* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download group4(Philosophy_of_AI) - Department of Computer Science
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Turing test wikipedia , lookup
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Hard problem of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Chinese room wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
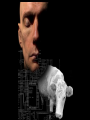
Food for thought.. Front Cover: Which of the two beings depicted on the front cover should be granted more rights than the other? The picture of the man is actually a computer generated 3D model from the NVIDIA Corporation, while the cow is indeed a photo of a real cow. This is just to show how we can be fooled in what gives us the impression of possessing intelligence. (source: Picture and Comments[1]) Philosophy of AI NIKHIL HOODA PRATEEK KHATRI K.P. ASHWIN HEMENDRA SRIVASTAVA Why Philosophy? Can a machine act intelligently? Can it solve any problem that a person would solve by thinking? Can a machine have a mind, mental states and consciousness in the same sense humans do? Can it feel? Are human intelligence and machine intelligence the same? Is the human brain essentially a computer? These three questions reflect the divergent interests of AI researchers, philosophers and cognitive scientists respectively Roots of AI in Philosophy AI occurred in philosophy as a new form of the behaviourist theory. Behaviourism is the theory that tries to explain human behaviour in terms of fixed rules that are derived from observing human behaviour. To account for the changes in the brain behaviourists proposed the presence of a black box. (black box theory). Black Box theory eventually became AI with the progress in processing speeds of computers. What is intelligence : Turing Test Alan Turing, 50 years back, reduced the problem of defining intelligence to a simple experiment. You ask the computer any question. If it is able to reply to it in the same manner a normal human would, it is intelligent. Turing test : Online Chat Room Many participants in a chat room. One of the participants is a real person and one participant is a computer program. The program passes the test (is considered intelligent) if no one can tell which of the two participants is human. Turing Test: Criticism Russell and Norvig[2] : “aeronautical engineering texts do not define the goal of their field as ‘making machines that fly so exactly like pigeons that they can fool other pigeons.’ ” •Turing test does not directly test if the computer behaves intelligently •It only tests whether or not the computer behaves like a human being. •In general the two concepts are different. Courtsey: Wikipedia Machines can be intelligent Humans nervous system can be thought of as being modeled by physical and chemical processes. If the human brain follows the laws of physics, why cannot it be simulated by a machine? Human Intelligence : Symbol Processing Newell and Simon : A physical symbol system has the necessary and sufficient means of general intelligent action. Symbol Processing : Criticism Gödel’s Theorem : For any sufficiently powerful system its always possible to construct sentences not provable by the system . Seen by John Lucas[3] as proof that machines can never achieve human intelligence. Symbol Processing : Criticism(Contd.) Penrose goes on to expand Lucas’ concept. Humans can see the truth of these Gödel’s statements . Hence the human brain goes beyond mathematical axioms and is not based on a set of algorithms. Symbol Processing : Criticism(Contd.) Quantum Mechanics is the difference!!! The philosopher David Chalmers half- jokingly says: “consciousness is mysterious and quantum mechanics is mysterious, so maybe the two mysteries have a common source." Criticism of Criticism In the book Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid, Douglas Hofstadter explains that the "Gödelstatements" always refer to the system itself ,similar to statements that refer to themselves, such as "this statement is false" or "I am lying“(also known as the Epimenides paradox ). But, the Epimenides paradox applies to anything that makes statements, whether they are machines or humans, even Lucas himself. Consider: Lucas can't assert the truth of this statement. Criticism of Criticism Russell and Norvig state that Gödel's argument only applies to what can theoretically be proved, given an infinite amount of memory and time. But real machines (including humans) have finite resources and cannot prove many theorems. It is not necessary to prove everything in order to be intelligent. More Criticism Hubert Dreyfus argues that more than conscious symbolic manipulation , human intelligence and expertise depend primarily on unconscious instincts and argued that these unconscious skills would never be captured in formal rules. Criticism of Criticism Again Turing : Just because we don't know the rules that govern a complex behavior, this does not mean that no such rules exist. Russell and Norvig : In recent years progress has been made towards discovering the "rules" that govern unconscious reasoning. AI and Consciousness Morpheus : We have only bits and pieces of information, but what we know for certain is that some point in the early twenty-first century all of mankind was united in celebration. We marveled at our own magnificence as we gave birth to AI Neo : AI - you mean Artificial Intelligence? Morpheus : A singular consciousness