformer Impedance
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
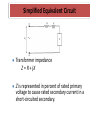
Transformer Impedance In Simple Terms • Transformer impedance is the % of rated voltage required to push 100% of the rated secondary current when the secondary winding is short circuited. Simplified Equivalent Circuit Transformer impedance Z = R + jX Z is represented in percent of rated primary voltage to cause rated secondary current in a short-circuited secondary. Transformer Impedance •Transformer Impedance Is A Major Parameter To Enable Parallel Operation Of Transformers •For Proper Paralleling The Following Are Required: – Same Percentage Impedance For All Units (With Some Tolerance) – Same Phase Relationship Between Windings – Same Voltage Ratios – Similar Power Ratings Maximum available fault current • Calculate the secondary (LS) current at the given MVA • Calculate what the impedance related voltage is based on the % impedance. • Calculate how many times the calculated voltage will go into the rated primary voltage. • Multiply this number by the full load current at the MVA Now The Easy Method • Fault Amps = Full Load Amps ÷ Impedance • FA = 656 ÷ 0.0791 • FA = 8293