that spawned an entire race of machines. The Matrix Some more Food for thought Can we achieve that Consciousness which Morpheus is referring to? For this we first need to answer why do we need conscious machines? According to Ricardo Sanz, there are three motivations to pursue artificial consciousness (Sanz, 2005): 1) Implementing and designing machines resembling human beings (cognitive robotics) 2) Understanding the nature of consciousness (cognitive science) 3) Implementing and designing more efficient control systems. Machines resembling human beings What is the need of resemblance to human beings? Answer:- Our belief of being the most intelligent creatures on Earth. Choice: Intelligent systems or conscious systems Does consciousness bring with it intelligence? Yes , it helps to achieve complex control in autonomous machines. Intuition, self-awareness, resilience all these are the result of our conscious or sub-conscious mind and helps us make better decisions. Understanding the nature of consciousness By building conscious machines we are trying to understand the cognitive science behind it. This can be seen as the sub-goal of our long term goal of understanding ourselves. It is impossible to build a conscious machine without understanding what is consciousness. Designing efficient control systems A conscious system is better controlled than an unconscious one which is working just on the basis of some hardcoded rules and facts learnt on their basis. Better control needs more than just experience. Emotions, feelings, intuitions are some of the things. MIT cog-project: the robot is programmed to remember his mother's face more than anybody else's. Predictable. Same behavior always. Not the case with humans. The above feeling comes through emotions. Various viewpoints about consciousness in machines Alexei V. Samsonovich: cognitive agent is one which can learn any arbitrary schemas with the help of an instructor. Owen Holland: robot should be able to create an internal model of itself, outer model of environment and the model of relationship between them. Some believe we don’t need conscious systems for making intelligent machines. Some say consciousness is the by-product of our complex structure, so don’t focus on consciousness. Building a complex structure like us will automatically lead to conscious agents. Can a symbol processing machine have a mind? Chinese Room Criticism: Chinese Room Searle’s argument: What computer does can not be called thinking. It’s just a simulation and not intelligence in the way we want it to have. The computer does not understand Chinese. Criticism of criticism: Chinese Room Some argue that individual component of that room don’t have consciousness but room as a complete unit consisting of the computer, the man, the program and the cards understands Chinese. Elements of Ethics in AI Three aspects in ethics: Treat AI ethically Ethics in AI machines Using AI ethically Ethics: AI Consider some moral and legal issues If we can make AI machines with thinking prowess comparable to human beings… Ethics : Sentience Sentience : The ability to feel pleasure or pain. Animal Rights : Sentience is the most important feature that forces society to honor the rights of animals. If a machine exhibits sentience, i.e., it is able to feel pleasure and pain, then we must give it rights. Such a machine is expected to be made within 20 years. Ethics : Creating ethical AI Machines will make choices and plan actions on their own, without the consent of their programmers Responsibility to behave ethically follows naturally. i-Robot Ethics : Using AI ethically AI : powerful technology. Need to use it ethically Humans must behave ethically using AI. Ethics : Opposition Lot of opposition to giving ethics to AI AI should not replace Doctors Judges Police officers,etc Wiezenbaum[4] : “Artificial intelligence, if used in this way, represents a threat to human dignity” Conclusion "people might lose their sense of being unique. Weizenbaum (1976) ... points out some of the potential threats that AI poses to society. One of Weizenbaum's principal arguments is that AI research makes possible the idea that humans are automata -- an idea that results in a loss of autonomy or even of humanity. We note that the idea has been around much longer than AI, going back at least to L'Homme Machine (La MMettrie, 1748). We also note that humanity has survived other setbacks to our sense of uniqueness: De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (Copernicus, 1543) moved the Earth Away from the center of the solar System and Descent of Man (Darwin, 1871) put Homo Sapiens at the same level as other species. AI, if widely successful, may be at least as threatening to the moral assumptions of 21st centure society as Darwin's theory of evolution was to those of the 19th century." References [1]Philosophy of Consciousness and Ethics in AI, Shawn Kilmer, December 2007 [2]Russell, Stuart J.; Norvig, Peter (2003), Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (2nd ed.), Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-790395-2 [3]Lucas, J. R. (1961) Minds, machines and Gödel. Philosophy 36: 112-117. [4]Why ethics is a hurdle for AI, Drew McDermott, North American Conference on Computers and Philosophy (NA-CAP) Bloomington, Indiana, July, 2008 Artificial Intelligence and Consciousness, Antonio Chella, Riccardo Manzotti, 2007 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philosophy_of_AI